Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes (1257–1303)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) provide the physician with an important insight into the patients’ perception of lupus disease activity. Technology and the widespread use of digital platforms have made it possible for patients to access and respond to disease specific PROMs from home using their own device.
This study aims to assess agreement in various PROMs, with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Activity Questionnaire (SLAQ) global health as primary outcome, between a web application (app) on the patient’s own smartphone/tablet and an outpatient touchscreen among patients with SLE.
Methods: The study was a randomised, crossover, agreement trial (NCT04411407). Patients diagnosed with SLE for ≥ 12 months was assessed for eligibility. Participants were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to: 1) Group web app → touchscreen i.e. PROMs answered on the web app and after a “washout period” on the outpatient touchscreen or 2) Group touchscreen → web app i.e. vice versa. The “washout period” was pre-specified to be one to two days to minimise recall bias. Agreement between the two device types was assessed using mixed linear models.
Results: In total, 34 patients were enrolled as visualised in Figure 1.
An excellent agreement for SLAQ global health between the two device types was observed, visualised in the Bland-Altman plot (Figure 2). Mean difference in SLAQ global health between the two device types was -0.21, (95% confidence interval [95% CI]: -0.65 to 0.23) (Table 1); thus, equivalence was demonstrated as the 95%CI was within the pre-specified equivalence margin of ± 0.75. Furthermore, equivalence was proven for all other PROMs except Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) global health. However, the observed difference in VAS global health is within the limits of the pre-specified minimum clinically important difference (MCID); thus, not anticipated to have any clinical relevance.
Thirty-one (91.2%) patients preferred the DANBIO web app over the outpatient touchscreen.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, equivalence between two electronic device types has not previously been demonstrated for a collection of various PROMs among patients with SLE. A very high patient preference for the web app was observed. Implementation of the device is expected to be of great value for patients with SLE; thereby, improving management of their disease.
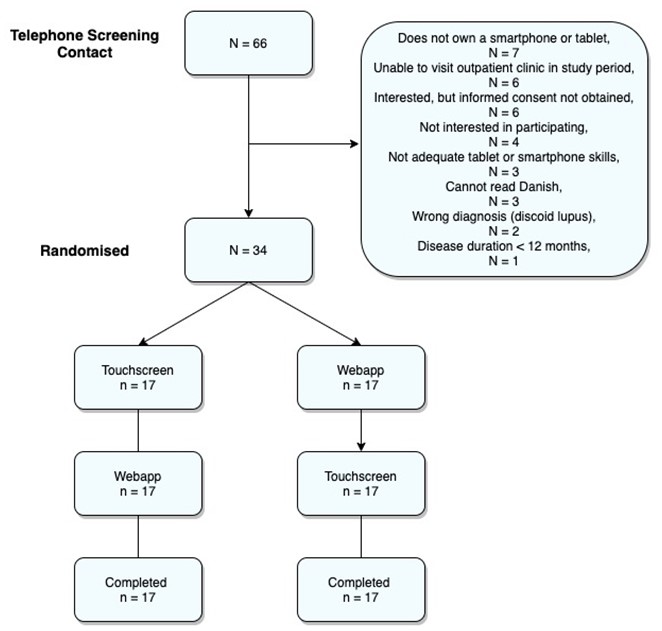 Figure 1: Flow diagram of patient recruitment
Figure 1: Flow diagram of patient recruitment
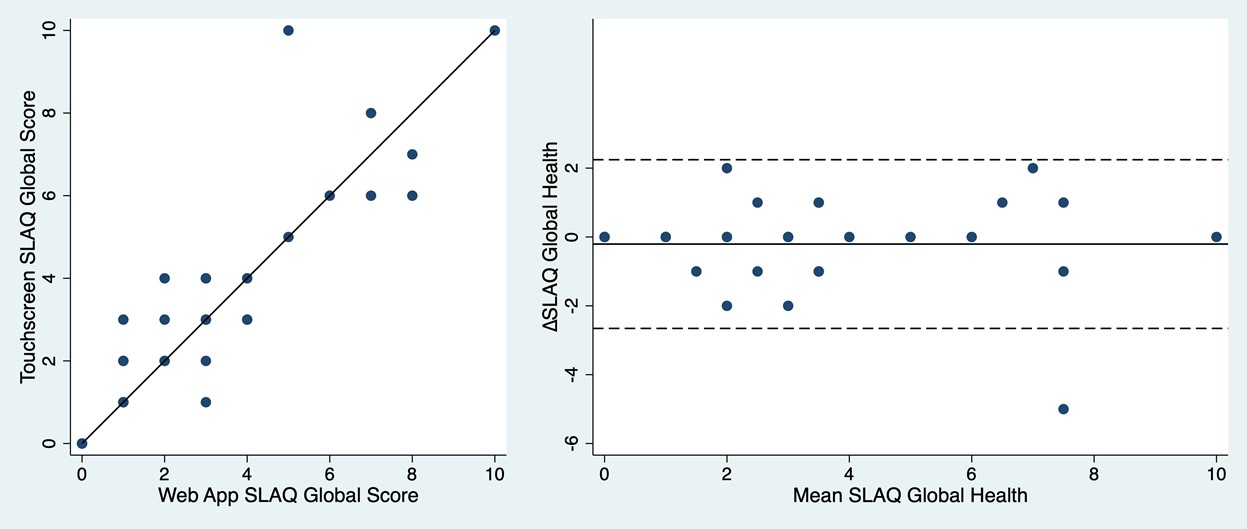 Figure 2: Bland-Altman plot on SLAQ global health registered on the two device types
Figure 2: Bland-Altman plot on SLAQ global health registered on the two device types
 Table 2: Comparison between intervention groups for all PROMs
Table 2: Comparison between intervention groups for all PROMs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Uhrenholt L, Høstgaard S, Pedersen J, Christensen R, Dreyer L, Leffers H, Taylor P, Strand V, Jacobsen S, Voss A, Gregersen J, Kristensen S. Digital Solution for Collection of Patient-reported Outcome Measures in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Randomised, Crossover, Agreement Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/digital-solution-for-collection-of-patient-reported-outcome-measures-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-randomised-crossover-agreement-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/digital-solution-for-collection-of-patient-reported-outcome-measures-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-randomised-crossover-agreement-study/
