Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
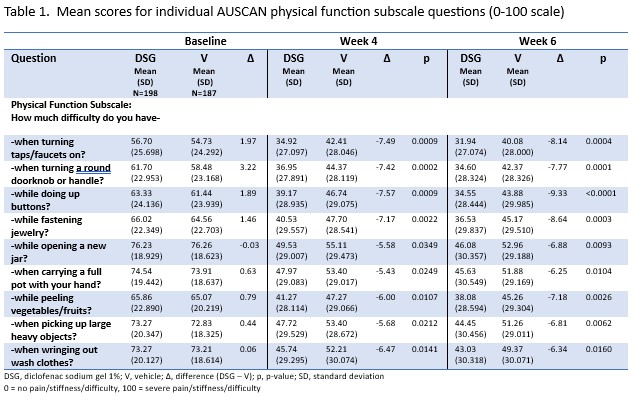
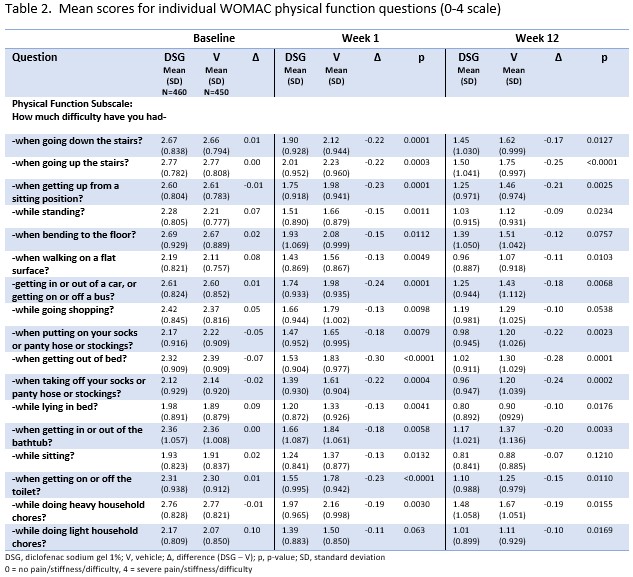
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, with hand and knee being among the most afflicted joints. Symptoms of OA include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can negatively impact performance of activities of daily living. The Australian/Canadian Osteoarthritis Hand Index (AUSCAN) and the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) are key functional surveys for hand and knee OA, respectively, and each is organized into three subscales: pain, stiffness, and physical function. While results are typically reported as a total index and/or subscale scores, the individual questions from each index are more granular endpoints that are relevant to patients’ daily activities such as getting dressed, turning faucets, walking, and going up and down stairs. The purpose of this analysis was to evaluate the efficacy of diclofenac sodium 1% gel (DSG) using the scores from the individual questions of the physical function subscales of one 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled hand OA study (Altman RD, et al. J Rheumatol 2009 ;36:1991-9) and two pooled 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled knee OA trials (Barthel HR, et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2009;39(3):203-212; Baraf H, et al, Phys & Sportsmed 2010; 38(2):19-28).
Methods: A post-hoc analysis was conducted of the mean AUSCAN physical function scores (0-100; 0 = no difficulty, 100 = extreme difficulty) at week 6 from one 8-week trial and WOMAC physical function scores (0-4; 0 = no difficulty, 4 = severe difficulty) at 12 weeks from two pooled 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials evaluating DSG vs vehicle for the treatment of hand or knee OA, respectively. Mean scores for each question were assessed and compared between treatments at each timepoint using Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) with baseline as a covariate in the model; there was no multiplicity correction required.
Results: DSG demonstrated reductions in AUSCAN physical function question scores at week 6 between 39-45% (27-33% for vehicle) and in WOMAC physical function question scores at week 12 between 46-60% (37-52% for vehicle). Statistically significant differences favoring DSG over vehicle were observed in all AUSCAN questions and in 14 of 17 WOMAC physical function scores. Specifically, the questions with the greatest separation from vehicle involved difficulty turning doorknobs and faucets, difficulty getting dressed, and cooking for hand OA, and getting out of bed, going up stairs and putting on and taking off socks for knee OA. Questions that did not separate from placebo demonstrated a trend favoring DSG.
Conclusion: This analysis demonstrates that the mean scores of the individual physical function questions from the AUSCAN and WOMAC indexes show significant improvements from baseline with DSG treatment vs vehicle over a 6-week and 12-week period, respectively. The results highlight the effectiveness of these endpoints in evaluating the impact of treatment on daily activities relevant to OA patients. They may provide meaningful new ways for healthcare providers to communicate the benefits of using DSG as a treatment for both hand and knee OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nicholson K, Sanchez E, Maybaum N, Petruschke R. Diclofenac Sodium 1% Gel Improves Physical Function in the Performance of Important Activities of Daily Living in Patients with Hand or Knee Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diclofenac-sodium-1-gel-improves-physical-function-in-the-performance-of-important-activities-of-daily-living-in-patients-with-hand-or-knee-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diclofenac-sodium-1-gel-improves-physical-function-in-the-performance-of-important-activities-of-daily-living-in-patients-with-hand-or-knee-osteoarthritis/