Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with inflammatory arthritis (IA) are at increased risk of prosthetic joint infections, yet differentiating between septic and aseptic failure is a challenge in patients with IA. Synovial fluid biomarkers, may be helpful for detection of PJI. The aim of our systematic review is to evaluate synovial fluid biomarkers and their efficacy at diagnosing PJI in patients with IA.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed in the following databases from inception – January 2018: Ovid MEDLINE, Ovid EMBASE, and The Cochrane Library . Studies retrieved were screened for eligibility against predefined criteria. Searches across the databases retrieved 367 results. After de-duplication, 2 of 5 (SM, CK, SR, JB, SG) independently screened a total of 298 citations. Discrepancies were resolved by a 3rd reviewer. After review of titles and abstracts, full text articles were pulled for further screening and data extraction. 20 articles were included. in this review. Due to methodological differences findings could not be pooled for meta-analysis. 5 studies that specifically investigated PJI in IA patients and non-IA patients were included and used to derive optimal cut points for common synovial tests.
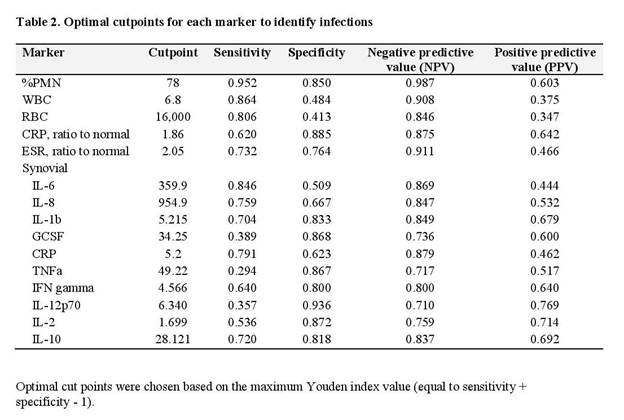
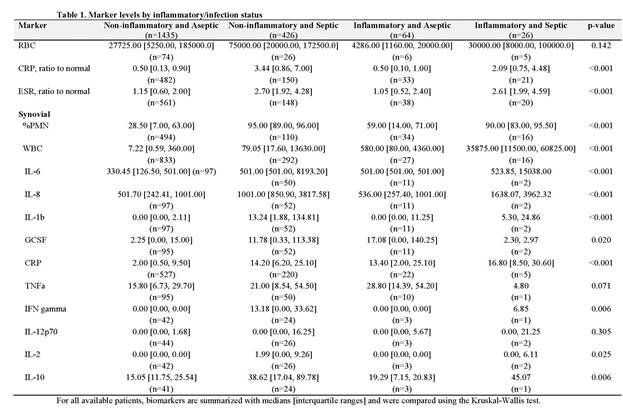
Results: Our final analysis included 1435 non-IA aseptic patients, 426 non-IA septic patients, 64 IA aseptic patients and 26 IA septic patients. There was a significant difference in detection amongst the four groups when using %PMN, WBC, serum CRP and ESR, synovial IL-6, IL-8, IL-1b and CRP (Table 1). Median values of WBC count, IL-6, IL-8, and serum CRP were significantly higher in patients with IA, and although sensitivity was high, specificity was low (Table 2). PMN% had the highest sensitivity (95.2%) and specificity (85.0%) to detect infections with a threshold of optimum sensitivity and specificity of 78%.
Conclusion: Few studies address the diagnosis of PJI in patients with inflammatory arthritis and no synovial biomarker demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity. . In contrast to PJI in patients with OA, we did not find synovial WBC count to be sensitive or specific in diagnosing PJI in IA patients. While diagnostic tests for synovial WBC, IL-6, IL8 and serum CRP appear higher in patients with inflammatory arthritis, there is overlap with those who are not infected. Further studies are needed to explore diagnostics tests that will better detect PJI in patients with IA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mirza SZ, Richardson S, Kahlenberg C, Blevins J, Demetres M, Martin L, Szymonifka J, Sculco PK, Figgie MP, Goodman SM. Diagnosing Prosthetic Joint Infections in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnosing-prosthetic-joint-infections-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnosing-prosthetic-joint-infections-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis/