Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is a heterogeneous disease, in which multiple manifestations are associated with considerable morbidity and mortality. Cross sectional studies have shown that compared to patients with other rheumatic diseases, health-related quality of life (HRQoL) is significantly more affected in SSc. How disease specific determinants influence HRQoL over time has not been described thus far.
We aim 1) to evaluate if and how HRQoL changes over time, and 2) to assess how different SSc domains contribute to variations in HRQoL measured over time.
Methods: All SSc patients of the Leiden Combined Care in SSc cohort who fulfilled the ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria for SSc and had at least two visits were included. HRQoL was annually assessed using the EuroQol (EQ5D) and the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF36): mental component score (MCS), and physical component score (PCS). Longitudinal data on clinical characteristics including organ involvement, organ progression and functional assessments were collected. Firstly, we evaluated the mean scores of the EQ5D, MCS and PCS over time and compared these between disease progressors and non-progressors. Secondly, linear mixed-effect regression models were applied to assess changes in HRQoL during the observation time, to control for repeated measurements, and to identify predictive factors. Separate models with the primary outcomes EQ5D, MCS and PCS were applied, first with the independent variables of organ involvement and second with the independent variables of the functional assessments, all adjusted for confounders.
Results: Four-hundred-ninety-two SSc patients were included, with a median follow-up duration of 3.4 years (range 2-6). Over time, both the MCS and PCS worsened with respectively 1.32 points and 1.30 points per year (p < 0.001 scale 0-100), while the EQ5D showed slight improvement (0.01 points per year, on a scale of -0.57-1, p< 0.001). Progression of organ involvement was numerically associated with lower HRQoL scores, indicating a worse HRQol in progressors (figure 