Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The patient global assessment of disease activity (PtGA) is a key
variable in assessing RA disease activity and remission (REM). Typically
assessed on a 10cm visual analogue scale (VAS), its widely employed wording is:
ÔConsidering
all of the ways your arthritis has affected you, how do you feel your arthritis
is today?Ô. This wording may
be misinterpreted by patients, not addressing symptoms related to RA in detail.
We investigated how different wordings of the question influence results
obtained for the PtGA.
Methods: In 4 international centers, RA patients filled in VAS of 6
differently phrased PtGA covering 2 aspects: one set using
the traditional phrasing (PtGA_trad; see above), and
one using a version including a detailed explanation of RA disease activity (“Active arthritis
can cause joint swelling OR stiffness, pain OR discomfort in your joints. WITH
ACTIVE ARTHRITIS, You CAN BE tired during the day, even when you’ve slept
well“; PtGA_expl); each set was divided into 3 questions with
different reference periods: today (TD), last week (LW)
or last month (LM). Questions were on a separate page, and the order of the questions was
random. Also, one question on global health was added (PtGA_GH).
To assess agreement of different PtGAs we
calculated intra-class correlation (ICC); mean values of different PtGA were
compared using paired t-test. The percentage of patients fulfilling Boolean
defined REM (SJC²1; TJC²1; EGA²10mm; PtGA²10mm) and CDAI REM (²2.8) was
calculated using different PtGA.
Results: 105 randomly selected patients (age 57.7±13.1 years, disease
duration 17.9±10.4 years; 84.8% female, 91.4% white, 81% seropositive)
participated in the study. Disease specific characteristics at baseline were:
swollen joint count 1.5±2.4; tender joint count 1.6±3.9; pain 21.2±22.3 mm;
fatigue 26.7±25.3 mm; HAQ
0.44±0.51; evaluator global (EGA) 15.3±15.8 mm. ICC was high across different
PtGA (ICC 0.83 to 0.94; p<0.01), with lower ICCs between GH and the other 6 PtGA (0.53 to 0.65; p<0.05). Paired T-test revealed
significantly higher mean values for PtGA_expl as
compared to PtGA_trad, independent of the reference
period (TD: 27.3±23.2 vs. 23.7±21.7; LW: 26.5±22.3 vs. 24.0±20.8; LM: 30.8±25.5
vs. 24.5±21.2; p<0.01 PtGA_expl vs. PtGA_trad respectively). In the total cohort, the
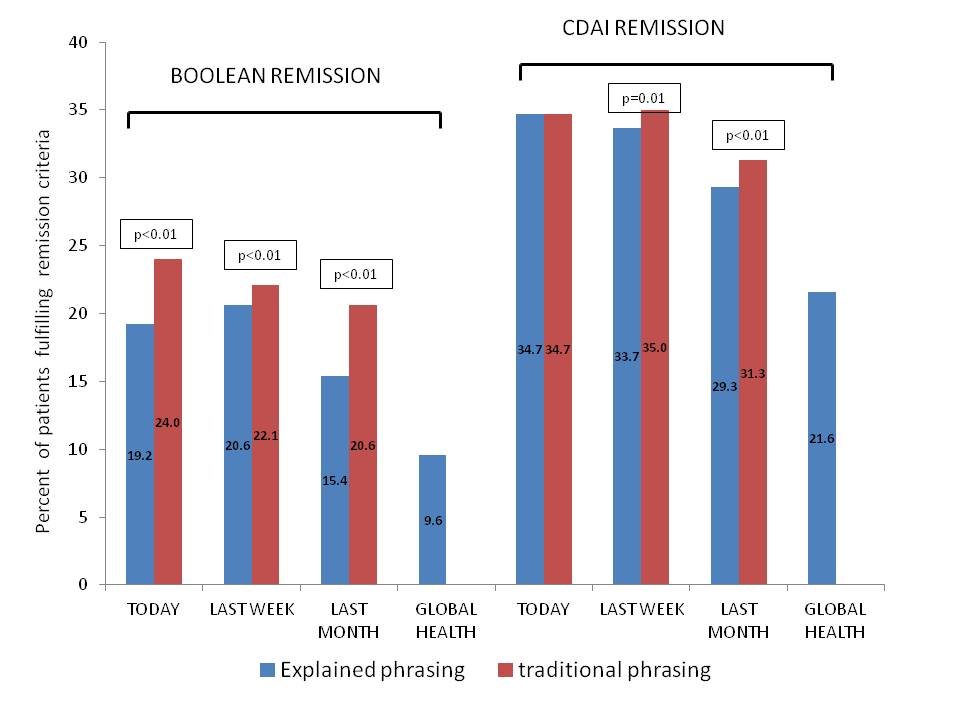
percentage fulfilling either CDAI or Boolean REM was lowest when using PtGA_GH (Boolean REM 9.6%; CDAI REM 21.6%). By using PtGA_expl significantly fewer patients fulfilled CDAI and
Boolean REM criteria compared to using the traditional phrasing of PtGA (figure).
Conclusion: Against our expectations, a more detailed explanation of “disease
activity” led to higher ratings on the PtGA scale, and
lower REM rates. It appears to increase awareness of and attention to specific symptoms
related to RA disease activity, which would otherwise be discounted.
Figure. Percentage of patients fulfilling CDAI REM and Boolean REM using
different wording of PtGA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Radner H, Studenic P, Cohen SB, Shadick N, Iannaccone C, Lie E, Mjaavatten MD, Cohen ML, Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Different Wording of the Patient Global Assessment Scale Leads to Different Rating of Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-wording-of-the-patient-global-assessment-scale-leads-to-different-rating-of-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-wording-of-the-patient-global-assessment-scale-leads-to-different-rating-of-disease-activity/