Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Breathe: RA-ILD
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: RA is associated with several forms of lung disease including interstitial lung disease (ILD), bronchiectasis, and emphysema. Risk factors for the development and progression of RA-related lung disease are incompletely understood. Previous prospective ILD screening studies mostly focused on patients with prevalent RA, limiting the ability to investigate disease activity and early lines of therapy. We aimed to identify predictors of RA-related lung disease early in the RA disease course within an ongoing multicenter, prospective study of patients with early RA.
Methods: We enrolled patients into SAIL-RA (Study of Inflammatory Arthritis and ILD in Early RA), an ongoing prospective, multicenter longitudinal study of patients recently diagnosed with RA at five U.S. sites between 2017 and 2024. All participants were diagnosed with RA within 2 years prior to study enrollment and were assessed with surveys, chest high-resolution CT (HRCT) imaging, pulmonary function tests, physical examination, and peripheral blood testing. The presence of RA-related lung disease, including clinical or subclinical ILD, bronchiectasis, or emphysema were determined through visual inspection of HRCT by three expert thoracic radiologists. We evaluated patient characteristics associated with RA-related lung diseases at the baseline visit using descriptive statistics and multivariable logistic regression.
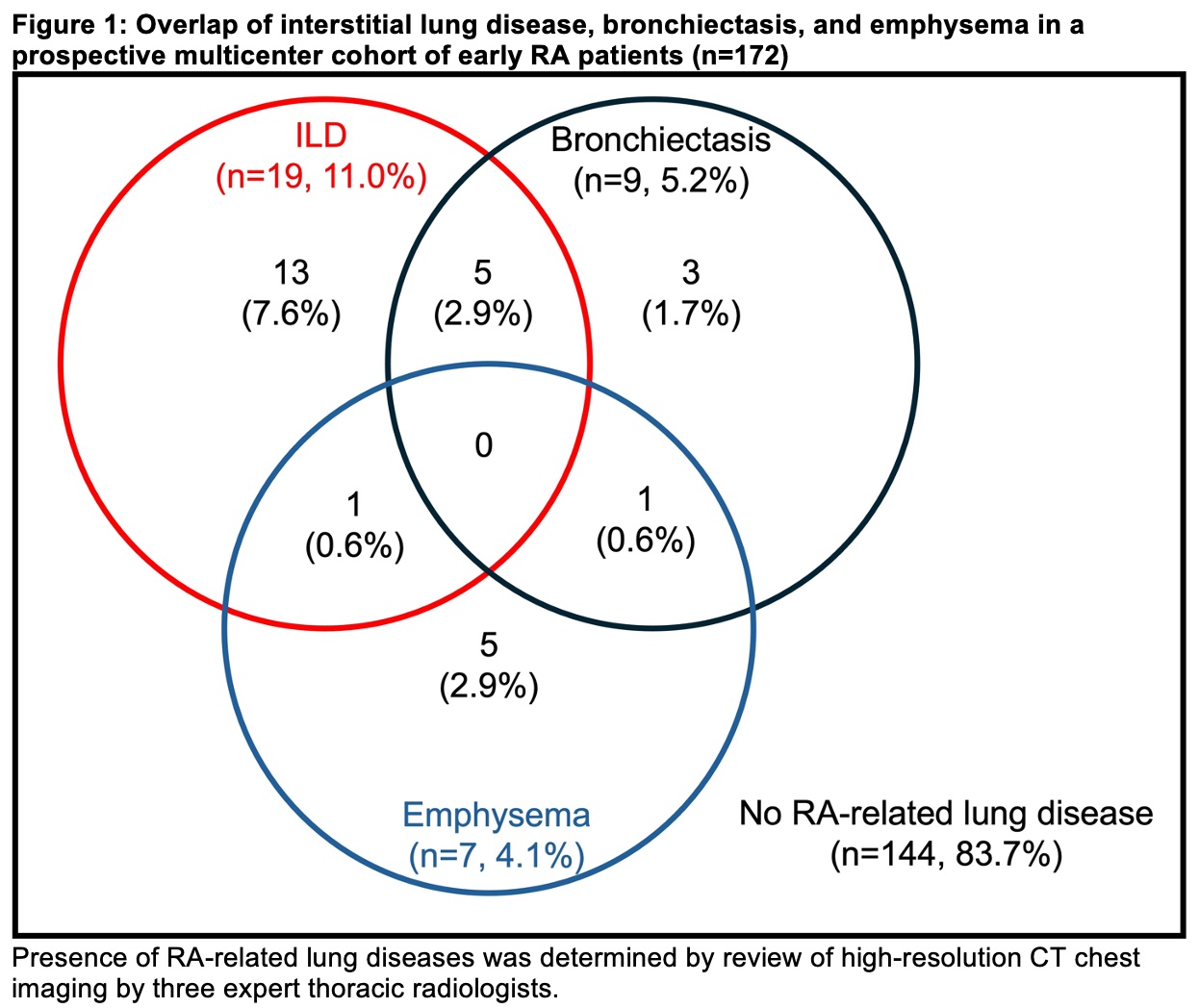
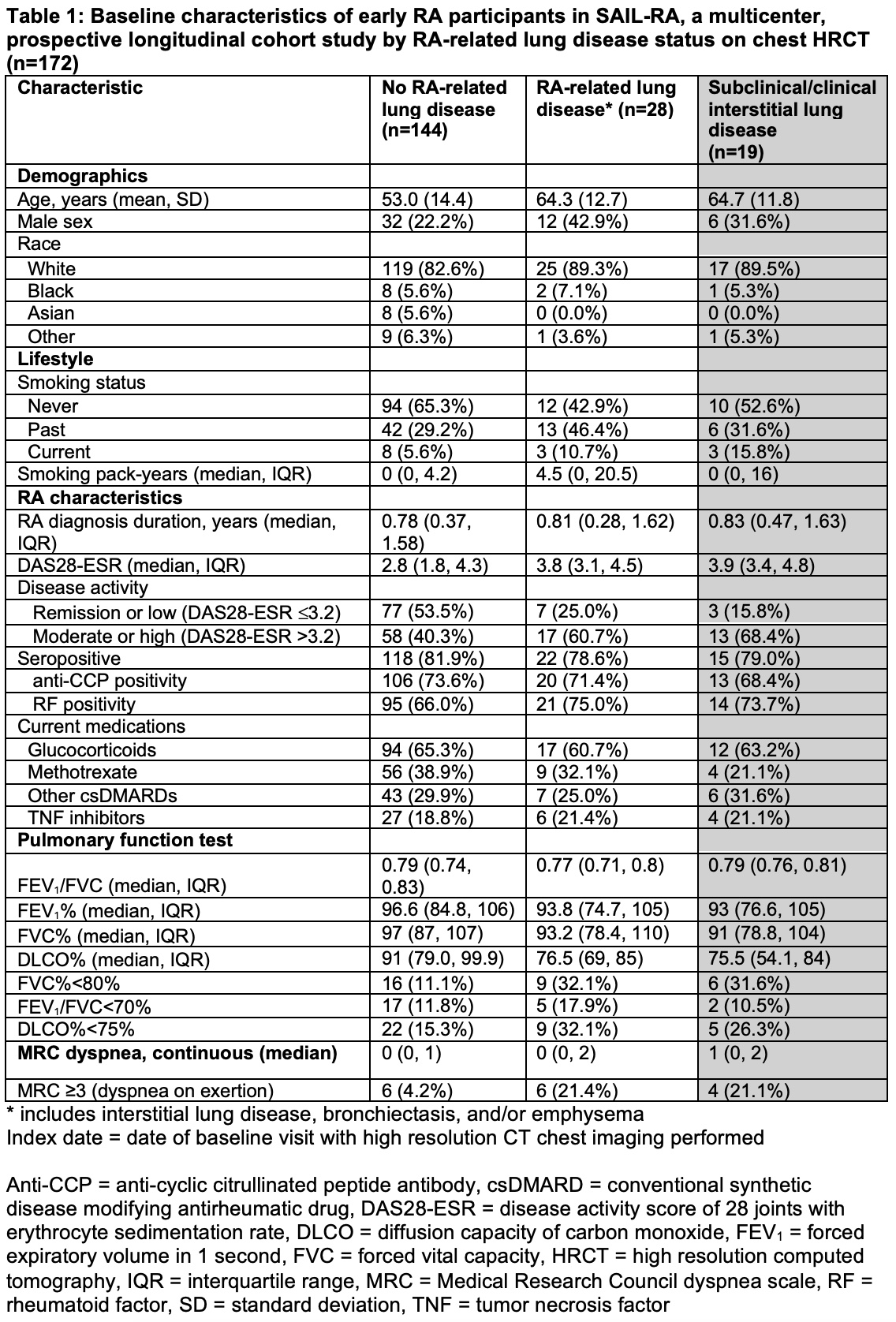
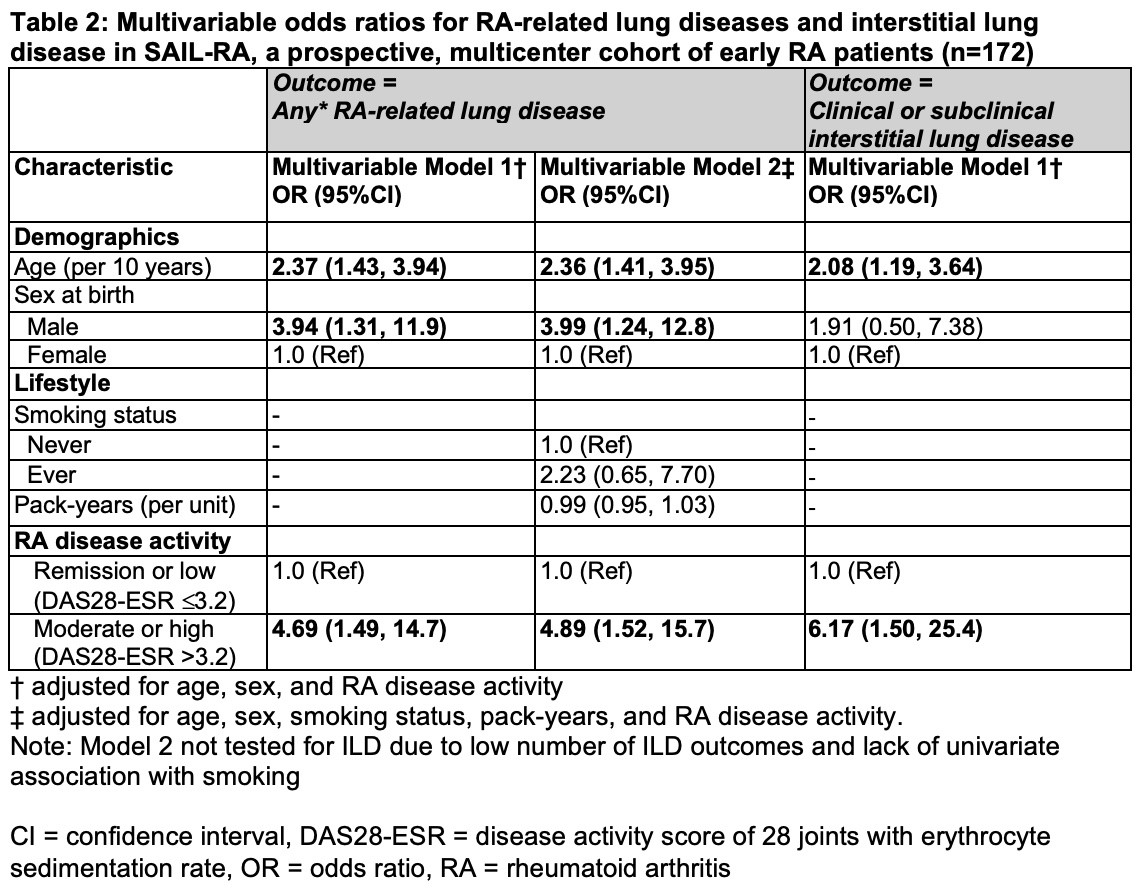
Results: We studied 172 participants with early RA (median RA duration 0.78 years) who completed baseline study visits (mean age 54.8 years, 74% female, 82% seropositive). Of those, 28 (16%) had evidence of ILD, bronchiectasis, and/or emphysema on baseline HRCT imaging (Figure 1). ILD was the most common RA-related lung disease, occurring in 11.0%. Participants with RA-related lung diseases were older (64.3 vs 53.0 years, p=0.0001), more likely to be male (42.9% vs 22.2%, p=0.02), and ever smokers (57.1% vs 34.7%, p=0.03). Participants with RA-related lung disease were also more likely to have moderate or high disease activity by DAS28-ESR at enrollment (60.7% vs 40.3%, p=0.01) compared to those without lung disease (Table 1). There were no associations of DMARDs or serostatus with RA-related lung disease. In multivariable models, age (OR 2.36, 95%CI 1.41-3.95), male sex (OR 3.99, 95%CI 1.24-3.95), and moderate or high DAS28-ESR (OR 4.89, 95%CI 1.52-15.7) were associated with RA-related lung disease (Table 2). When limiting the outcome to ILD, moderate/high disease activity remained strongly associated (multivariable OR 6.17 95%CI 1.50-25.4).
Conclusion: In this prospective, multicenter study, the prevalence of ILD, bronchiectasis, or emphysema in early RA was 16%. Active RA during the early RA period was associated with 6-fold higher odds of ILD and >4-fold higher odds of RA-related lung diseases. These findings suggest that disease activity in the early RA period may play a pivotal role in the development of RA-related lung disease. Early diagnosis and initiation of effective DMARDs during this “window of opportunity” in RA may have important articular and extra-articular benefits.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McDermott G, Gill R, Byrne S, Gagne S, Wang X, Paudel M, Kowalski E, Qian G, Bade K, Mueller K, Saavedra A, Vanni K, Bolden C, Mahajan T, Mulcaire-Jones E, Kortam N, Juge P, J Doyle T, Wallace Z, Bolster M, Deane K, Khanna D, England B, Sparks J. Disease Activity Is Strongly Associated with RA-related Lung Disease and Interstitial Lung Disease in Early RA: Results from a Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-is-strongly-associated-with-ra-related-lung-disease-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-early-ra-results-from-a-multicenter-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-is-strongly-associated-with-ra-related-lung-disease-and-interstitial-lung-disease-in-early-ra-results-from-a-multicenter-prospective-cohort-study/