Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1147–1190) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Panniculitis refers to inflammatory disorders of subcutaneous fat that pose diagnostic challenges due to nonspecific clinical features and overlapping histopathological patterns. Although it can occur in immune-mediated diseases (IMIDs), its characterization in rheumatologic settings remains limited. This study aimed to describe the clinical, immunological, histological features and treatments of panniculitis cases jointly evaluated by Rheumatology and Dermatology.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, observational study of patients diagnosed with panniculitis via electronic health records at Hospital Universitario La Paz between January 2022 and March 2025, during the implementation of a multidisciplinary approach involving adult and pediatric Rheumatology and Dermatology. Patients were identified using the keyword “panniculitis.” Data collected included sociodemographics, diagnosis dates, histological pattern (when available), etiology, associated rheumatologic disease, clinical context (initial or subsequent manifestation), lab findings, treatments, and outcomes (remission or recurrence). Statistical analysis was performed using R v4.4.1.
Results: Of 70 patients identified, 63 with cutaneous panniculitis were included (7 pediatric). Most were women (87.3%), with a median age of 49.5 years (Table 1). The leading causes were idiopathic erythema nodosum (EN: 33.3%), Behçet’s disease (BD: 11.1%), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE: 9.5%), infections (15.9%), and sarcoidosis (7.9%). Panniculitis was the initial manifestation of an IMID in 33.3%. Among BD patients (n=7), it was the first sign in 85.7%; in SLE (n=6), it preceded diagnosis in 50%. Histopathology was available in 27 cases, with septal panniculitis without vasculitis being most common (55.6%), associated with sarcoidosis, BD, and idiopathic EN. Lobular panniculitis without vasculitis was linked to SLE. Of 35 non-biopsied cases, 26 had idiopathic or infectious causes, likely guiding the decision to omit histology. Panniculitis achieved remission in 73% (n=46), mainly in idiopathic EN (15) and infectious causes (10), most of whom (98%) responded to symptomatic or antimicrobial therapy. Recurrences occurred in 27% (n=17), linked to idiopathic EN (5), BD (3), SLE (2), autoinflammatory syndrome (AIS: 2), or other IMIDs (5). Of these, 82% required immunomodulatory treatment: c-DMARDs (n=6) and b/s-DMARDs (n=8). All received b/s-DMARDs except one patient with juvenile idiopathic arthritis who underwent four treatment lines. Biologic and targeted therapies included TNF inhibitors (n=6), anifrolumab (n=1), anti-IL1 (n=1), anti-IL6 (n=1), anti-CD20 (n=1), and JAK inhibitors (n=2).
Conclusion: Cutaneous panniculitis may be an early or evolving feature of systemic IMIDs, particularly BD and SLE. While idiopathic and infectious cases often remit with symptomatic or antimicrobial therapy, recurrent or immune-mediated forms typically require immunosuppression, including biologics and JAK inhibitors. Multidisciplinary evaluation improves diagnostic accuracy and treatment individualization in complex cases.
