Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Combination therapy with DMARDs for treating RA is considered as a standard of care. However, certain rates of adverse events (AEs) are unavoidable. The stigma are how to predict the risk and how to define drug withdrawl sequence for optimal risk reductions if AEs persist. The decisions made are always empirical.
To develop a risk prediction model and an algorithm for drug withdrawl sequence based on data mining from the SSDM
Methods: SSDM is an interactive mobile disease management tool, including two application systems (APPs) for both the doctors and the patients. The patients can input medical records (including medication and laboratory test results) and perform self-evaluation (DAS28, HAQ) via App. The patients’ data synchronizes to mobiles of authorized rheumatologists through cloud and doctors’ advices could be delivered. In previous studies, we demonstrated that patients could master SSDM after training.
In order to develop a prediction model and the master algorithm, abnormal white blood cell counts (WBC) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation were targeted. Data was collected, extracted, validated, and Bayesian networking, data mining, modeling were performed. WBC under 4k/ml is defined as leukocytopenia (LP), over 10k/ml as infection predisposing (IP), and ALT > 40 U/L as ALT elevation.
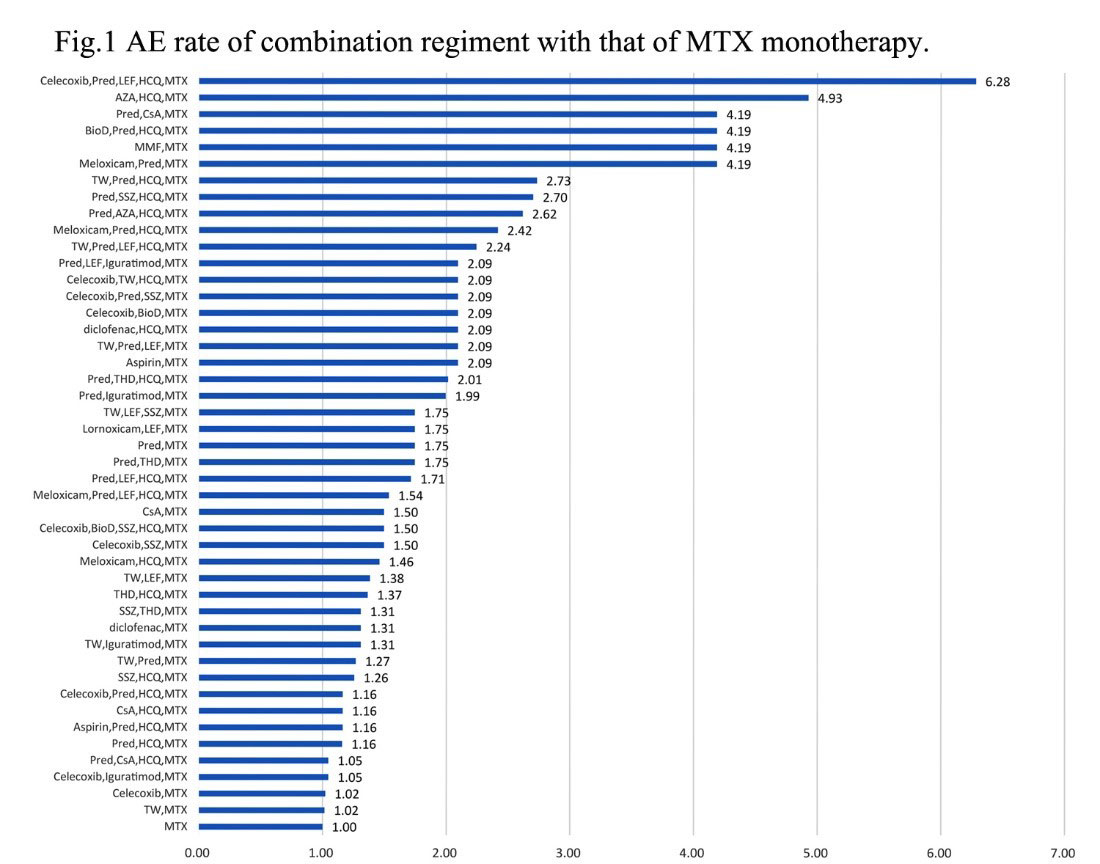
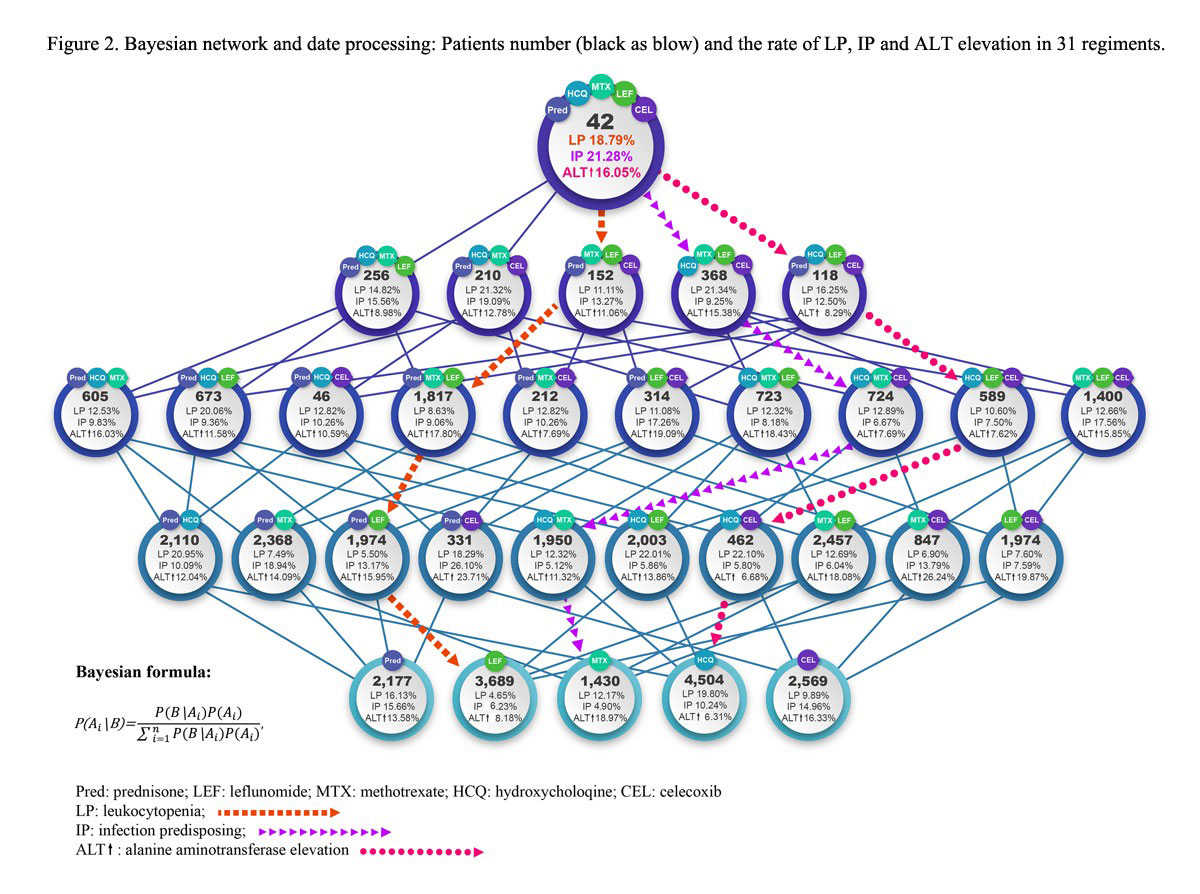
Results: From Jun 2014 to May 2019, 54,149 RA patients from 587 centers registered in SSDM. 135 different drugs and 1,220 combination therapies are identified. LP happens at 341 and IP at 344, ALT elevation at 325 cases in 752 treatment regiments. Among them, MTX based regiments are 291 types, and the risk ratio (RR) are profiled as prediction model by comparing each AE rate of combination regiment with that of MTX monotherapy (Fig 1). The RR ranges from 0.28 to 6.28. The highest risk combination of prednisone (Pred), leflunomide (LEF), methotrexate (MTX), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and Celecoxib (Cel) is selected (RR=6.28) to develop a master algorithm. Figure 2 shows Bayesian network, in which, quartet correlates with 31 different regiments. Based on Bayesian method, the probabilities of LP, IP and ALT elevation are plotted through 64 modeling, and the algorithm for drug withdrawl strategies is generated. Drug withdrawl sequence for LP is HCQ, then Cel, then LEF, then Pred, the risks of LP are reduced by 41%, 22% 36% and 15%, respectively. For IP, withdrawl sequence is Pred, then LEF, then Cel, then HCQ, the risks of IP are reduced by 45%, 28%, 23% and 4%, respectively, For ALT elevation, withdrawl sequence is MTX, then Pred, LEF, then Cel, the risks of ALT elevation are reduced by 48%, 8%, 7% and 6%.
Conclusion: Through patterns extraction, data mining, modeling, and Bayesian networking, a risk prediction model and a master algorithm for drug withdrawl strategy in reduction of AEs are developed, which are expendable and replicatable. Via continuing data inputs and machine leaning, an artificial intelligent system in assisting clinical forecast and decision-making may be achieved with SSDM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhao Y, Li X, Mu R, Zuo X, Wei H, Dong L, Li S, Sun H, Gao G, Wu L, Wu B, Jia Y, Xiao H, Xu M, Zhou W, Chu A, Dong L, Yang H, Gui M, Min W, Zhang Z, Pan Y, Zhang J, He J, Chen H, Xiao F. Develop Risk Prediction Model and Drug Withdrawl Road Map Through Pattern Extraction and Data Mining: Create a Master Algorithm from the Smart System of Disease Management (SSDM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/develop-risk-prediction-model-and-drug-withdrawl-road-map-through-pattern-extraction-and-data-mining-create-a-master-algorithm-from-the-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/develop-risk-prediction-model-and-drug-withdrawl-road-map-through-pattern-extraction-and-data-mining-create-a-master-algorithm-from-the-smart-system-of-disease-management-ssdm/