Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Diagnosing neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) remains a challenge. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of anti-ribosomal P antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for the diagnosis of NPSLE with diffuse central nervous system manifestations.
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed patients with central diffuse neuropsychiatric manifestations at a tertiary center in Mexico City between 2017-2024, whose assessment included lumbar puncture for CSF measurement of anti-ribosomal P antibodies. Patients were classified into three groups based on their final clinical diagnosis: NPSLE (group 1), SLE with neuropsychiatric manifestations unrelated to SLE (NP-non-SLE, group 2), and patients with non-autoimmune neuropsychiatric disease (non-AINPD, group 3). SLE diagnosis was based on the ACR/EULAR 2019 criteria, and NPSLE manifestations were classified according to the ACR 1999 nomenclature. Demographic, clinical, and serological variables were collected. Disease activity and damage accrual in SLE patients were evaluated using the SLEDAI-2K and the SDI. Serum levels of complement fraction levels were documented. Automated ELISA was used to measure levels of anti-ribosomal P antibodies in both serum and CSF. The optimal cut-off point for CSF anti-ribosomal P antibodies and their ratio with serum levels were determined using the Youden index. Diagnostic statistics were computed for each cut-off value.
Results: The analysis included 69 patients with CSF samples Group 1: 17 NPSLE, Group 2: 30 NP-non-SLE, and Group 3: 22 non-AINPD.
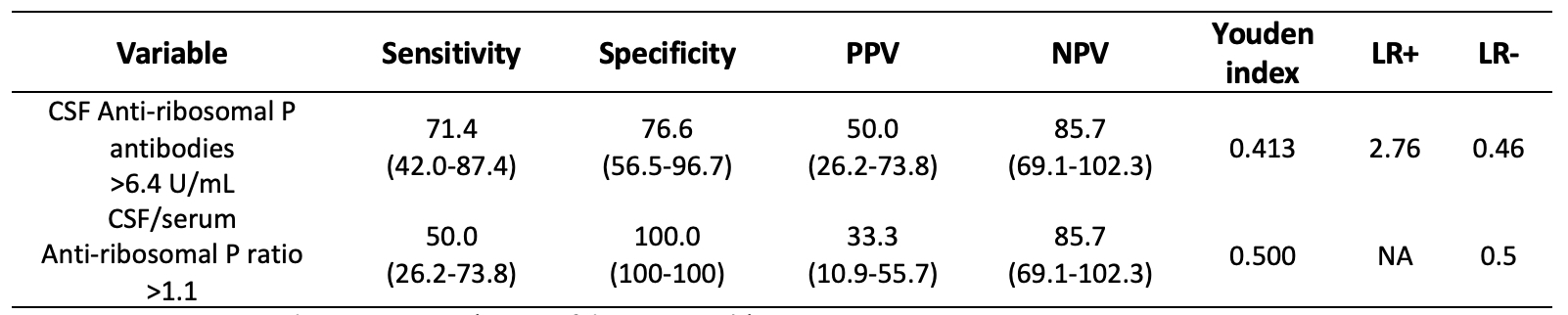
NPSLE manifestations comprised 6 cases of seizure disorders, 3 acute confusional state, 3 psychosis, 3 myelopathy and 2 lupus headache. Group 1 exhibited significantly higher SLEDAI-2K score compared to group 2 (16 vs 4, p< 0.001). Patients with NPSLE showed elevated serum levels of anti-dsDNA (448 IU/mL vs. 51.70 IU/mL vs. 3.70 IU/mL, p=0.001), anti-ribosomal P (186.6 U/mL vs. 5.5 U/mL vs. 5.45 U/mL, p=0.028), and lower complement levels (C3 50 mg/dL vs. 82 mg/dL vs. 130 mg/dL, p< 0.001; C4 10 mg/dL vs. 12 mg/dL vs. 32 mg/dL, p=0.002). NPSLE patients showed higher CSF levels of anti-dsDNA (561 IU/mL vs. 13.5 IU/mL vs. 6.7 IU/mL, p=0.013) and anti-ribosomal P (7.1 U/mL vs 5.45 U/mL vs 4.90 U/mL, p=0.008) compared to the other groups. The optimal cut-off point for CSF anti-ribosomal P was 6.4 U/mL (AUC 0.702, sensitivity 71.4%, specificity 76.6%, Youden Index 0.413), while for the CSF/serum ratio of anti-ribosomal P was >1.1 (AUC 0.375, sensitivity 50.0%, specificity 100%, Youden Index 0.250) (Table 1).
Conclusion: Patients diagnosed with NPSLE presented higher disease activity. CSF levels of anti-ribosomal P >6.4 U/mL and the CSF/serum ratio of anti-ribosomal P >1.1 could be useful for identifying NPSLE with diffuse central nervous system manifestations.
Data are expressed as percentages (95% confidence intervals). PPV: positive predictive value; NPV: negative predictive value; LR+: positive likelihood ratio, LR-: negative likelihood ratio, NA: not assessed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sandino-Bermúdez M, Cimé-Aké E, Campos-Guzmán J, Briones-García E, G. Lazarini E, Núñez-Álvarez C, Fragoso-Loyo H. Diagnostic Performance of Anti-ribosomal P Antibodies in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Diffuse Central Nervous System Manifestations. Experience in a Tertiary Center in Mexico [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-performance-of-anti-ribosomal-p-antibodies-in-cerebrospinal-fluid-of-neuropsychiatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-with-diffuse-central-nervous-system-manifestations-experience-in-a-tertia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-performance-of-anti-ribosomal-p-antibodies-in-cerebrospinal-fluid-of-neuropsychiatric-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-with-diffuse-central-nervous-system-manifestations-experience-in-a-tertia/