Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with axial SpA (axSpA) can be classified into radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) and non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) based on the presence or absence of radiographic sacroiliitis. The PROOF study evaluated disease course and disease burden of pts with nr-axSpA and r-axSpA over 5 years.
Methods: PROOF was a real-world, prospective, observational study conducted in rheumatology clinical practices in 29 countries in 6 geographic regions. The study enrolled adults with current/past chronic back pain for ≥3 months and onset before 45 years of age. Study visits occurred at baseline (BL) and yearly thereafter. Clinical characteristics and disease burden of axSpA over 5 years were evaluated. Flares of SpA features (mean number over the previous year) were also assessed.
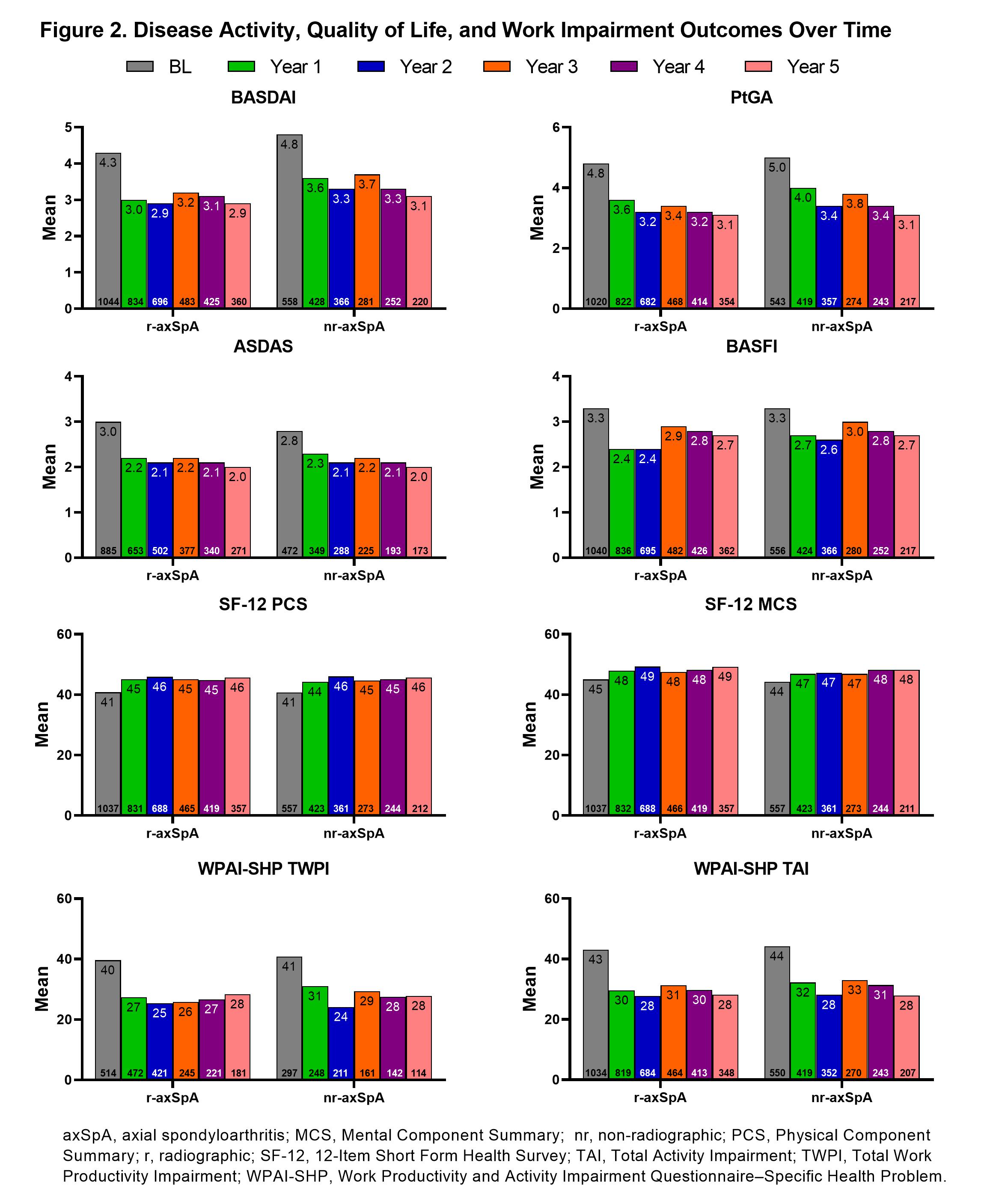
Results: Of 2633 enrolled pts, 2165 (82%) were diagnosed with axSpA and fulfilled the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) classification criteria for axSpA. Among these, 1612 (74%) were classified as having r-axSpA (1050 [65%]) or nr-axSpA (562 [35%]) based on fulfilling ASAS criteria by central reading; 27% and 53%, respectively, had active sacroiliitis on MRI (Table 1). Compared with r-axSpA, higher proportion of nr‑axSpA pts had enthesitis (40% vs 33%), psoriasis (10% vs 5%), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD, 4% vs 2%) at BL. Consistent with previous studies,1 higher proportions of r-axSpA vs nr-axSpA pts were men (71% vs 48%) and had elevated CRP (53% vs 33%; Table 1). A similar trend was observed over 5 years: higher proportion of pts with r-axSpA had elevated CRP, whereas psoriasis and IBD were more common among pts with nr-axSpA; occurrence of enthesitis was similar between r-axSpA and nr-axSpA on subsequent visits (Figure 1). The use of medications was similar between r-axSpA and nr-axSpA pts at BL (Table 1) and changes in treatment patterns (eg, reduced use of NSAIDs, corticosteroids, sulfasalazine, and other DMARDs and increased use of TNF inhibitors) were similar between populations over time. Pts with r-axSpA had a higher mean frequency of inflammatory back pain (IBP) flares per year at years 1 and 2 (22.2 and 17.4, respectively [vs 13.8 and 5.3 with nr-axSpA]) and peripheral arthritis flares per year at years 1 and 2 (8.9 and 19.0 [vs 4.2 and 4.5 with nr-axSpA]); however, no differences were observed throughout the rest of the study. Mean number of IBD (0.8–9.0 vs 0.5–0.9) and psoriasis (2.2–4.2 vs 1.1–1.5) flares was higher among pts with nr-axSpA vs r-axSpA, respectively, at each study visit. Disease activity decreased in both r-axSpA and nr-axSpA populations over time; results on physical function, pt global assessment of disease activity, quality of life, and work impairment were similar between populations through 5 years (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In this study, a higher proportion of pts were diagnosed with r-axSpA at baseline. Patients with r-axSpA and nr-axSpA share a similar clinical presentation, except for certain extra-articular manifestations (eg, psoriasis and IBD), which were more prevalent among nr-axSpA pts. Both groups showed a comparable burden of disease and treatment over 5 years.
1. López-Medina C, et al. RMD Open, 2019;5:e001108
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Poddubnyy D, Sieper J, Akar S, Muñoz-Fernández S, Haibel H, Ganz F, Inman R. Disease Course and Disease Burden in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from 5-year Multicountry Prospective Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-course-and-disease-burden-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-5-year-multicountry-prospective-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-course-and-disease-burden-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-5-year-multicountry-prospective-observational-study/