Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The development of a personalized medicine approach to identify responders and non-responders to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) inhibiting agents for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) would greatly improve patient outcomes. TNFα inhibitors are first-line treatments for moderate to severe RA, yet up to half of patients do not respond adequately, highlighting the need for predictive biomarkers to optimize treatment strategies. The objective of our study was to determine the impact of rs1061622 polymorphisms (TNFR2 vs TNFR2-M196R)1 on anti-TNFα therapy response in patients with RA.
Methods: We conducted a study to identify genetic biomarkers predictive of TNFα inhibitor response in RA patients. Specifically, we examined the association of the TNFR2 gene polymorphism (rs1061622) with treatment outcomes. Genomic DNA was extracted from patient blood samples, and genotyping was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequencing. Treatment responses were evaluated based on chart review of patient response, and statistical analyses were conducted to determine the correlation between the TNFR2 polymorphism and treatment efficacy.
Univariate comparisons were made between non-responders and responders using two-sample t-tests for continuous variables, or Chi-square/Fisher’s exact tests for categorical variables. To investigate whether the genetic marker is a risk factor for response status, a univariable logistic regression model was built. Odds ratios, 95% confidence intervals, and c-index were calculated.
Data management and analysis were performed using R (Version 4.0; Vienna, Austria). All tests were two-sided, assuming an alpha level of 0.05.
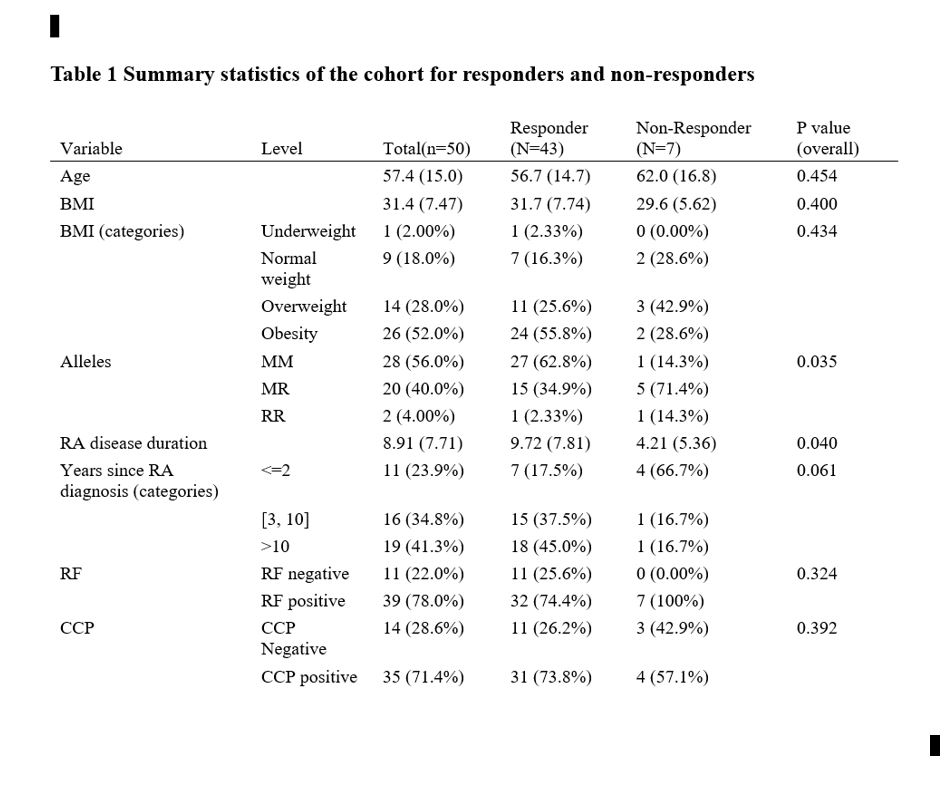
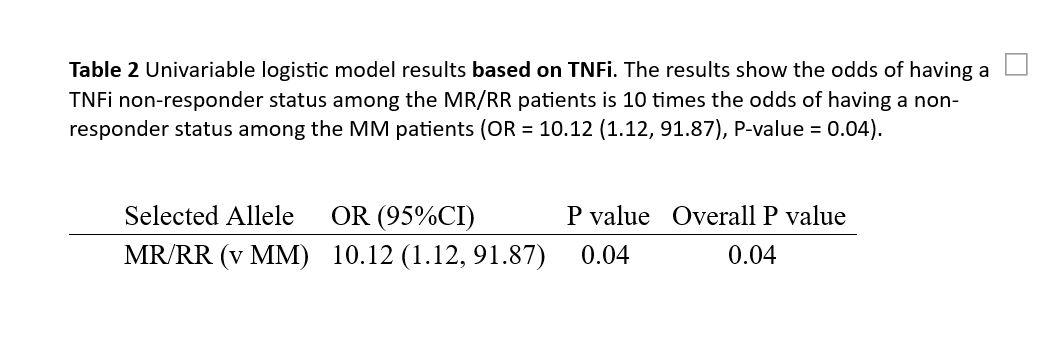
Results: 50 patients were included (average age is 57.4 years with SD+/- 15 years. average BMI = 31.7. Duration of RA diagnosis =8.9 years.) We have 43 responders and 7 non-responders in our RA cohort. Regarding our genetic markers, 28 patients (56%) are MM, 20 patients (40%) are MR, and 2 patients (4%) are RR. Our results indicate that patients with the MR/RR allele have ten times higher odds of being non-responders to TNFi therapy compared to patients with the MM allele (OR = 10.1, 95% CI: 1.12-91.87, P = 0.04). Interestingly, the majority of patients who did not respond to therapy contained a R allele. The c-index is 0.74, suggesting that the marker is moderately predictive of the outcome.
Conclusion: Identifying predictors for non-responsiveness to TNF antagonists and genotyping these polymorphisms in RA patients may be a valuable tool for predicting the efficacy of TNFi drugs. Our study demonstrated that RA patients with the MR/RR allele are ten times more likely to be non-responders to TNFi therapy compared to those with the MM allele. This personalized medicine-based approach could significantly improve RA treatment by enabling more targeted and effective therapy decisions.
1. Chen W, Xu H, Wang X, Gu J, Xiong H, Shi Y. The tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B polymorphisms predict response to anti-TNF therapy in patients with autoimmune disease: A meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015;28(1):146-153.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husni M, Zhang J, Lin J, Jin Y, Chandrasekharan U. Defining a Personalized Treatment Approach to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Using Genetic Markers of TNFi Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/defining-a-personalized-treatment-approach-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-genetic-markers-of-tnfi-response/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/defining-a-personalized-treatment-approach-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-using-genetic-markers-of-tnfi-response/