Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Cardiovascular Pulmonary Disease (0268–0295)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) can be detected in 20% to 60% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on high-resolution computed-tomography (HRCT) chest scan and is clinically significant in near 10%. Despite a high morbi-mortality rate, there are no definite strategy for preclinical ILD screening in patients with RA. To date, several factors have been reported to increase the risk of RA-ILD occurrence (i.e. older age at RA onset, ACPA positivity, male sex, RA disease activity, the MUC5B rs35705950 promoter variant…). However, none of these risk factors has been validated in a prospective cohort. The ESPOIR prospective cohort includes patients with recent arthritis (less than 6 months) and a definite or probable diagnosis of RA. The objective of our study was to develop and replicate a predictive score that could identify patients with preclinical RA-ILD.
Methods: An ILD detection by chest HRCT scan was systematically offered to every patient with definite RA after at least 10 years-follow-up. Potential predictors of ILD were prospectively collected from baseline to the date of the HRCT scan, and all included patients were genotyped for MUC5B rs35705950. A logistic model was used to identify independent predictors for the occurrence of ILD on HRCT scans. A predictive score for preclinical ILD occurrence was developed based on the identified predictors. The score was replicated in an independent population of patients with RA without pulmonary symptoms investigated with chest HRCT.
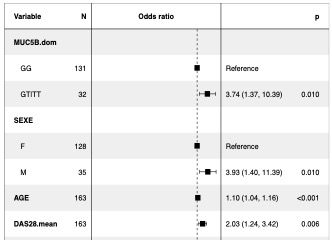
Results: 163 RA patients according to 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria, none of whom had pulmonary symptoms, were investigated with a chest HRCT scan in the ESPOIR cohort (128 women (78.5%), mean RA duration 13.7 ± 1.1 years, age at inclusion 47.6 y/o ± 10.4, mean disease activity score [DAS]-28 during follow up was 3.1 ± 1.0). ILD was detected in 31 patients (19.0%). After logistic regression, independent predictors for preclinical RA-ILD were male sex (OR=3.9 CI 95% [1.4-11.4]), older age at RA onset (OR=1.1 per year CI 95% [1.0-1.2]), mean DAS-28 score during the follow-up (OR=2.0 CI 95% [1.2-3.4]) and MUC5B rs35705950 T risk allele (OR=3.7 CI 95% [1.4-10.4]) (Figure 1). The logistic model could predict preclinical ILD occurrence with an AUC=0.82 CI 95% (0.72-0.91). A predictive score for preclinical RA-ILD based on the 4 identified predictive risk factors was developed (Sensitivity [Se] 80%, Specificity [Sp] 56%). The score was replicated in an independent population of 89 RA patients investigated with chest HRCT scan. 15 patients (16.9%) had preclinical RA-ILD. The score could predict RA-ILD in 13 patients (Se 86.7%, Sp 40.5%, negative predictive value 93.8%, positive predictive value 22.3%).
Conclusion: In this study, we developed and replicated a predictive score for preclinical RA-ILD that could help physicians identifying patients with RA in whom a HRCT scan should be performed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Juge P, Granger B, Debray M, Ebstein E, Louis-sidney F, Kedra J, Borie R, Constantin A, Combe B, FLIPO R, Mariette X, Vittecoq O, Saraux A, CARVAJAL-ALEGRIA G, Sibilia J, Berenbaum F, Kannengiesser C, Boileau C, Crestani B, Fautrel B, Dieudé P. Developing a Score to Predict Preclinical Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis – a Cross-Sectional Study from the ESPOIR Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/developing-a-score-to-predict-preclinical-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study-from-the-espoir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/developing-a-score-to-predict-preclinical-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-cross-sectional-study-from-the-espoir-cohort/