Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II (1565–1583)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Features of new bone formation (NBF) such as sclerosis and spurs are common on plain radiography in tophaceous gout. While a plain radiographic damage scoring system incorporating bone erosion and joint space narrowing has been developed, there are no published methods for scoring NBF in gout. The aim of this project was to develop a plain radiographic scoring system for NBF in patients with gout.
Methods: Following a systematic review of scoring systems for NBF in other bone and joint diseases, and a structured review of plain radiographs, a range of published scoring systems were tested in 80 individual joints (40 1st MTP joints and 40 5th MTP joints) from 20 patients with gout. Two readers scored the plain radiographs for sclerosis and spur using these scoring systems. Inter-reader reproducibility was assessed using intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC). In addition, construct validity was assessed by comparing plain radiography scores with gold standard computed tomography (CT) measurements of sclerosis and spur of the same joints. The best-performing scoring system was then tested in sets of hand and foot radiographs from an additional 25 patients with gout (n=52 sites/set, scores summed for each individual patient). Inter-reader ICCs were calculated, and NBF scores were correlated with plain radiographic erosion scores (using the gout-modified Sharp-van der Heijde system). All readers were blinded to each other’s scores.
Results: A semi-quantitative scoring system for spur and sclerosis (Table) was found to have high feasibility and face validity. In the individual joint analysis, the inter-observer ICC (95% CI) using this system was 0.84 (0.76-0.89) for sclerosis and 0.81 (0.72-0.87) for spur. Plain radiographic sclerosis and spur scores correlated with CT measurements (r = 0.65-0.71, P < 0.001 for all analyses). For the hand and foot radiograph sets, the inter-observer ICC (95% CI) was 0.94 (0.90-0.97) for sclerosis score, 0.77 (0.62-0.86) for spur score, and 0.92 (0.86-0.95) for combined sclerosis and spur score. The sclerosis and spur scores correlated highly with plain radiographic erosion scores (r = 0.81-0.94, P < 0.001 for all analyses).
Conclusion: A semi-quantitative plain radiographic scoring method is feasible and reproducible for assessment of NBF in gout. This method may facilitate consistent measurement of NBF in gout.
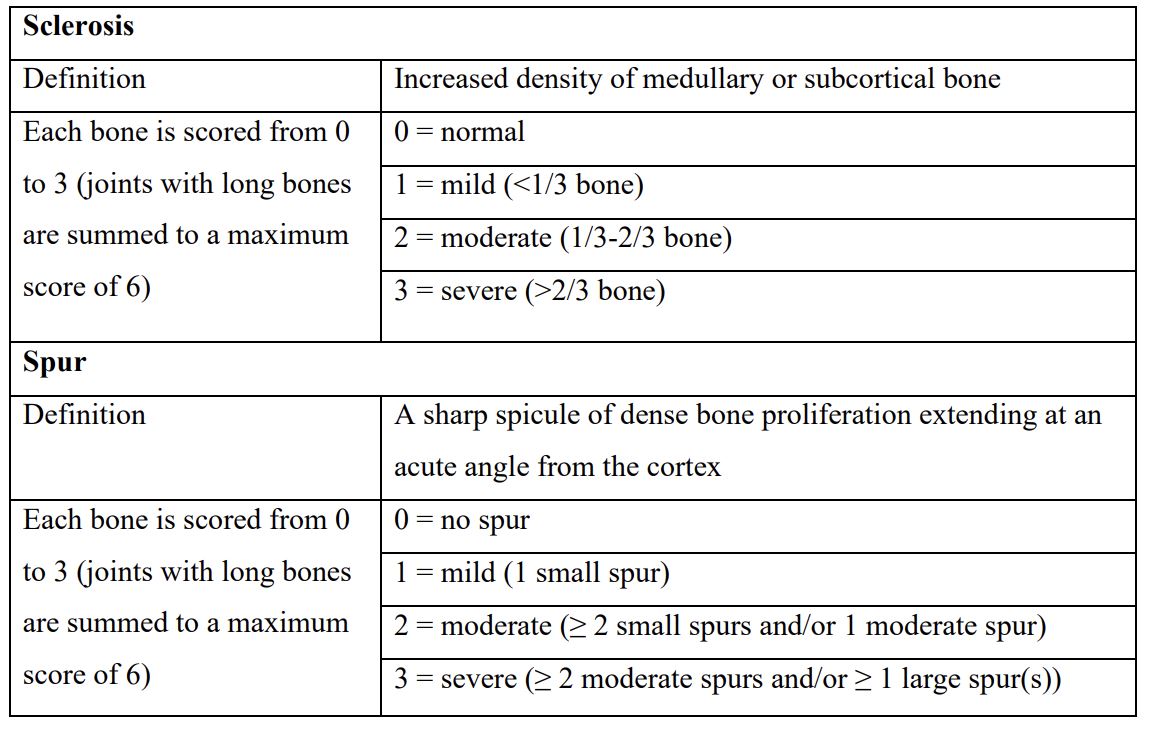 Definitions and scoring of new bone formation in individual joints.
Definitions and scoring of new bone formation in individual joints.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Son C, Cai K, Ferrier J, Tsai Y, Bardin T, Doyle A, Dalbeth N. Development of a Plain Radiographic Scoring System for New Bone Formation in Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-plain-radiographic-scoring-system-for-new-bone-formation-in-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-plain-radiographic-scoring-system-for-new-bone-formation-in-gout/
