Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The evaluation of axial spondyloarthritis relies on capturing various inflammatory back pain (IBP) features, represented in IBP criteria. This study examines the dimensionality of various IBP criteria focusing on how many distinct constructs or dimensions they measure in a nationally representative sample.
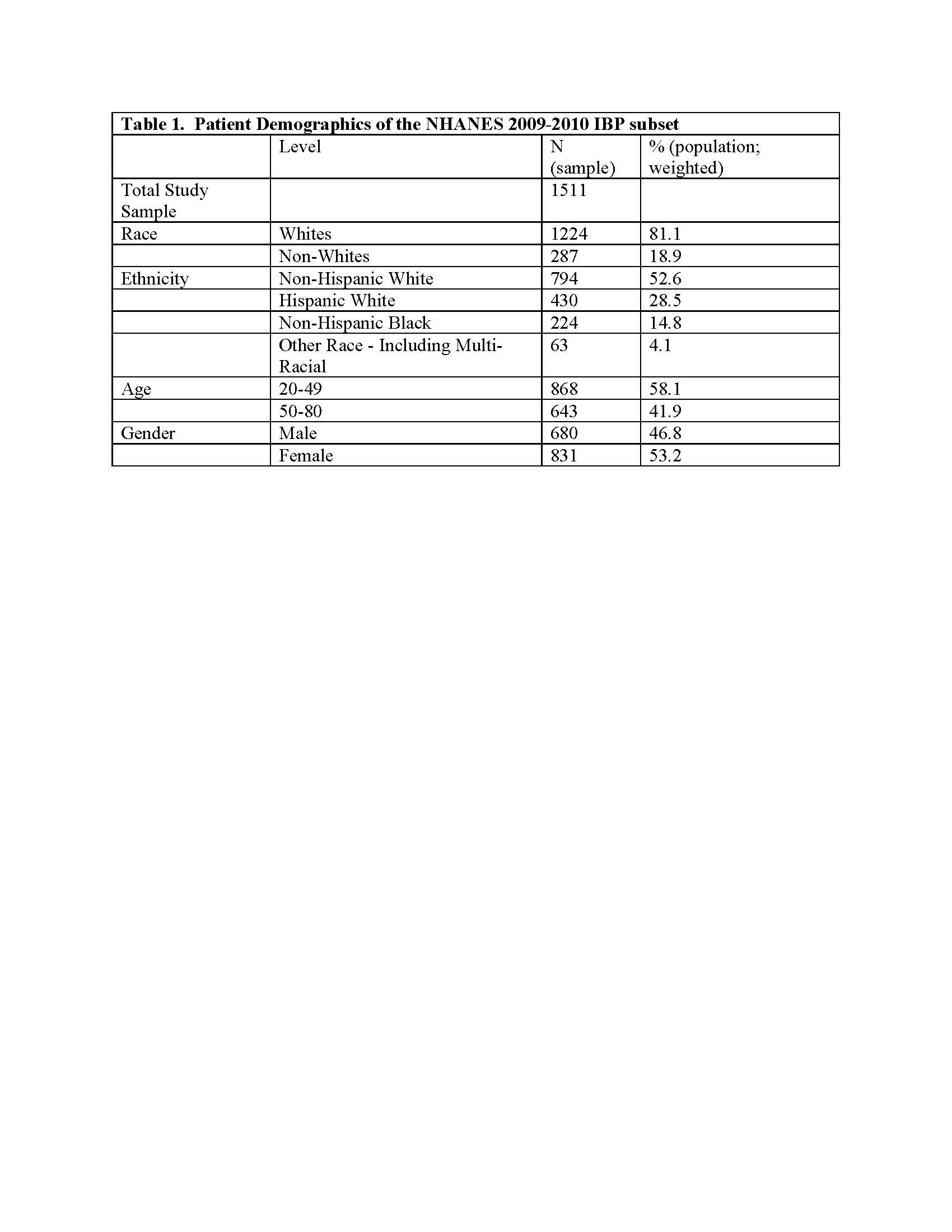
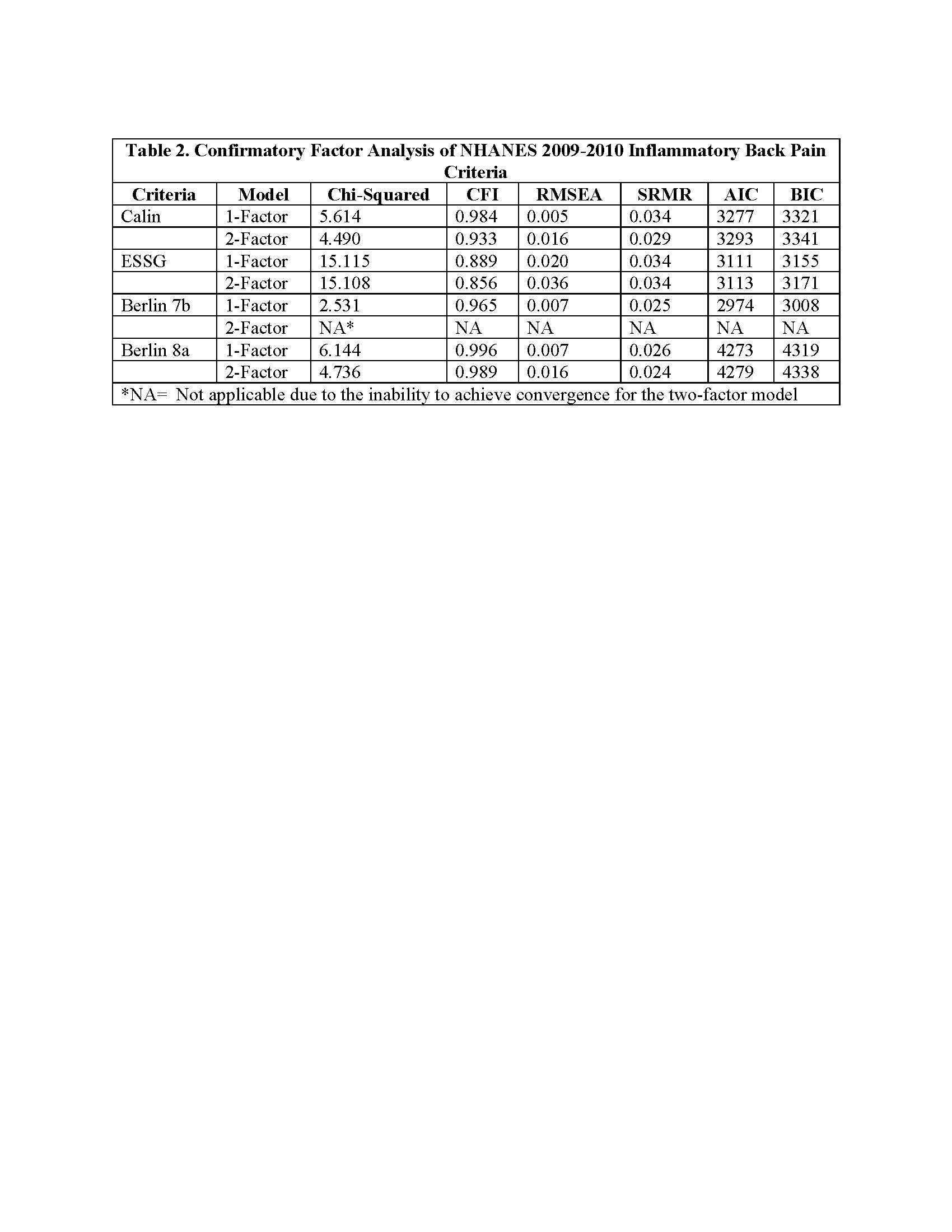
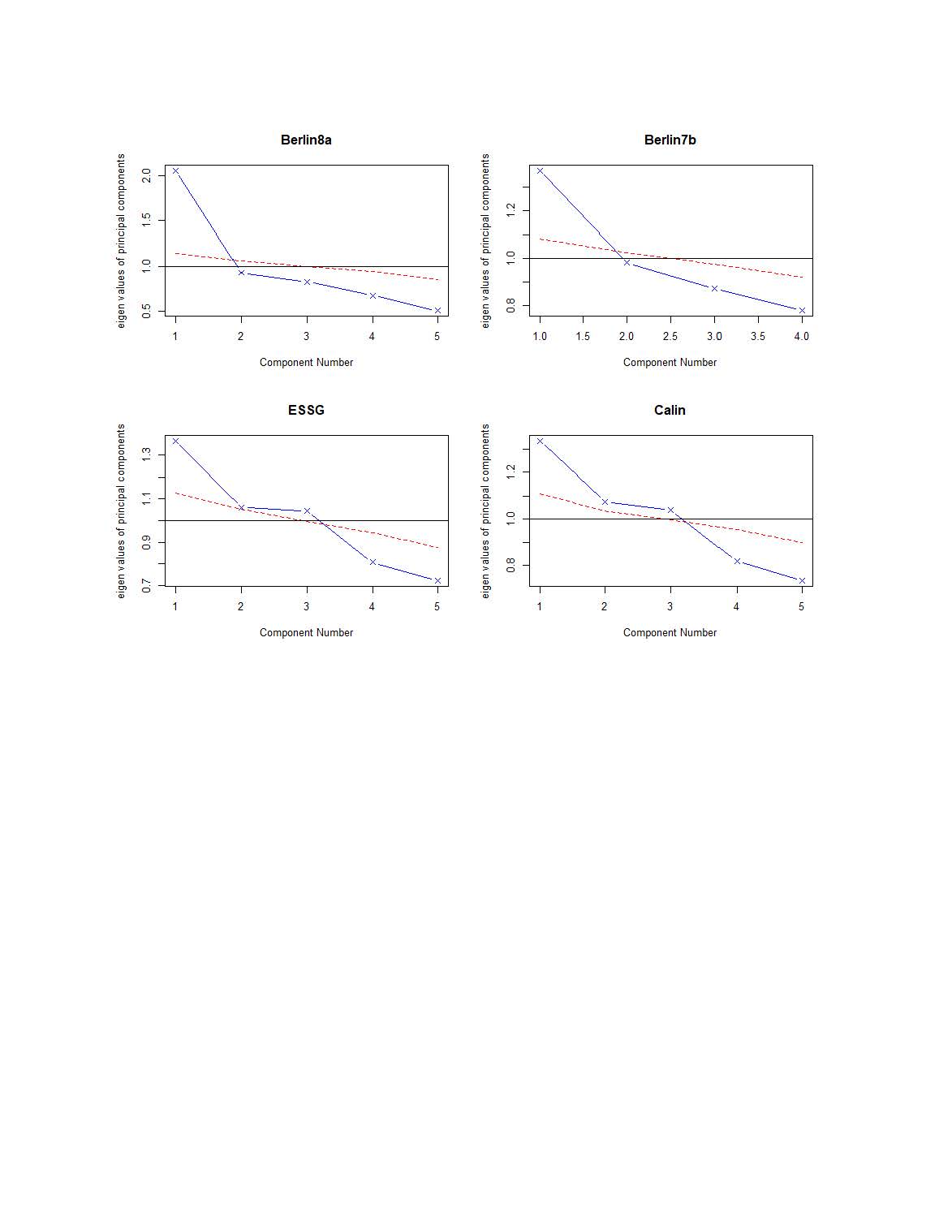
Methods: We studied the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2009-2010 dataset, a US nationally representative data collection with demographic weighting. A one-time collection in NHANES contained the Arthritis Questionnaire (ARQ) in the 2009-2010 dataset, which included all questions from Calin, European Spondyloarthropathy Study Group (ESSG), and Berlin criteria (8a and 7b)(1). Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was performed to assess if there are latent constructs underlying the observed items such as symptoms of back