Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The PsA core domain set developed by the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology working group includes musculoskeletal disease, fatigue, physical function, and structural damage, of which arthritis activity, pain, and fatigue were identified as essential by both patients (Pts) and physicians (Phs).1-2 Assessing agreement between Pt and Ph global assessments (GA) may provide valuable insight into differential importance of specific PsA manifestations to Pts vs Phs. Although previous studies have assessed Pt/Ph disagreement, they have not evaluated potential variation over time.3 This study assessed the agreement of PtGA and PhGA through week (W) 24 and identified factors driving disagreement between PtGA and PhGA using pooled data (N=1120) from the phase 3 DISCOVER (D)1 & 2 studies of the fully human IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, guselkumab (GUS).
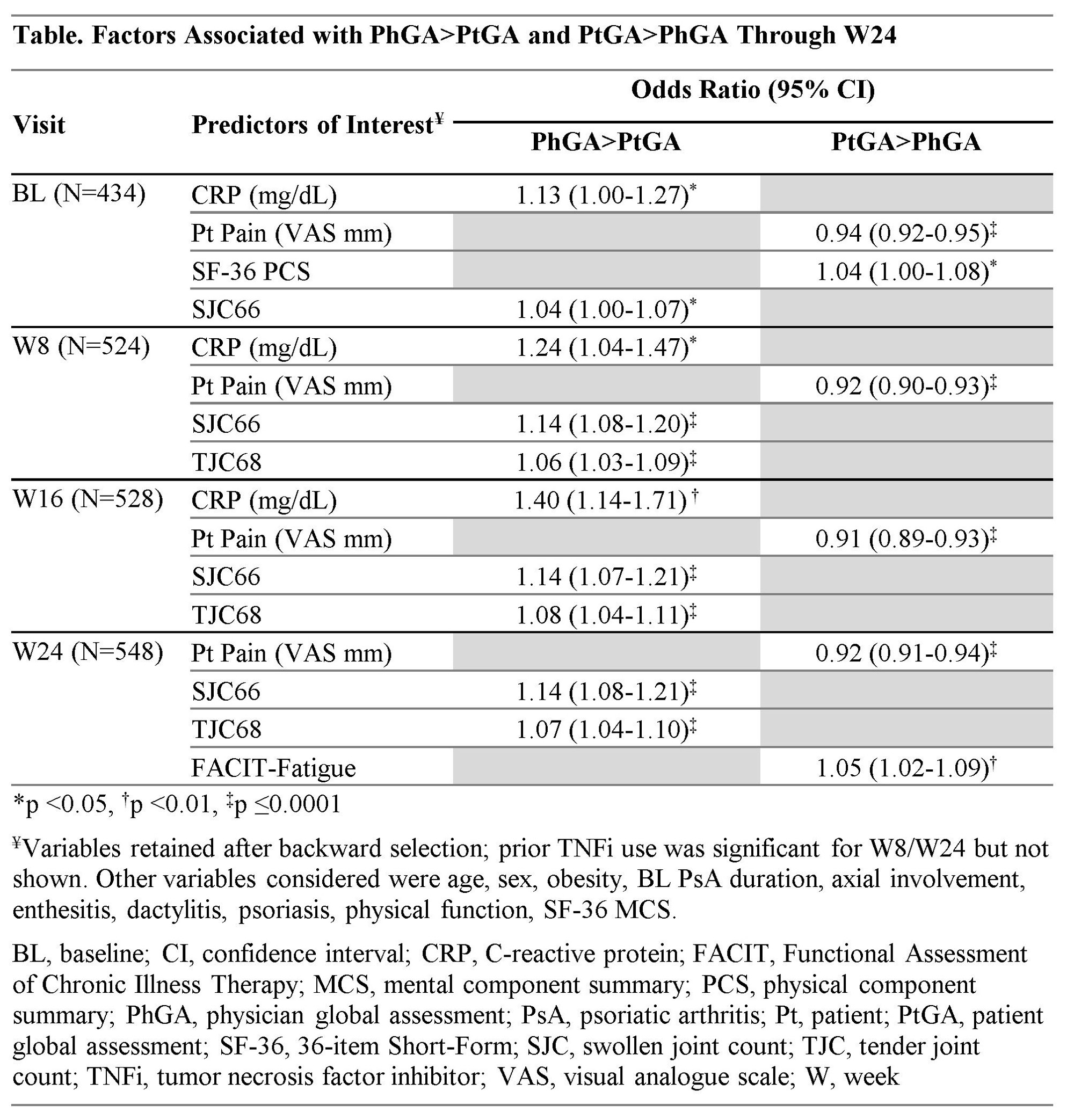
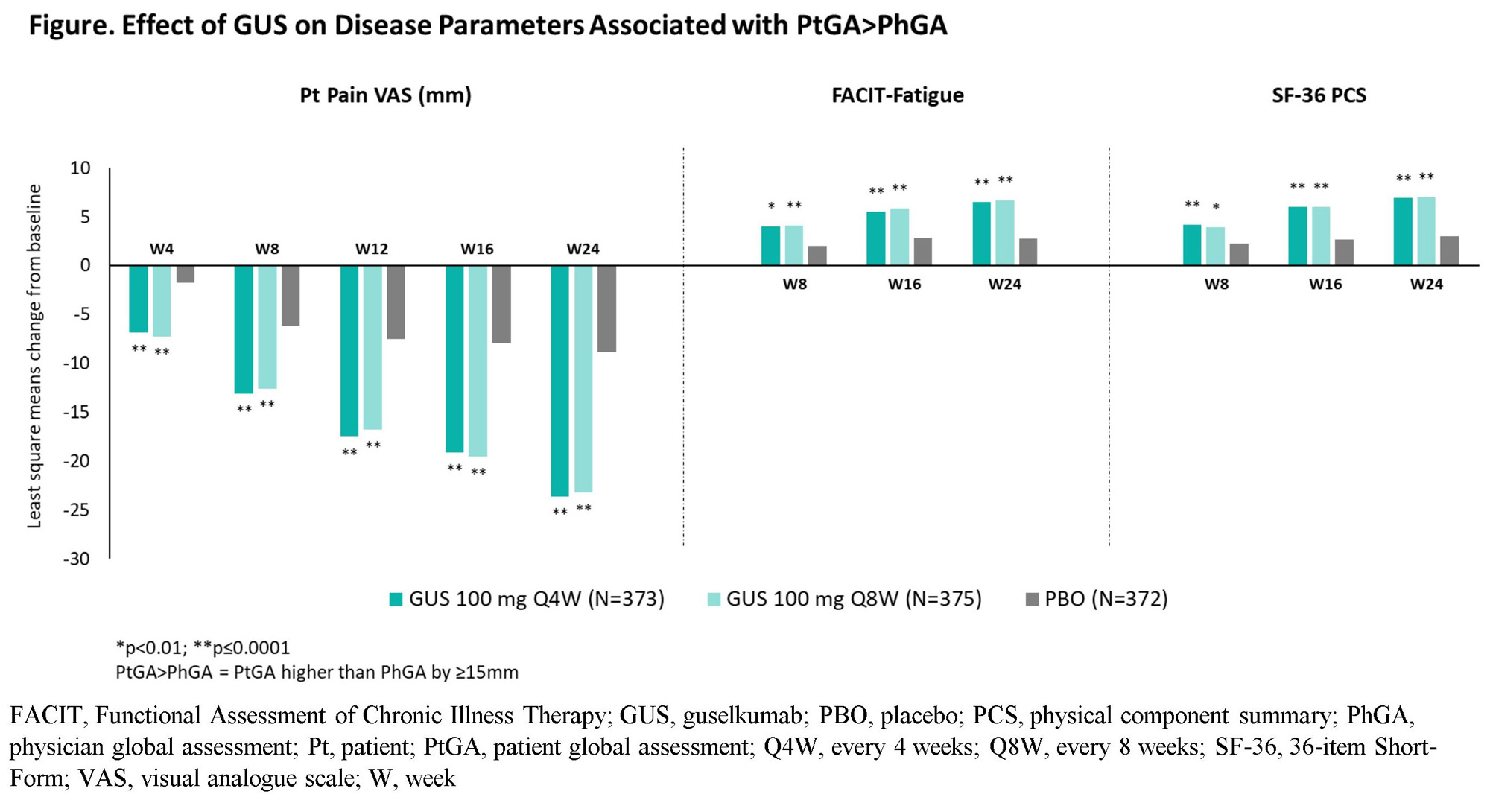
Methods: Pts with active PsA despite standard therapies (D1: ≥3 swollen/tender joint counts [SJC/TJC], CRP ≥0.3 mg/dL, ~30% with prior TNF inhibitors [TNFi]; D2: ≥5 SJC/TJC, CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL, biologic-naïve) were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, Q8W; or placebo. Pt/Ph agreement was defined as a difference of -15< PhGA-PtGA< 15. Determinants of PhGA exceeding PtGA by ≥15 (PhGA >PtGA) and PtGA exceeding PhGA by ≥15 (PtGA >PhGA) among Pts with PtGA/PhGA disagreement were assessed with the same logistic regression model considering Pt demographics, disease characteristics, and Pt-reported outcomes (PROs). The effect of GUS on disease parameters identified as determinants of PtGA vs PhGA disagreement was assessed with repeated measures mixed models adjusting for treatment group, baseline (BL) levels, prior TNFi use, and BL DMARD use.
