Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster I: Patient-Reported Outcomes
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Injection site pain (ISP) is a component of the patient experience with injectable drugs. A new formulation of etanercept was developed to reduce ISP. In this work, we assessed ISP associated with a new formulation of etanercept compared to the prior formulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: This phase 3b, randomized, double-blind, 2-period, 2-sequence crossover study (NCT02986139) enrolled etanercept-naïve patients with RA or PsA (inclusion based on the Classification criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis [CASPAR criteria]). The 2-week treatment period was followed by a 30-day safety follow-up. Patients were randomized 1:1 to prior formulation first followed by new formulation or new formulation first followed by prior formulation; administered 1 week apart, consistent with labeled dosing (50mg weekly). ISP was assessed within 30 seconds after administration and was measured using a validated ISP scale based on a visual analog scale ranging from 0 mm (no pain at all) to 100 mm (worst pain imaginable).
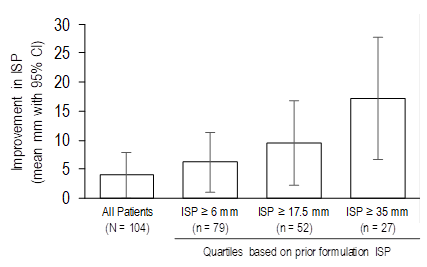
Results: Of 111 patients enrolled (56 prior77.5%/new sequence; 55 new/prior sequence), 77.5% had RA, 22.5% had PsA. Of these, 104 patients received both doses. Overall, the mean change (least squares mean; 95% confidence interval [CI]) in ISP between prior and new formulations was 4.0 mm (0.03, 7.98) (Table). Patients with higher ISP scores from the prior formulation (by quartile cut points) had greater ISP improvements with the new formulation (Table, Figure). The reduction in ISP (95% CI) for those with prior formulation ISP scores above the arithmetic mean (23.6 mm) was 12.2 mm (3.1, 21.3) and for those below the mean was –0.9 mm (–3.9, 2.1). Injection site reactions were few in number and similar between formulations.
Conclusion: The new formulation of etanercept was associated with lower mean ISP compared to the prior formulation. Patients with higher levels of pain with the prior formulation showed greater pain reduction with the new formulation.
|
|
n |
Prior Formulation |
New Formulation |
Reduction in ISP |
P-value |
|
All patients |
104 |
23.1 |
19.1 |
4.0 (0.03, 7.98) [17.3%] |
0.048 |
|
Cut point analyses based on: |
|||||
|
Prior formulation ISP quartiles |
|||||
|
≥ 6 mm |
79 |
30.8 |
24.5 |
6.2 (1.1, 11.3) [20.2%] |
0.017 |
|
Prior formulation ISP mean |
|
|
|
|
|
|
≥ 23.6 mm |
39 |
52.3 |
40.1 |
12.2 (3.1, 21.3) [23.3%] |
0.01 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Samad A, Karis E, Stolshek BS, Trivedi M, Zhang H, Aras GA, Kricorian G, Chung J. Decreased Injection Site Pain Associated with New Etanercept Formulation in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-injection-site-pain-associated-with-new-etanercept-formulation-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-or-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-injection-site-pain-associated-with-new-etanercept-formulation-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-or-psoriatic-arthritis/