Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: COVID-19 is of particular concern to patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Previous literature has shown that cancer screening visits decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic; however, no literature exists that examines the rates of new RA, PsA or SLE cases. The objective of this study is to demonstrate the changes in the identification of these diseases during the pandemic.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of Fully Insured Commercial and Medicare patients in a large health plan without a diagnosis of RA, PsA or SLE at the start of the study. Patients were included if they had continuous eligibility for the 12 months prior to study initiation through the end of the study period. Patients were followed from 3/1/2019 through 2/28/2021 and were considered a case on the first visit for RA (ICD-10 code M05.X or M06.X), PsA (ICD-10 codes L40.5X) or SLE (ICD-10 codes M32.X). Patients were excluded if their first visit occurred prior to 3/1/2019. Incidence rates were examined between the pre-COVID (3/1/2019-2/29/2020) and COVID (3/1/2020-2/28/2021) periods and monthly. Incidence rate differences (IRD) and ratios (IRR) were calculated for the pre-COVID and COVID comparison. P-values < 0.05 were significant.
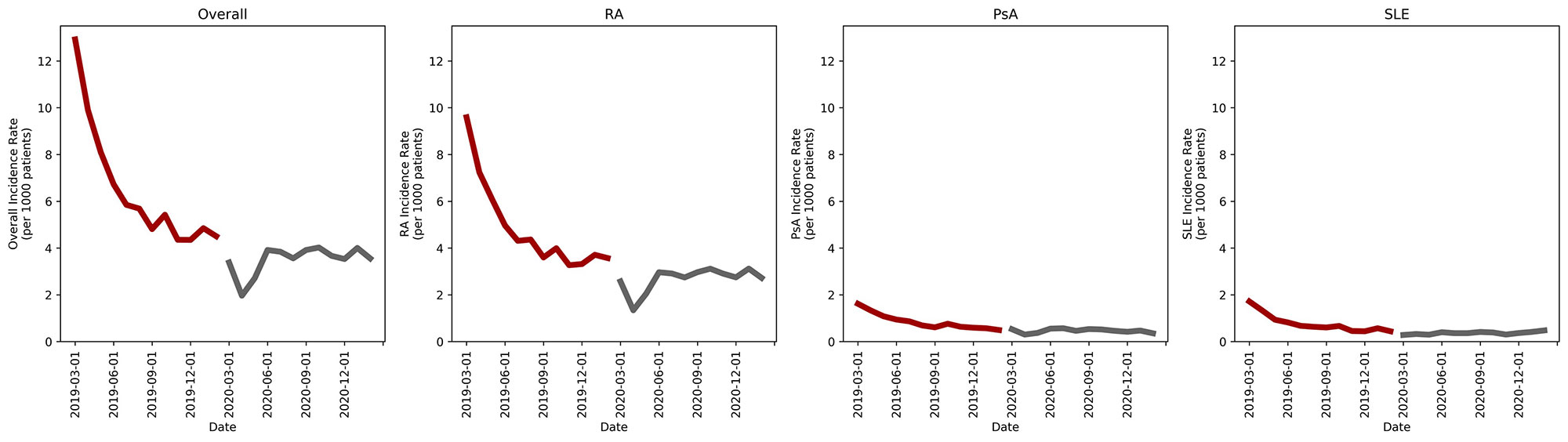
Results: Of the 1,714,867 patients included, 20,384 (1.2%) were diagnosed with RA, PsA or SLE in the two-year study. More patients were diagnosed in the pre-COVID period compared to the COVID period (7.72 [7.59-7.85] cases/1,000 patients vs. 4.2 [4.1-4.3] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRD 3.52 [3.36-3.68], p< 0.0001; IRR 1.84 [1.79-1.89], p< 0.0001). Results for each disease state were similar to the overall finding (RA: 5.8 [5.68-5.91] cases/1,000 patients vs. 3.21 [3.13-3.3] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRD 2.58 [2.44-2.73] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRR 1.8 [1.74-1.86], p< 0.0001; PsA: 0.93 [0.89-0.98] cases/1,000 patients vs. 0.44 [0.41-0.47] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRD 0.5 [0.44-0.55] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRR 2.13 [1.95-2.33], p< 0.0001; SLE: 1.03 [0.98-1.1] cases/1,000 patients vs. 0.56 [0.52-0.59] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRD 0.47 [0.41-0.53] cases/1,000 patients, p< 0.0001; IRR 1.85 [1.71-2], p< 0.0001). Monthly incidence rates were similarly higher in the pre-COVID period (mean [SD]: 6.46 [2.64] cases/1,000 patients vs. 3.51 [0.60] cases/1,000 patients; p=0.001); however, this was driven by higher incidence rates in the first six months of the study period and possibly influenced by our lookback period (Figure 1). Similar results were seen in the disease-specific monthly rates.
Conclusion: RA, PsA and SLE diagnoses were significantly reduced in the 12 months after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to the preceding 12-month period individually and as a composite. Higher rates in the first six months of the study period may have influenced the observed annual incidence rates. Further evaluations of the incidence data are warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rutter W, Cavers W, Park J, Avalos-Reyes E, Johnson K. Diagnoses Rates in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients During COVID-19 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnoses-rates-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-during-covid-19/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/diagnoses-rates-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-during-covid-19/