Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: In a previous study, we found daily proton pump inhibitor (PPI) intake to be associated with decreased bone mineral density in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRMDs) [1]. The underlying pathomechanism is unclear. Similar findings in other populations in the past were repeatedly explained by decreased intestinal calcium absorption and increased levels of intact serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) [2, 3]. Our objective was to assess whether daily PPI use is associated with changes in serum calcium or PTH in patients with IRMDs.
Methods: We used cross-sectional baseline data from the single-center Rh-GIOP cohort [4]. Patients with IRMDs have been prospectively enrolled since 2015. Patients receive DXA scans, laboratory testing and complete bone-health-related questionnaires. This study excluded patients with hyperthyroidism and multiple myeloma. The exposure – daily PPI use – was ascertained by a combination of self-reporting by patients and chart review. Co-primary outcomes were serum levels of calcium and PTH. Analyses were based on general linear models, considering complete cases only. As part of a gatekeeping procedure, adjusted analyses were performed for the respective outcomes only if unadjusted analyses identified statistically significant differences between PPI users and non-users. For adjustment, we used 1) a conventional multiple regression approach and 2) inverse probability of treatment weighting. Potential confounders included age, body mass index (BMI), self-reported degree of physical activity, smoking status, presence of diabetes mellitus type I or II, chronic kidney disease stage, cumulative and current GC dose and serum C-reactive protein. For weighting, included covariates were allowed to affect the outcome only [5], so 25-OH-vitamin D deficiency was additionally included. A sensitivity analysis excluded patients with a prior diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism.
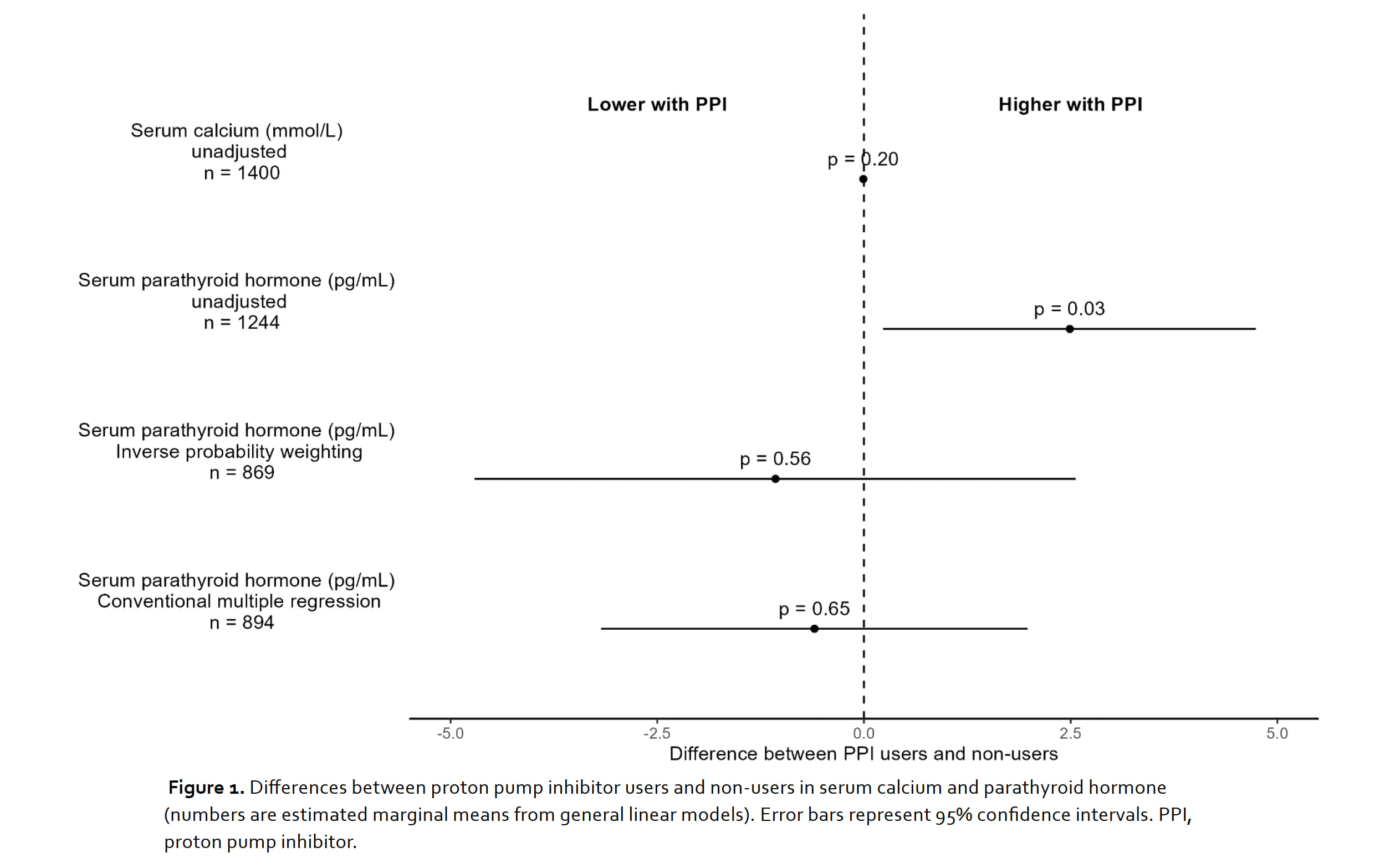
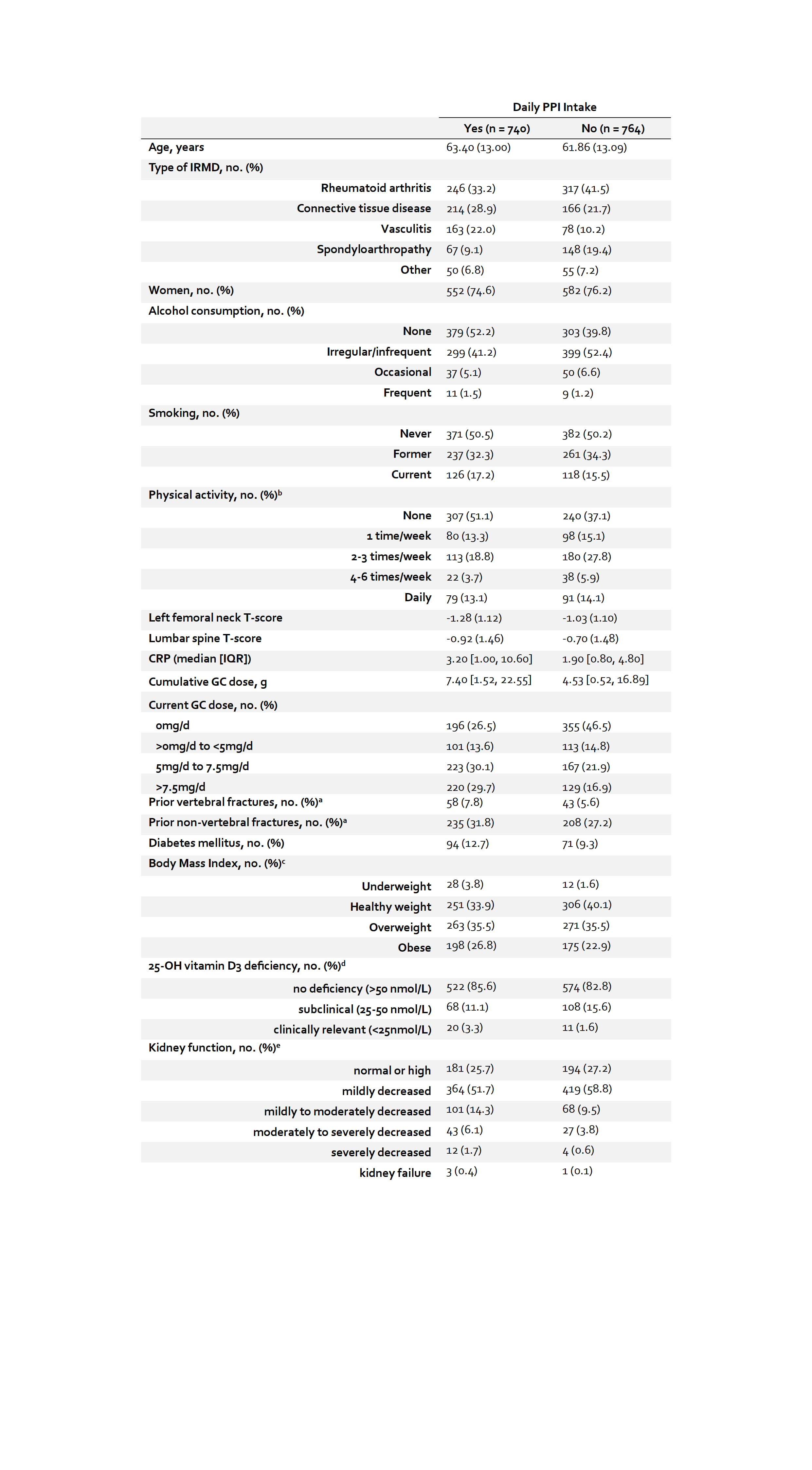
