Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes I: Assessment Tools
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease (SARD) are often tasked with monitoring ambiguous and unpredictable physical symptoms on their own. Higher levels of uncertainty in rheumatic disease (URD) are associated with increased anxiety, depression, and sickness impact (J Rheum 2022;49:1059). Existing measures to evaluate URD are adapted from longer instruments (e.g., 22 items), limiting the ability to implement routine assessment in clinical practice. We aimed to develop a brief measure of URD and perform an initial validation of this brief measure.
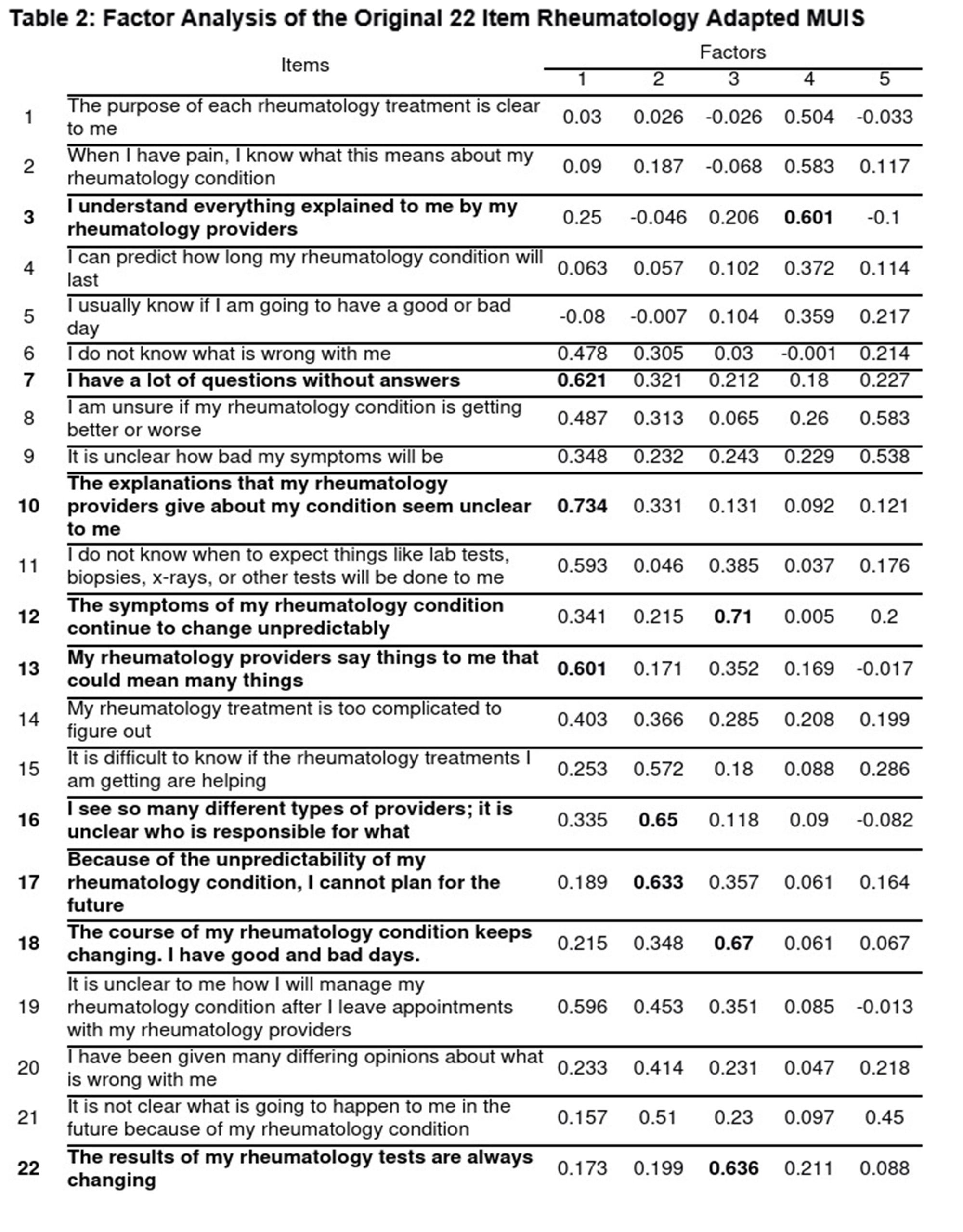
Methods: Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis (AAV), IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), and systemic sclerosis (SSc) seen at a rheumatology clinic at a large academic hospital completed a cross-sectional survey assessing URD (rheumatology-adapted version of the Mishel Uncertainty in Illness Scale, Survivor Version; MUIS-S), anxiety (GAD-7), depression (PHQ-8), and sickness impact (SIP). First, we performed an exploratory factor analysis of the previously adapted rheumatology-specific 22-item MUIS-S to identify the amount of variance loaded across each item following the established convention of 0.6 (stopping rule of 75% variance explained per factor) to select the final items. Second, we tested the brief URD measure for internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha) and convergent validity. Third, we performed a series of hierarchal regression models assessing variance explained, controlling for age and sex.