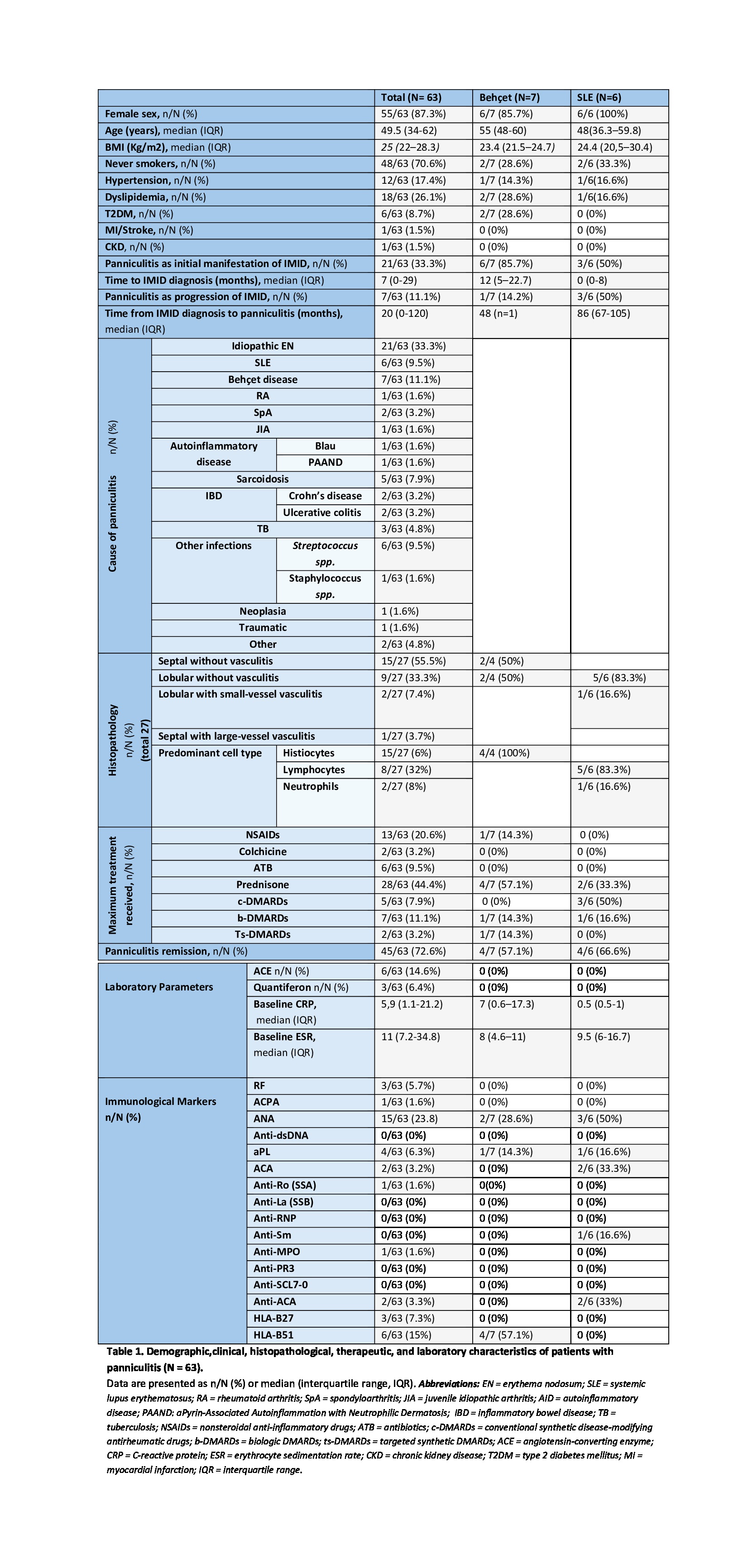 Table 1. Demographic,clinical, histopathological, therapeutic, and laboratory characteristics of patients with panniculitis (N = 63).
Table 1. Demographic,clinical, histopathological, therapeutic, and laboratory characteristics of patients with panniculitis (N = 63).
.jpg) Figure 1. Distribution of diagnoses by histopathological pattern.
Figure 1. Distribution of diagnoses by histopathological pattern.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Campos-Fabre C, Ureta-Moneva C, Sendagorta E, Rodríguez-Gago J, Beato M, Remesal A, Alcobendas R, Udaondo C, Bonilla G, Nuño L, Monjo Henry I, Tornero C, Plasencia-Rodríguez C. Cutaneous Panniculitis in Rheumatology: A Descriptive Cohort Study from a Multidisciplinary Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cutaneous-panniculitis-in-rheumatology-a-descriptive-cohort-study-from-a-multidisciplinary-experience/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cutaneous-panniculitis-in-rheumatology-a-descriptive-cohort-study-from-a-multidisciplinary-experience/