pain and stiffness and their dimensionality in the context of these criteria. CFA models were assessed and compared using Chi-squared log-likelihood (LR) test (χ2) Comparative fit Index (CFI), Root Mean Square Error (RMSEA), and Standardized Root Mean Square Residual Aikike Information Criteria (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criteria (BIC) Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) was also conducted using the Principle Component Analysis (PCA) method with eigenvalues >1 and scree plot inflection points considered to determine optimal domains.
Results: There were 1511 patients with complete ARQ IBP questionnaires analyzed (Table 1). For all IBP criteria (e.g., Calin, ESSG, Berlin 8a and Berlin 7b), CFA favored 1-factor models with non-significant chi-squared test, improved RMSEA, AIC and BIC observed as compared to 2-factor models. However, there was potential multidimensionality observed on EFA in IBP questionnaires given the Scree plot inflection points of 3,3,1,1 factors for the Calin, ESSG, Berlin 8a and 7b questionnaires, respectively (Figure 1.).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that IBP predominantly measure a single underlying construct, suggesting consistency in capturing a core aspect of axial spondyloarthritis. Despite some indications of multidimensionality in Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), the overall findings support the use of these criteria in clinical settings for a comprehensive patient assessment, particularly in the Berlin IBP criteria. Further research is needed to confirm the validity of these findings across different subpopulations on a national level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hwang M, Kim S, Assassi S, Ogdie A, Weisman M, Reveille J, Green C. Dimensionality of Inflammatory Back Pain Criteria in the US Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dimensionality-of-inflammatory-back-pain-criteria-in-the-us-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dimensionality-of-inflammatory-back-pain-criteria-in-the-us-population/