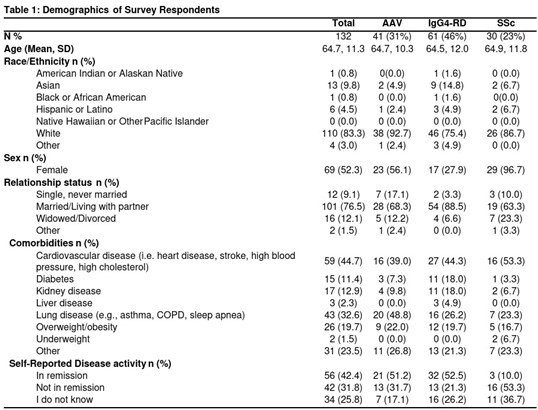
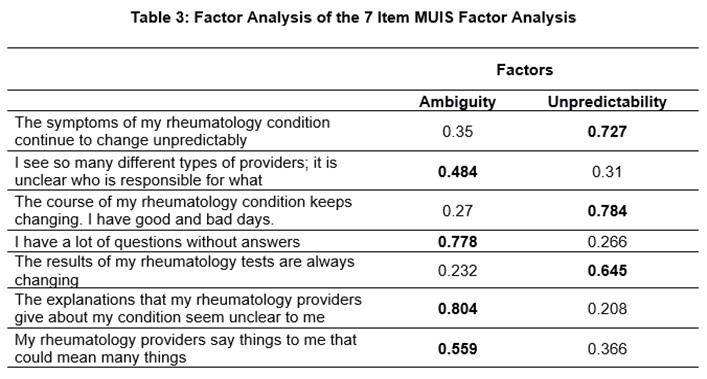
Results: We included 132 patients: 41 (31%) with AAV, 61(46%) with IgG4-RD, and 30 (23%) with SSc (Table 1). The mean age was 64.7 years, the majority were White (83%) and female (52%). The exploratory factor analysis of the 22-item MUIS-S identified 9 items to retain (Table 2). In further factor analysis of these 9 items, 7 were retained and captured 2 factors: ambiguity and unpredictability (Table 3). There was high internal consistency for the overall composite 7-item URD measure (alpha=.85) and its subscales: ambiguity (alpha=.79) and unpredictability (alpha=.81). Convergent validity was found between the 7-item measure with anxiety (r=0.417, p< .001), depression (r=0.473, p< .001), and sickness impact (r=0.335, p< .001). URD, as measured using the 7-item measure, explained a significant amount of variance: 14.2% in anxiety (r2 = 0.142, F(2,113) = 11.25, p< .001), 23.2% in depression (r2 = 0.232, F(2,113) = 19.685, p< .001), and 14.8% in sickness impact (r2 = 0.148, F(2,113) = 10.177, p< .001) after controlling for age and sex.
Conclusion: We developed a brief, 7-item measure of URD with high internal consistency and convergent validity with measures of anxiety, depression, and sickness impact. Given the burden of anxiety, depression, and other mental health comorbidities in these conditions, this instrument can be useful for tailoring screening and referral pathways for healthcare services and consultation visits (e.g., specialists, supportive care). This measure may also be useful as part of research studies developing interventions aimed at improving resiliency in the face of URD. Additional validation is needed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bolden C, Cook C, Finkelstein-Fox L, Fu X, Castelino F, Choi H, Perugino C, Stone J, Park E, Wallace Z, Hall D. Development and Initial Validation of a Brief Measure of Uncertainty in Rheumatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-initial-validation-of-a-brief-measure-of-uncertainty-in-rheumatic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-and-initial-validation-of-a-brief-measure-of-uncertainty-in-rheumatic-disease/