Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) has gained popularity in the United States over the last few decades. Herbal supplements have adverse medical effects. We observed two patients with acute onset/flare of their classic dermatomyositis after the ingestion of IsaLean®, an herb-based weight-loss product. The purpose of this study was to investigate and characterize the immunostimulatory properties of the herbal and dietary supplement IsaLean® underlying the acute onset/flare of dermatomyositis in two patients.
Methods : Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from 5 dermatomyositis patients and 5 control patients stimulated with increasing concentrations of IsaLean®: 0, 0.05, 0.5, and 5 µg/ml to evaluate the cellular production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), interferon alpha (IFN-α), and interferon beta (IFN-β), key pathogenic cytokines in dermatomyositis. The cells were also incubated with IsaLean® and lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and the effect of neutralizing anti-TLR4, quinacrine (QC), and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) on the cellular production of TNFα was examined. Cytokine production was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was used to compare the level of TNF-α, IFN-α, and IFN-β after stimulation with Isalean and treatment with Anti-TLR4, QC, and HCQ.
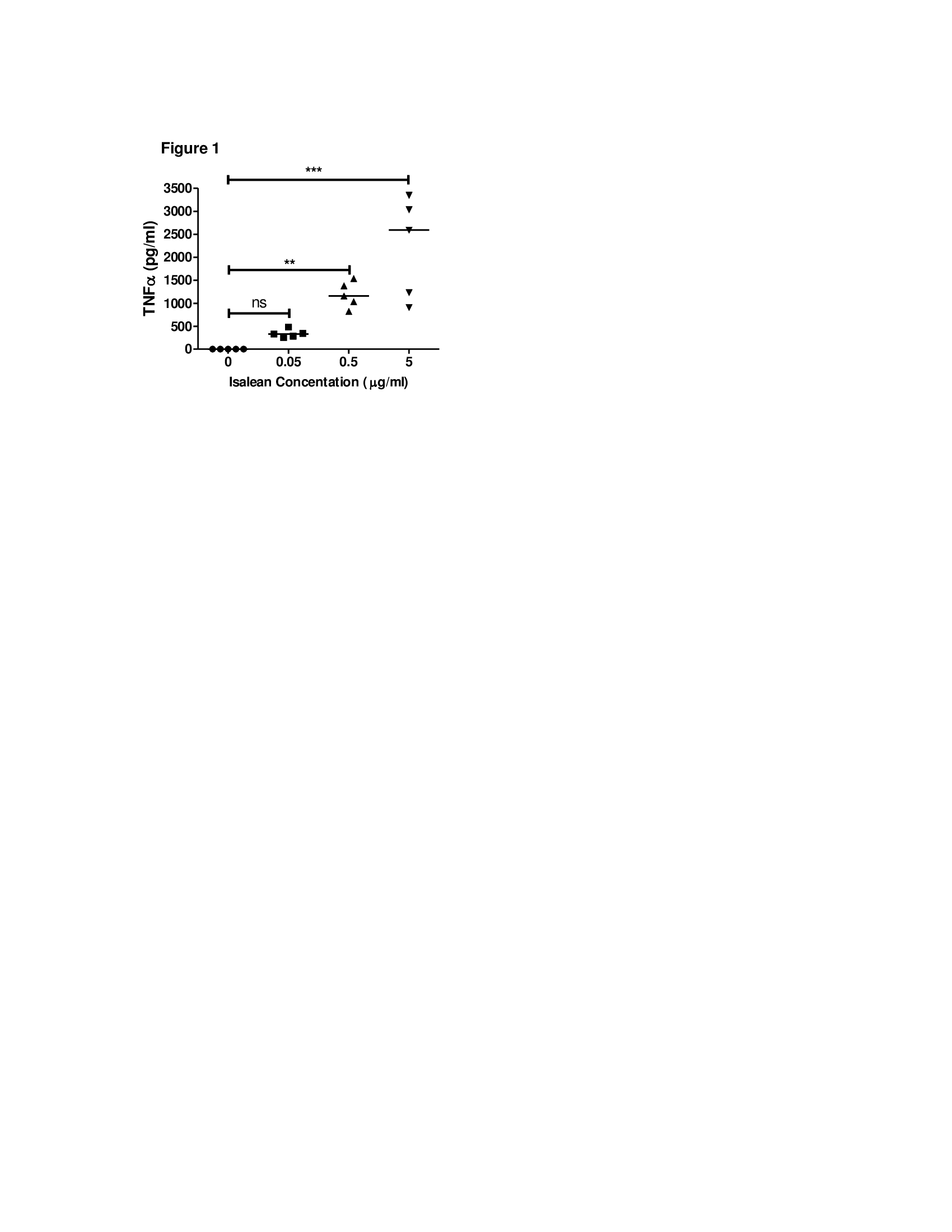
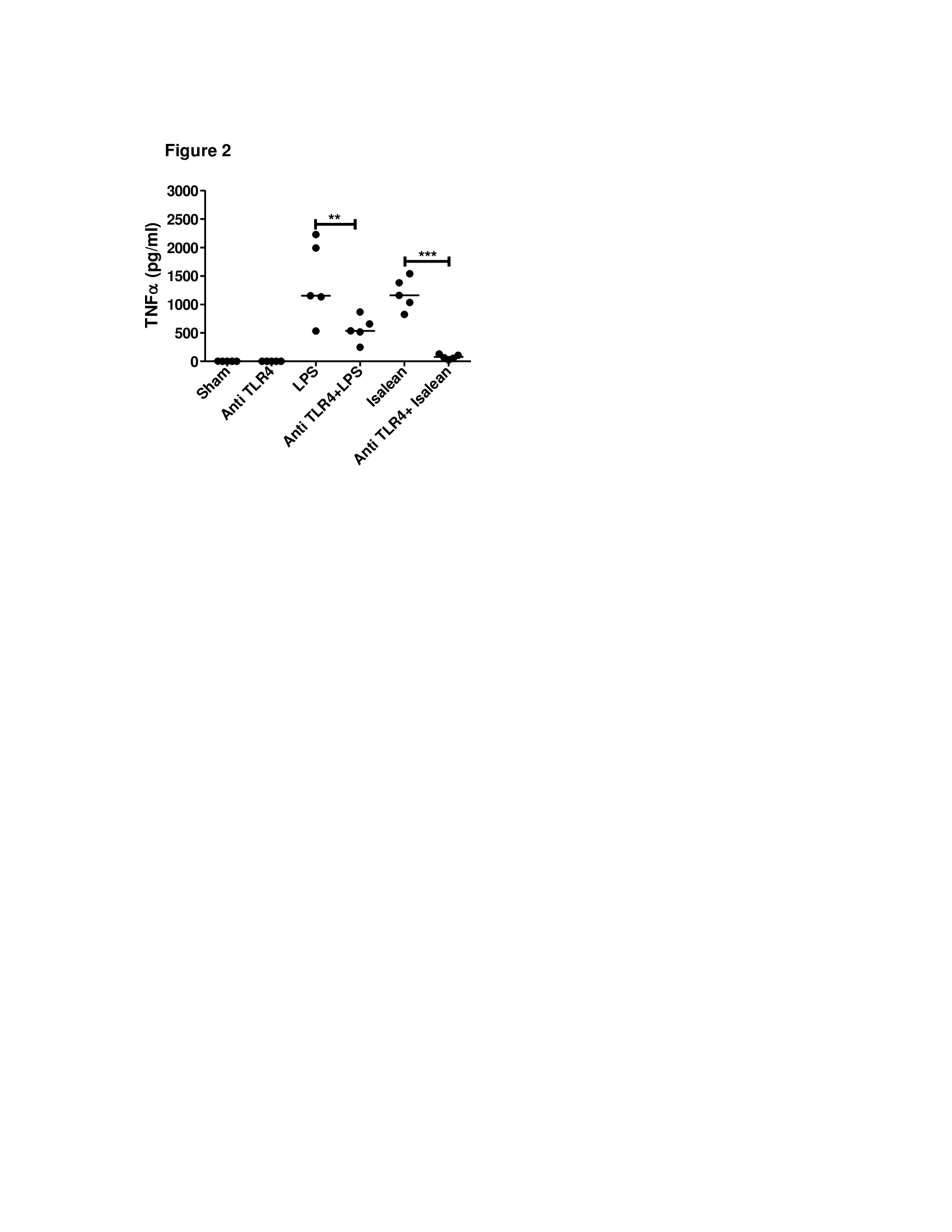
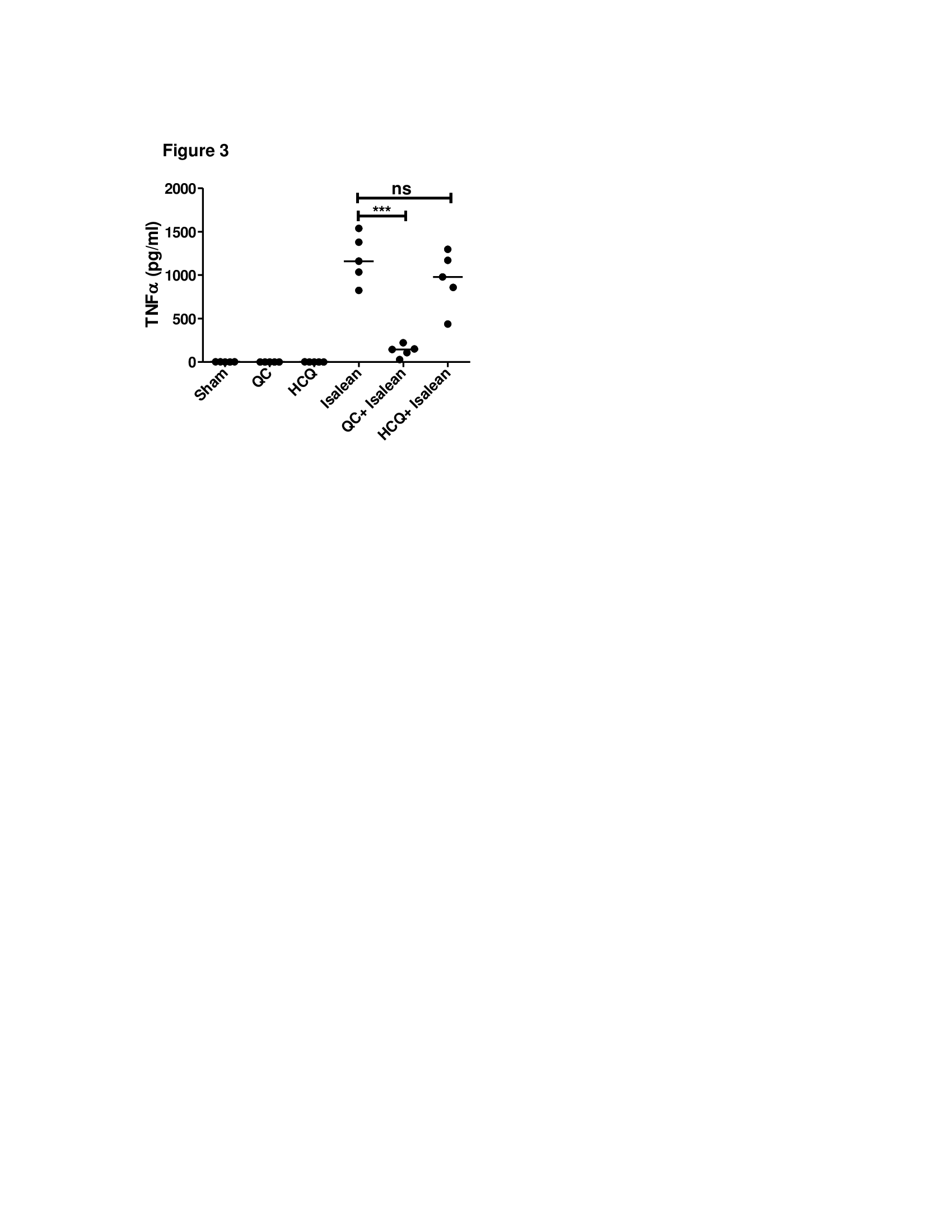
Results : The IsaLean® stimulated cells secreted mean (standard error) TNFα levels of 1.78 (0.38), 339.5 (39), 1188 (125.5) and 2224 (488.7) pg/ml at 0, 0.05, 0.5, and 5 µg/ml concentrations of IsaLean®, respectively. IsaLean® increased cellular secretion of TNFα at 0.5 µg/ml (p<0.01) and 5 µg/ml (p<0. 001) (Figure 1). Anti-TLR4 suppressed cellular secretion of TNFα from IsaLean® (p<0.001) and LPS-stimulated cells (p<0.01) (Figure 2). QC significantly reduced the production of TNFα from IsaLean® (p<0.001) and LPS-stimulated (p<0.05) compared to HCQ (Figure 3).
Conclusion : IsaLean®, an herb-based weight-loss product, induced secretion of TNFα, IFN-α, and IFN- β from immune cells of dermatomyositis patients in vitro. These cytokines are thought to be key immunostimulatory cytokines causing cutaneous dermatomyositis. These studies demonstrate that the pro-stimulatory effects of IsaLean® are mediated through TLR4.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zeidi M, Chansky PB, Werth VP. Dermatomyositis Acute Onset/Flares Following Ingestion of Isalean® Herbal Supplement: Clinical and Immunostimulatory Findings [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-acute-onsetflares-following-ingestion-of-isalean-herbal-supplement-clinical-and-immunostimulatory-findings/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dermatomyositis-acute-onsetflares-following-ingestion-of-isalean-herbal-supplement-clinical-and-immunostimulatory-findings/