Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Information regarding the degree and the predictors of damage in patients with Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) is limited. This study aimed to characterize damage and identify predictors of damage in patients with TAK.
Methods: Patients with TAK enrolled in a multicenter, longitudinal study were included. Measures of disease damage, including the Vasculitis Damage Index (VDI) and the Large-Vessel Vasculitis Index of Damage (LVVID), were assessed at baseline and follow-up visits. Results from patients with a diagnosis of TAK made within 6 months prior to entry to the cohort were also separately analyzed. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to analyze development of new damage. Univariate statistics and multivariate Cox regression modeling was used to analyze clinically-relevant baseline predictors of new damage.
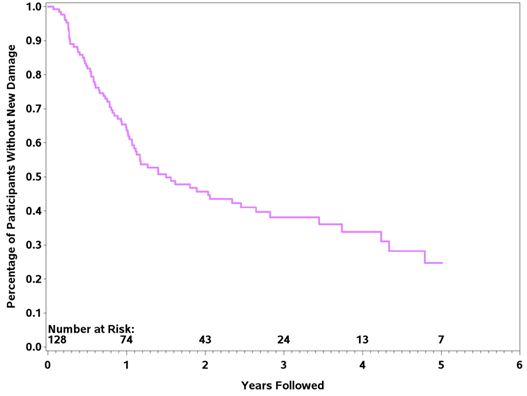
Results: The study included 128 patients with TAK: 94% female, 89% Caucasian, and median duration of follow-up 3.5 years (1.9, 6.2). At entry into the cohort, 113 patients (88%) had at least one damage item recorded on VDI and LVVID [VDI median score 3 (IQR: 1-5)] and [LVVID median score: 2 (1-4)]. 31/128 (24%) of patients had a diagnosis of TAK made within 6 months prior to study entry, 81% of whom had at least 1 item documented on VDI and LVVID. During the follow-up period 96 patients (75%) accrued at least one new damage item, most of which occurred in the first year of follow-up (Figure 1). The cardiac and peripheral arterial systems accounted for most of the damage captured at baseline and follow-up. Results of univariate and multivariate analysis of clinically-relevant baseline predictors are shown in Table 1. Patients with new-onset disease (diagnosed ≤ 6 months within study entry) had a higher risk of new damage than patients with longer disease duration. The use of glucocorticoids was not associated with development of new damage.
Conclusion: Damage predominantly related to disease rather than treatment is present in the majority of patients with TAK, even within 6 months of diagnosis. Although damage accrues more commonly early in the disease course, the majority of patients with TAK continue to accrue new damage, mostly related to disease, even after several years of follow-up. Future research should address the question of whether treatment of TAK during the early stages of the disease reduces accumulation of disease-related damage.
Figure 1. Time to development of new damage on the Vasculitis Damage Index or the
Large Vessel Vasculitis Index of Damage in 128 patients with Takayasu’s arteritis
|
Table 1. Baseline predictors of new damage during follow-up for patients with Takayasu’s arteritis |
||||||
|
Predictors of damage |
Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
||||
|
|
Hazard Ratio |
95% CI |
p value |
Hazard Ratio |
95% CI |
p value |
|
Age > 35 at baseline |
0.940 |
0.592-1.494 |
0.794 |
0.861 |
0.526-1.411 |
0.553 |
|
Duration of the disease |
2.343 |
1.397-3.930 |
0.001 |
1.957 |
1.025-3.738 |
0.041 |
|
Presence of damage at baseline |
1.943 |
0.888-4.252 |
0.096 |
1.512 |
0.636-3.595 |
0.349 |
|
Sex |
0.698 |
0.698-0.280 |
0.439 |
1.060 |
0.396-2.835 |
0.907 |
|
Race |
1.129 |
0.540-2.360 |
0.747 |
1.381 |
0.638-2.992 |
0.412 |
|
No disease activity |
0.629 |
0.395-1.001 |
0.050 |
0.747 |
0.448-1.246 |
0.263 |
|
No glucocorticoids at baseline |
0.729 |
0.456-1.164 |
0.185 |
0.681 |
0.418-1.109 |
0.122 |
|
No immunosuppressive therapy at baseline |
1.579 |
0.994-2.508 |
0.053 |
1.239 |
0.709-2.164 |
0.451 |
|
No previous flare at baseline |
1.471 |
0.925-2.339 |
0.102 |
1.200 |
0.678-2.124 |
0.531 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sreih AG, Kermani TA, Cuthbertson D, Carette S, Khalidi NA, Koening CL, Langford CA, McAlear CA, Monach PA, Moreland LW, Pagnoux C, Seo P, Warrington KJ, Ytterberg SR, Merkel PA. Damage and Predictors of Damage in Takayasu’s Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/damage-and-predictors-of-damage-in-takayasus-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/damage-and-predictors-of-damage-in-takayasus-arteritis/