Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Systemic Sclerosis, Fibrosing Syndromes and Raynaud's - Clinical Aspects and Therapeutics Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: As there is currently no existing index for
quantifying organ damage in systemic sclerosis (SSc),
we sought to develop a disease damage index in SSc (SSc-DI) for use in interventional and observational studies.
Methods: The SSc-DI
working group, together with patient partners and expert advisors from disciplines
other than rheumatology, has developed the initial SSc-DI
using the following steps: (1) Definition
of the concept of damage in SSc using consensus
methods in survey form (Figure 1); (2) Item generation and definition through
systematic literature review; (3) Item reduction using an online survey
distributed to over 300 SSc experts internationally, together with Rasch modelling. (5) Univariable and
multivariable regression modelling to (i) determine
the relationship between the reduced list of items and death and (ii) to weight
the items, using prospectively acquired data from the Australian Scleroderma
Cohort Study (ASCS).
Results: A total of 83 items from 7 domains (organ systems) were
included in the online survey. A total of 93 responses from SSc
experts representing Australasia, North America and Europe were analysed. 58/83
items were retained based on the Delphi survey responses (³60% experts deemed
item appropriate). A further 27 items were dropped after Rasch
modelling, leaving 31 items to be considered for inclusion in the SSc-DI. Eight of the 31 remaining items were not collected
in the ASCS and therefore were unable to be analysed in regression models. The
cohort data set consisted of 1,544 patients, with 172 deaths (11.4%). The univariable relationship with death was statistically
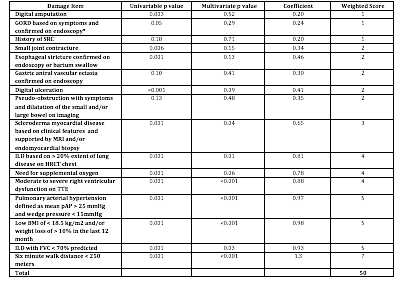
significant in 16 items. The final SSc DI with weighted
scores can be seen in Table 1. Four items, although dropped in the Rasch analysis, were included in the final index by the investigators
as they were felt to reflect damage and conferred a mortality risk. The model
demonstrated good discrimination and calibration power (area under ROC curve =
0.83 and Hosmer-Lemeshow p = 0.54)
Conclusion: The combined use of consensus and data driven methods has
resulted in a weighted 16-item Damage Index that predicts mortality. Further work
includes creation of a separate index reflective of morbidity and external
validation of these indices using prospective cohort data.
Figure 1: Consensus definition of “damage” in SSc
Table 1: Systemic Sclerosis Damage Index (SSc-DI)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ferdowsi N, Huq M, Burchell J, Mancuso S, Tay T, Stevens W, Rabusa C, Hudson M, Sundararajan V, Prior D, Proudman S, Baron M, Nikpour M. Development of a Disease Damage Index in Systemic Sclerosis Using Consensus and Data Driven Methods [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-disease-damage-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-consensus-and-data-driven-methods/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-disease-damage-index-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-consensus-and-data-driven-methods/