1). The results of the linear mixed model showed that over time the clinical characteristics with the highest impact on deterioration of HRQoL were: digital ulcers (DU) (on the PCS β-3.36), modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) > 15 (PCS β -3.8 and EQ5D β -0.06), Raynaud VAS (on the MCS β-0.10, PCS β-0.12 and EQ5D β-0.002), and severe gastro-intestinal involvement (GI) (EQ5D β-0.05). A worse score on any of the functional assessments, including the six-minute walking test (MCS β 0.007, PCS β 0.009), mouth opening distance (MCS β 0.03, PCS β 0.02) fingertip-to palm distance (MCS β -0.07, PCS β -0.05) and grip strength (MCS β 0.05, PCS β 0.03) was associated with deterioration in HRQoL over time as measured by SF36 (p< 0.001).
Conclusion: Over time, HRQoL in patients with SSc slightly worsens and is mainly determined by skin problems including DU, Raynaud and mRSS, and by GI affection. More severe functional impairments also contribute to worsening in HRQoL over time, while impact of ILD seems smaller. These observations underline the heterogeneous nature of SSc and can contribute to interpretation of changes in HRQoL reported in clinical trials.
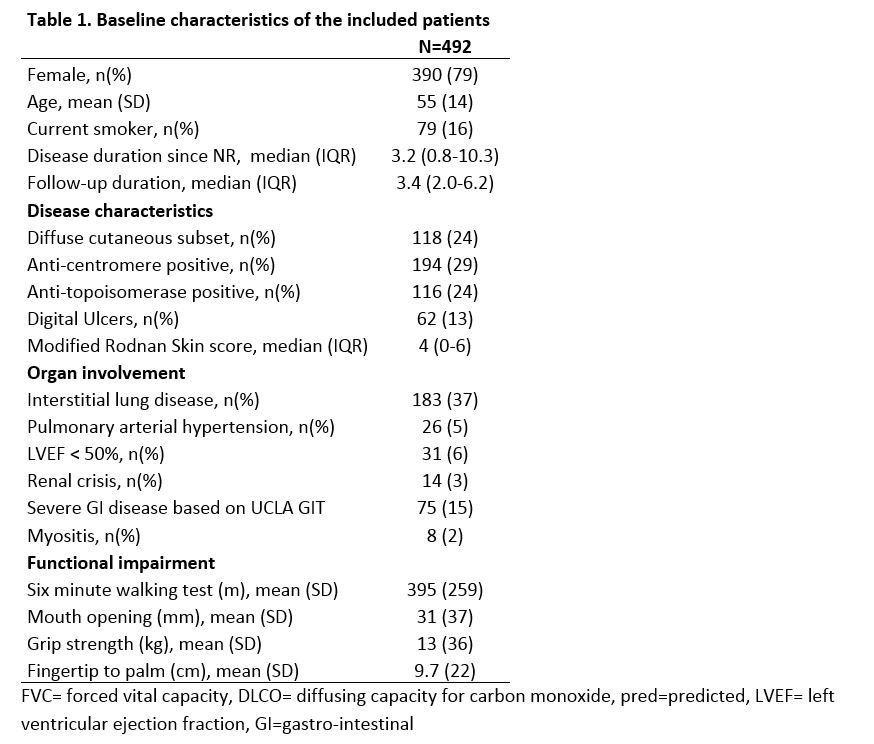 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the included patients
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the included patients
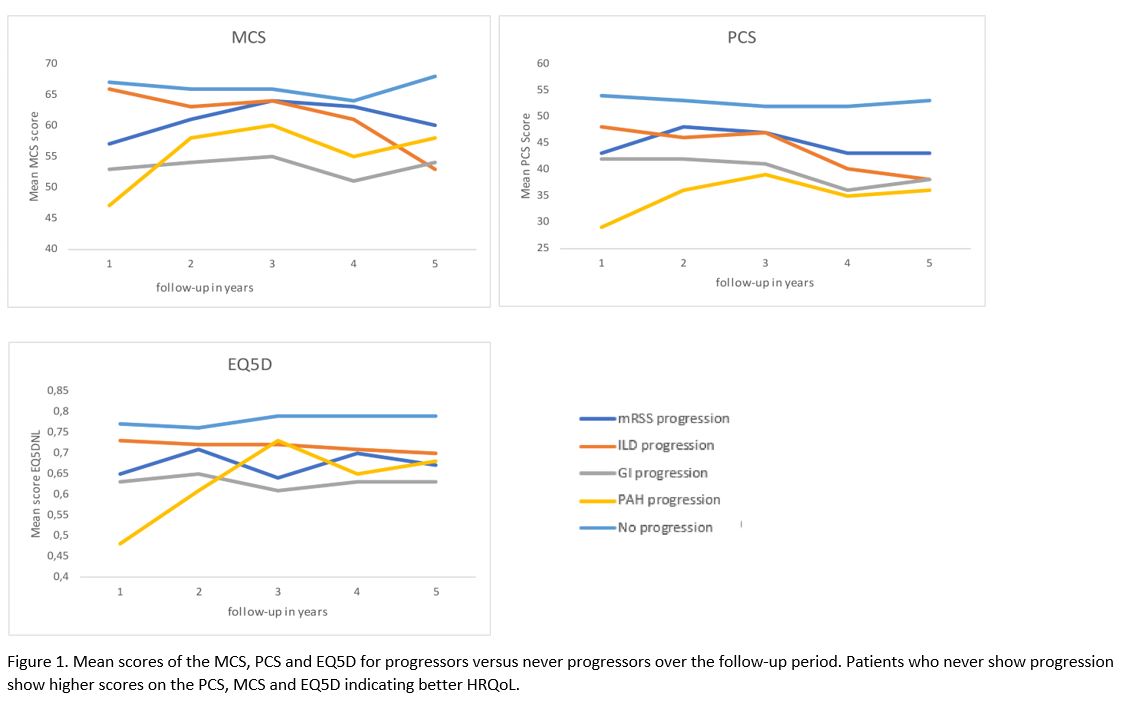 Figure 1. Mean scores of the MCS, PCS and EQ5D for progressors versus never progressors over the follow-up period. Patients who never show progression show higher scores on the PCS, MCS and EQ5D indicating better HRQoL.
Figure 1. Mean scores of the MCS, PCS and EQ5D for progressors versus never progressors over the follow-up period. Patients who never show progression show higher scores on the PCS, MCS and EQ5D indicating better HRQoL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Leeuwen N, Ciaffi J, Liem S, Huizinga T, de Vries-Bouwstra J. Determinants of Health-related Quality of Life in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/determinants-of-health-related-quality-of-life-in-systemic-sclerosis/
