Session Information
Title: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Clinical Aspects I - Renal, Malignancy, Cardiovascular Disease
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Often systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) patients with Lupus Nephritis (LN) require frequent visits with their health care providers, follow up, and exposure to immunosuppressive medications with potential for significant side effects (e.g. fertility). Thus far, studies have not examined the adverse effects of LN using a disease specific patient reported outcome tool, which can address these concerns. Herein, we compare quality of life (QOL) in patients with and without history of LN using a disease specific quality of life (QOL) questionnaire-LupusPRO.
Methods:
791 SLE patients from North and South America, the Philippines and Turkey completed LupusPRO, which has 12 domains involving health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and non-health related quality of life (N-HRQOL) construct in 33 questions (Domain scores range 0-100; Hi=Better QOL). Health outcomes including Physician Global Assessment (PGA), Systemic Lupus Erythematous Disease Activity Index (SELENA-SLEDAI) and the SLICC Damage Index were physician-assessed cross-sectionally. Rheumatologists indicated on the ACR criteria if patients had a history of LN (irrespective of current activity). These patient and physician outcomes were compared using Chi square and non parametric statistical tests; p value of ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Results:
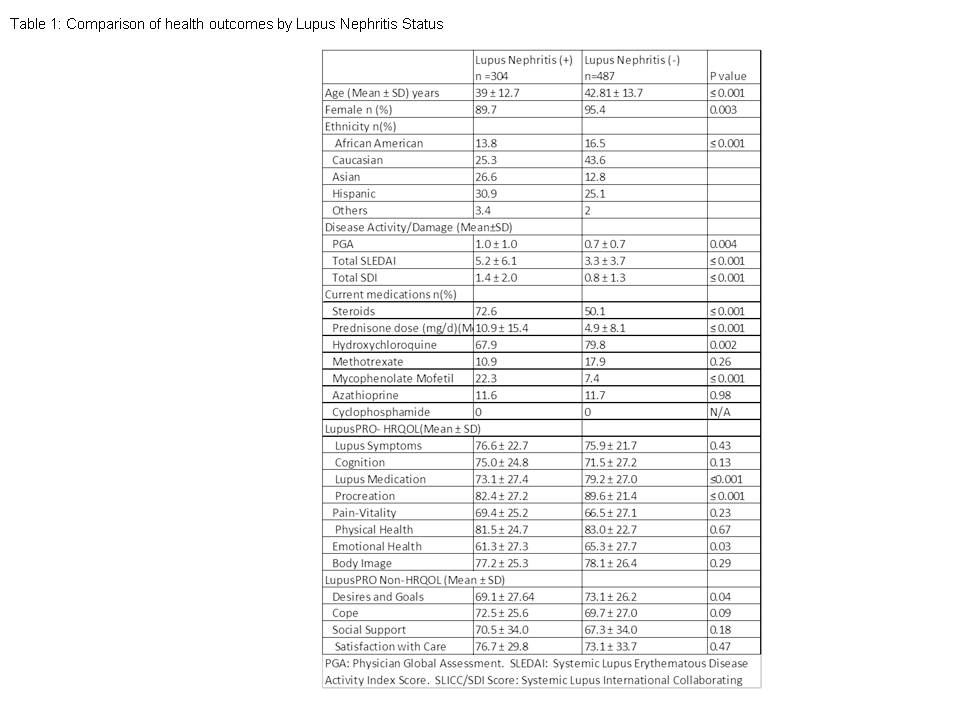
304/ 791 SLE patients had LN. Renal biopsy results were available on 184/304 LN patients: 7 LN-WHO Class I; 25-LN Class II; 120 LN Class III or IV or combinations; 29 LN-Class V; 3 LN-Class VI. Demographic, physician assessed and patient reported outcomes are shown in Table 1.
LN patients were younger, had greater disease activity and damage, were more often and on greater dose of prednisone, more often on mycophenolate-mofetil, and reported poorer health outcomes than SLE patients without LN, in both the HRQOL (Lupus medications, procreation, and emotional health) and the NHRQOL (Desires-Goals) constructs.
Conclusion:
LN patients have worse physician and patient reported health outcomes than those without LN. They voiced concerns on several areas (concerns about lupus medications side effects, procreation, emotional health and effects on their personal goals and aspirations), which can be easily assessed with LupusPro.
Table 1: Comparison of health outcomes by Lupus Nephritis Status
Disclosure:
M. Jolly,
GSK,
5,
GSK,
5,
Medimmune,
5,
Medimmune,
5;
Z. Aouhab,
None;
S. Toloza,
None;
A. M. Bertoli,
None;
I. Blazevik,
None;
L. M. Vila,
None;
I. Moldovan,
None;
K. M. D. Torralba,
None;
A. Kaya,
None;
B. Goker,
None;
M. E. Tezcan,
None;
S. Haznedaroglu,
None;
J. Bourré-Tessier,
None;
A. E. Clarke,
None;
D. J. Wallace,
None;
M. H. Weisman,
None;
G. S. Alarcon,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-specific-quality-of-life-domains-are-impaired-in-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/