Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In clinical trials encompassing axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients, bone marrow edema (BME) in the sacroiliac joints (SIJs) is assessed with standardized and validated semi-quantitative scoring systems such as the Berlin MRI method(1) and the SPARCC method(2), which both are based on the semi-coronal scan plane. However, in routine care the inflammation sensitive MRI sequence (e.g. STIR) is frequently obtained in the semi-axial scan plane. This limits use of routine care MRI for systematic follow-up of assessment and prediction of treatment effect in patients recorded in clinical databases. It is important to investigate such patients, since they represent a broader spectrum of the disease than patients recruited to clinical trials (3). The objective of this study was to develop semi-axial MRI scoring methods for assessment of SIJ BME in patients with axSpA, and to compare the reliability with equivalent semi-coronal scoring methods.
Methods: Two semi-axial MRI scoring methods were based on the principles of the Berlin and SPARCC MRI inflammation methods. The intra-reader and interreader reliability of the semi-axial and semi-coronal methods were assessed with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and smallest detectable change (SDC) as absolute values and percentages of the highest observed score (SDC-HOS) were used to assess reproducibility and sensitivity to change, and linear regression analysis to compare the 2 methods
Results: Inter-reader and intra-reader ICCs for status scores were excellent for the semi-axial MRI scoring methods (Berlin: 0.88 and 0.93-0.95; SPARCC: 0.92 and 0.92-0.97) and comparable to the semi-coronal methods (Berlin: 0.92 and 0.96-0.97; SPARCC: 0.92 and 0.96). The ICCs for the semi-axial change scores were moderate for the Berlin method (0.50) and good for the SPARCC method (0.78), whereas it was good for the semi-coronal methods (Berlin: 0.87; SPARCC 0.89). The association between semi-axial and semi-coronal scores was high for both the Berlin and SPARCC method (linear regression, R2=0.93 and 0.88; change: R2=0.82 and 0.87, respectively, see Figure 1). The SDCs and SDC-HOC for the Berlin vs. SPARCC semi-axial methods were 2.6 and 12.8% vs. 5.5 and 9.8%, respectively, and for the semi-coronal methods 1.4 and 5.9% vs. 3.2 and 6.4%, respectively.
Conclusion: Detection of SIJ BME in the semi-axial scan plane is feasible and reproducible. However, slightly lower reliability and sensitivity to change of the semi-axial methods support the general practice of using the semi-coronal scan plane in therapeutic studies. References: 1. Song IH et al. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 70, 590-596; 2. Maksymowych WP et al. Arthritis Rheum. 53, 703-709; 3. Roland M. et al. BMJ 316, 285. Figure 1 Comparison of semi-coronal and semi-axial scores for baseline and change score for mean of readers. The linear regression lines are shown. 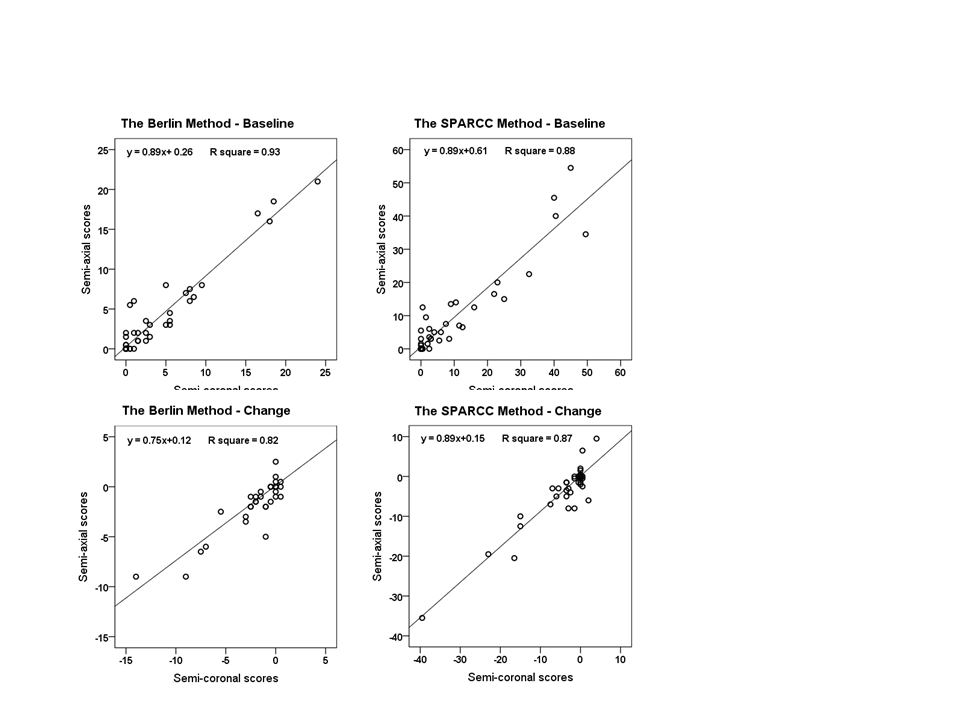
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hededal P, Østergaard M, Sorensen IJ, Loft AG, Hindrup J, Thamborg G, Asmussen K, Hendricks O, Nørregaard J, Møller JM, Jurik AG, Morsel-Carlsen L, Balding L, Pedersen SJ. Development and Validation of Berlin and Sparcc MRI Sacroiliac Joint Scoring Methods for the Semi-Axial Scan Plan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-berlin-and-sparcc-mri-sacroiliac-joint-scoring-methods-for-the-semi-axial-scan-plan/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-validation-of-berlin-and-sparcc-mri-sacroiliac-joint-scoring-methods-for-the-semi-axial-scan-plan/