Results: 1,504 patients (75.3% women; mean age 62.6 ± 13.1 years; 49% with daily PPI use) were included (Table 1). Most patients (79.6%) received vitamin D3 supplements and were within normal ranges as measured by 25-OH-vitamin D3. Missingness regarding exposure and outcome variables was as follows: PPI use: 0%; calcium: 7%; PTH: 17%. In the unadjusted analyses, serum PTH was higher in PPI users (difference = 2.49pg/mL; 95% CI 0.23 to 4.74; p = 0.031). Serum calcium was similar in PPI users and non-users and omitted from further adjusted analyses. After adjustment for confounders, statistically significant differences in serum PTH between PPI users and non-users vanished with both adjustment procedures (Figure 1). In the conventional multiple regression model, age, BMI, chronic kidney disease stage and current GC intake were statistically significantly associated with serum PTH. These results were consistent in the sensitivity analysis which excluded patients with a prior diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism.
Conclusion: In our cohort of patients with IRMDs, the previously observed reduction in bone density with PPI does not seem to be mediated by changes in serum calcium or PTH. Prior studies with such findings might have been subject to confounding.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Palmowski a, Boydzhieva Z, Hoff P, Hermann S, Muche b, Simon D, Krönke G, Wiebe E, DR. BUTTGEREIT F. Detrimental Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors on Bone Mineral Density Are Not Mediated by Changes in Serum Calcium or Parathyroid Hormone in Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: A Cross-sectional Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detrimental-effects-of-proton-pump-inhibitors-on-bone-mineral-density-are-not-mediated-by-changes-in-serum-calcium-or-parathyroid-hormone-in-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-cross-sect/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/detrimental-effects-of-proton-pump-inhibitors-on-bone-mineral-density-are-not-mediated-by-changes-in-serum-calcium-or-parathyroid-hormone-in-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-a-cross-sect/