Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodies are the most specific markers for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Different generations of assays (CCP1-CCP3) have been developed which show variability regarding their performance. This may have considerable impact on diagnostic decision making because serological testing is an important diagnostic tool especially in the early stages of disease. Therefore the comparability of different assays is an important issue to address.
Methods: This study aimed to investigate the diagnostic performance of IgG and IgA anti-CCP2 detected by EliATM (Thermo Fisher Scientific) compared to the combined IgG/IgA Quanta LiteR anti-CCP3.1 assay (Inova Diagnostics) in sera of 184 early RA patients, 98 healthy subjects and 360 disease controls.
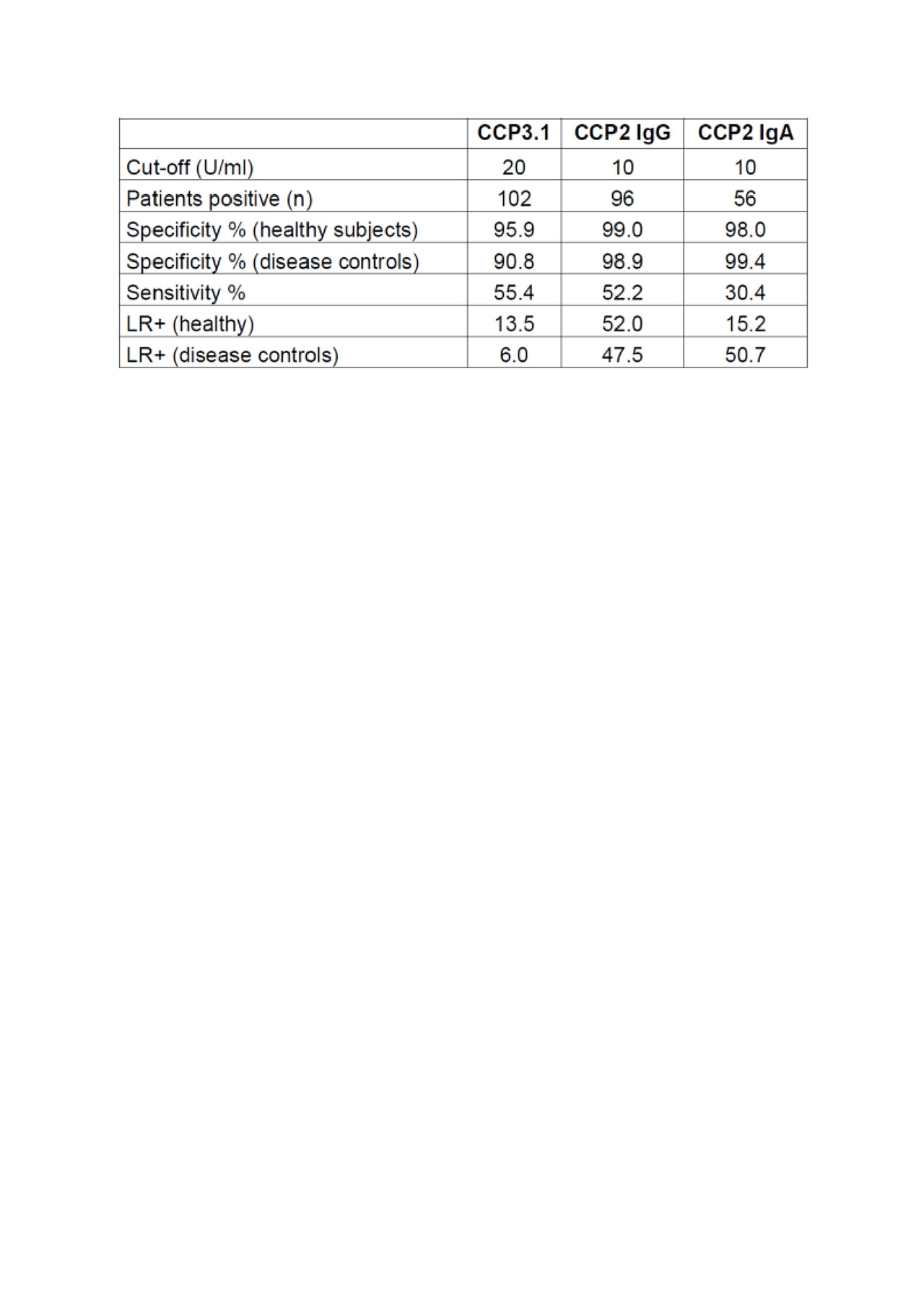
Results: Anti-CCP2 IgG and IgA assays were found having very high specificities versus healthy subjects (98.9%; 98%) as well as disease controls (98.8%; 99.4%). Sensitivities were 52.2% for anti-CCP2-IgG and 30.4% for anti-CCP2 IgA, respectively. This resulted in high positive likelihood ratios (LR+) of 47.5 for the IgG and 50.7 for the IgA assay. However, anti-CCP2 IgA antibodies did not show an added diagnostic value since all positive patients were also anti-CCP IgG positive. The anti-CCP3.1 assay was found to be slightly more sensitive than the anti-CCP2 IgG assay with 55.4% of early RA patients being positive. However, specificity was markedly lower and amounted to 95.9% versus healthy subjects and 90.8% versus disease controls which resulted in a relatively low LR+ of only 6.0. The data are summarized in Table 1. When adjusting the cut-off value of the CCP3.1 assay to >98% specificity against disease controls, sensitivity (52.7%) became comparable to the anti-CCP2 assay and LR+ increased to 26.4 which was still somewhat lower than the LR+ of the CCP2 assays.
Conclusion: Thus, when interpreting the results of diagnostic assays the issue of test to test variability must be taken into account as reduced specificity might lead to an increase in false positive diagnosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sieghart D, Konrad C, Swiniarski S, Haslacher H, Aletaha D, Steiner G. Diagnostic Performance of Anti-cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (CCP) 2 and CCP3.1 Assays in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-performance-of-anti-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-ccp-2-and-ccp3-1-assays-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnostic-performance-of-anti-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-ccp-2-and-ccp3-1-assays-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/