Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Response to the global coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has resulted in shelter-in-place orders and major changes to how people go about their daily lives. The impact of such stressors on disease activity in individuals with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is unclear. The primary aim of this study is to examine whether stress and anxiety are associated with disease activity, after accounting for important factors.
Methods: We administered a survey to an axSpA cohort from a single center with well-defined demographic and disease characteristics. The survey included questions about changes in job status, exercise, medication use, disease activity (by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index [BASDAI]), and psychological factors (stress, depressive symptoms, and anxiety). Two separate multivariable linear models examined the associations between perceived stress with BASDAI, and anxiety with BASDAI.
Results: After adjustment for potential confounders, those with higher levels of stress had a statistically significant 0.54-point higher BASDAI, on average, compared to those with lower levels of stress (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.11, 0.97). Those with higher levels of anxiety also had a statistically significant higher BASDAI, on average, compared to those with lower levels of anxiety (β 0.95, 95% CI 0.18, 0.99). We did not find differences in these associations among subgroups of age, job status, or county of residence.
Conclusion: Individuals with axSpA with higher levels of stress and anxiety had significantly higher disease activity levels. Further studies are needed to evaluate the trajectory of disease activity as the pandemic continues to evolve.
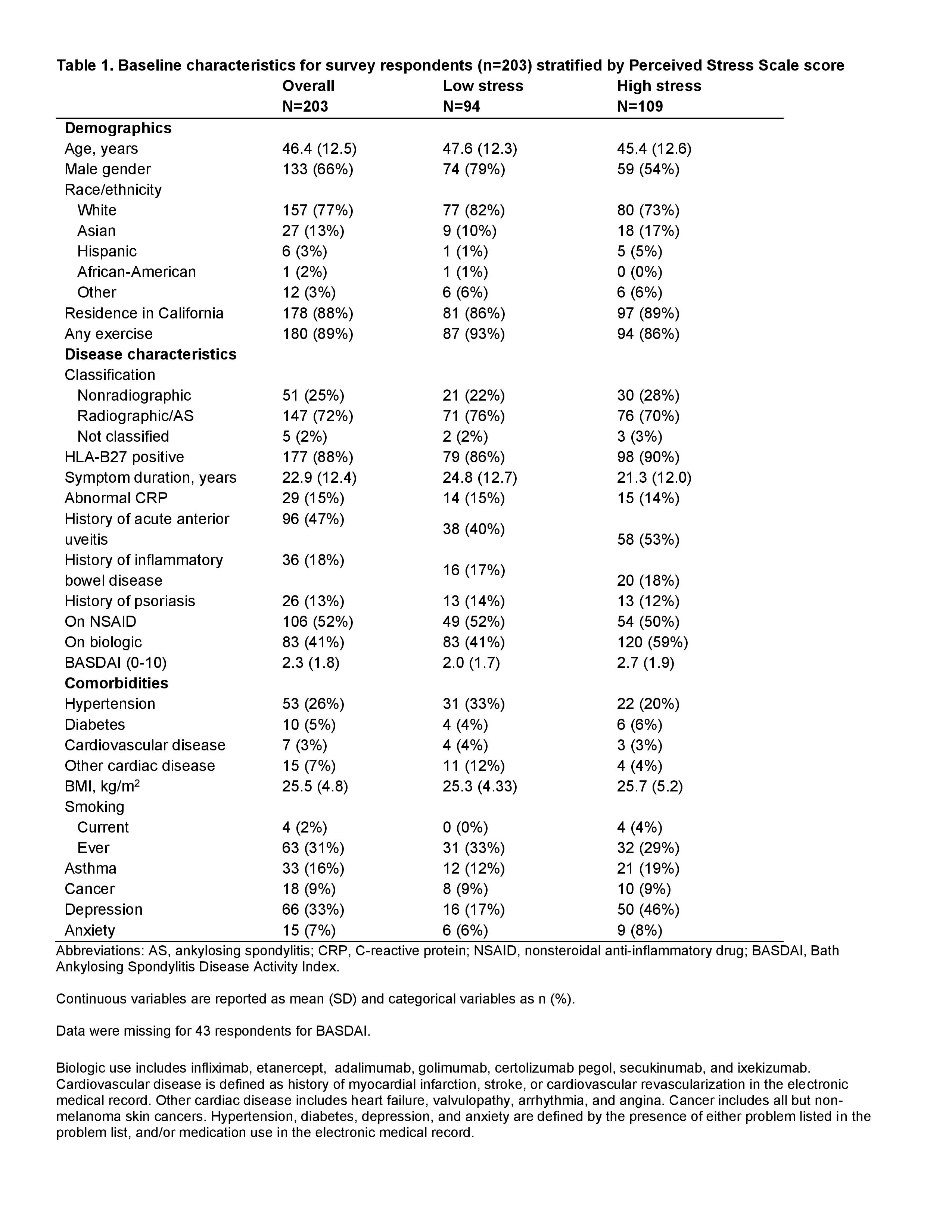 Table 1. Baseline characteristics for survey respondents (n=203) stratified by Perceived Stress Scale score
Table 1. Baseline characteristics for survey respondents (n=203) stratified by Perceived Stress Scale score
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liew J, Castillo M, Zaccagnino E, Katz P, Haroon N, Gensler L. Disease Activity in an Axial Spondyloarthritis Cohort During the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-in-an-axial-spondyloarthritis-cohort-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disease-activity-in-an-axial-spondyloarthritis-cohort-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/
