Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Studies have demonstrated equivalence in term of efficacy and safety of biosimilars (bsDMARDs) compared to the originals treatments (boDMARDs) and in switching situation. Less is known about what happen when initiating a bsDMARDs in a molecule naïve patient. Objectives of our study were to compare treatment retention of subcutaneous boDMARDs and bsDMARDs globally, depending on disease (rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), or psoriatic arthritis (PsA)), molecule (etanercept (ETN) or adalimumab (ADA)), treatment’s line, or presence of citrate in the context of first use of each molecule (namely initiation), and to analyse predictive factors of treatment’s retention.
Methods: This multicentre retrospective study used data from shared medical records of the RIC-FRANCE network, encompassing prescription of hospital rheumatologist and attached practitioner, of patients with RA, SpA, or PsA, beginning ETN between 10/03/2016 and 07/31/2020, or ADA between 10/23/2018 and 07/31/2020. Clinical data were collected from medical records. Retention analysis was performed using Kaplan Meier curves and log-rank test. Predictive factors of retention were analysed using Cox proportional-hazard ratio. P-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
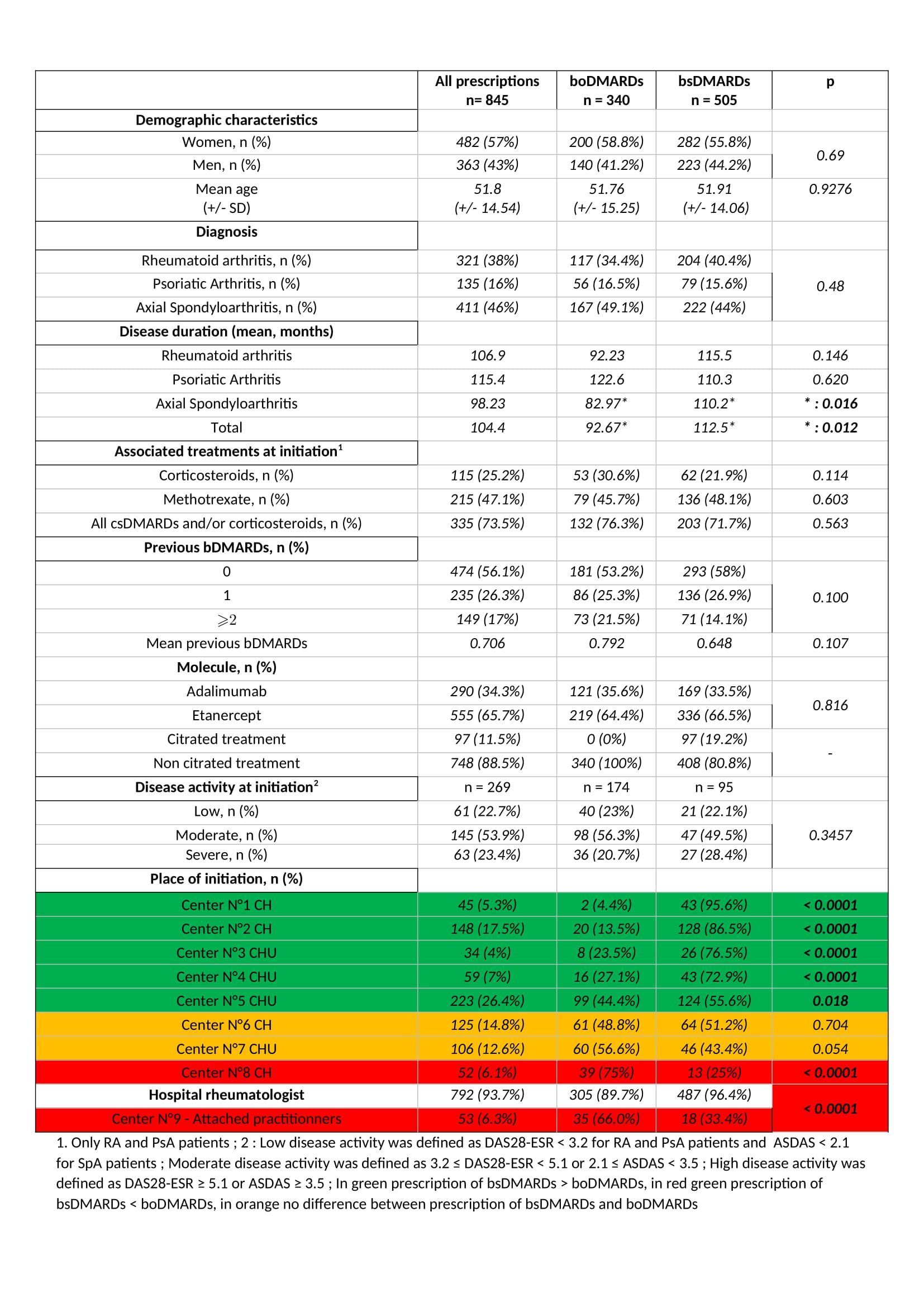
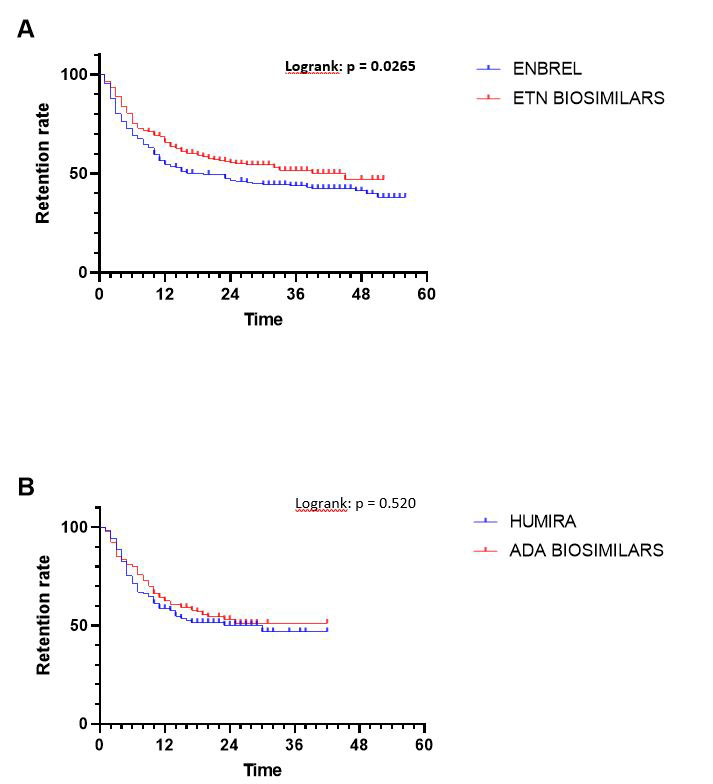
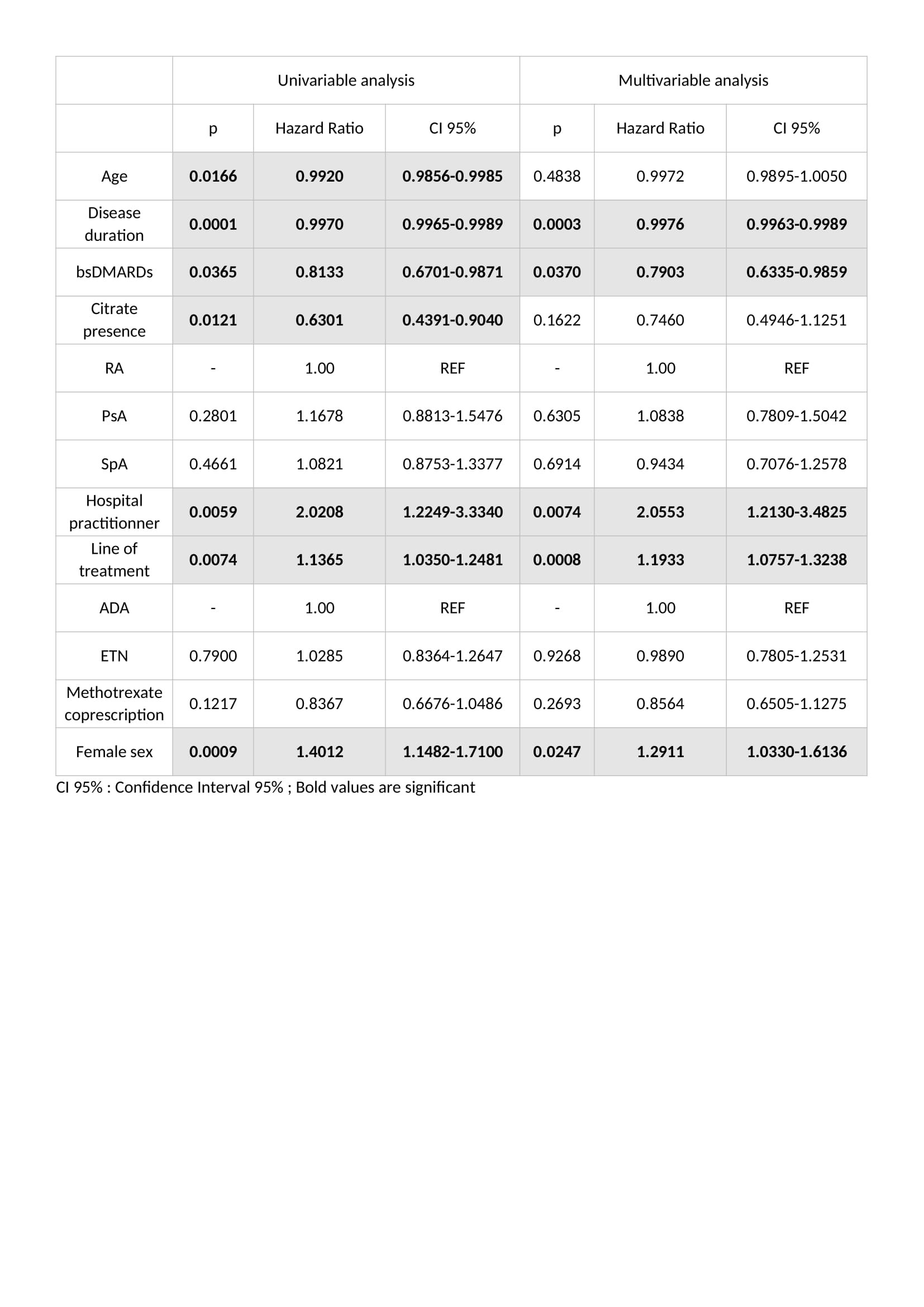
Results: 845 prescriptions were analysed: 340 boDMARDs, and 505 bsDMARDs. 57% of prescriptions concerned women, mean age was 51.8 years-old, 38% were prescriptions for RA, 16% for PsA, and 46% for SpA. An increase in the initiation over time was observed for both ETN and ADA. Retention rate of bsDMARDs was superior to boDMARDs’ one (39 vs. 23 months; p=0.045). When molecules are compared, differences was significant only for ETN (45 vs. 19 months for boDMARD; p=0.0265). When diseases are compared, differences in favour of bsDMARDs was significant in RA patients only (p=0.041). Citrated treatment displayed better retention compared to citrate-free treatments (p=0.0137). Multivariable analysis of predictive factors for treatments cessation found shorter disease duration, boDMARDs prescription, hospital practitioner prescription, late line of treatment, and female sex as significant. More side effects were observed with boDMARDs especially more infections (17.8% vs. 7.8%).
Conclusion: Even if bsDMARDs’ prescription increases over time, its penetration rate is still below expectations. bsDMARDs displayed better retention compared to boDMARDs, especially for ETN, and in RA patients. Citrated treatments had a better retention. Prescription by a fully hospital based rheumatologist is associated with poorer retention.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
LARID G, Baudens G, DANDURAND A, COQUERELLE P, Goeb V, Guyot M, Marguerie L, MAURY F, Eric V, Houvenagel E, SALMON J, Flipo R, gervais e. Differential Retention of Adalimumab and Etanercept Biosimilars Compared to Originator Treatments: Results of a Retrospective French Multicentre Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-retention-of-adalimumab-and-etanercept-biosimilars-compared-to-originator-treatments-results-of-a-retrospective-french-multicentre-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-retention-of-adalimumab-and-etanercept-biosimilars-compared-to-originator-treatments-results-of-a-retrospective-french-multicentre-study/