Results: At BL, mean (SD) SJC=11.5 (7.4), TJC=20.6 (13.3), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT)-Fatigue score=29.9 (10.0), PtGA=66.9 (19.9), and PhGA=64.8 (15.9) were consistent with moderate to high disease activity. Agreement between PtGA and PhGA was seen in most instances (61.2%); 23.2% of cases were characterized by PtGA >PhGA and 15.7% by PhGA >PtGA. The proportion of Pts with PtGA >PhGA increased to 39.1% at W24, while that with PhGA >PtGA decreased to 11.2%. The main determinant of PtGA >PhGA was higher Pt Pain (all time points); additional factors included worse physical health-related quality of life at BL and worse fatigue at W24 (Table). Conversely, Phs emphasized objective disease measures, namely higher SJC (all time points) and TJC (W8 to W24), and elevated CRP (BL to W16). GUS treatment was associated with prompt and sustained significant improvements in all identified determinants, including those driving PtGA >PhGA (Figure).
Conclusion: PtGA and PhGA were aligned in most encounters. PtGA >PhGA disagreement was driven by pain, fatigue, and physical health being weighed more by Pts than Phs. These findings have important implications in shared decision making and highlight the need to prioritize treatments addressing the full spectrum of PsA symptoms, including PROs.
References
1. Leung YY, et al. J Rheum. 2020 (Suppl);96:46
2. Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81:879
3. Desthieux C, et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2017;69:1606
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rahman P, Coates L, Nash P, Deodhar A, Nantel F, Rampakakis E, Bessette L, Marrache A, Lavie F, Shawi M, Tillett W. Disagreement Between Patient and Physician Global Assessment over Time in Psoriatic Arthritis: Insight into Treatment Priorities [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disagreement-between-patient-and-physician-global-assessment-over-time-in-psoriatic-arthritis-insight-into-treatment-priorities/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disagreement-between-patient-and-physician-global-assessment-over-time-in-psoriatic-arthritis-insight-into-treatment-priorities/