Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Ustekinumab (UST), an anti-IL-12/23 p40 monoclonal antibody, showed significantly greater improvement at week (wk) 24 compared with placebo (PBO) in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI-2K) response (≥4-point improvement from baseline, BL) in a Phase 2 study.1 Post hoc analysis revealed more UST than PBO patients (pts) achieving ≥50% improvement in total Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area & Severity Index (CLASI) activity score. Harmonization of measures of disease activity and improvement in SLE trials is important since the same clinical manifestations are defined differently among various assessment indices. Here, we examine the relationships of CLASI activity responses to SLEDAI-2K (S2K) mucocutaneous disease responses.
Methods: This phase 2 study enrolled adults with active SLE (S2K ≥6, ≥1 BILAG A and/or ≥2 BILAG B scores) despite standard of care therapy. Pts (n=102) were randomized (3:2) to UST IV ~6 mg/kg or PBO at wk 0, followed by SC injections of UST 90 mg or PBO every 8 wks beginning at wk 8, both added to standard of care. The S2K index, used in this analysis, measures complete improvement from BL. S2K Responder Index-50 (S2K RI-50) evaluates partial improvement and was used to assess partial (≥50%) improvement in S2K rash. CLASI rash was defined as the sum of erythema and scale/hypertrophy score. Independent adjudication of SLE assessments was performed to ensure medical plausibility and consistency of SLE disease activity scores in conjunction with all relevant pt data. In post hoc analysis, improvement in CLASI total activity score at wk 24 was calculated using increasing thresholds of BL disease activity and various cut points of improvement to define treatment response.
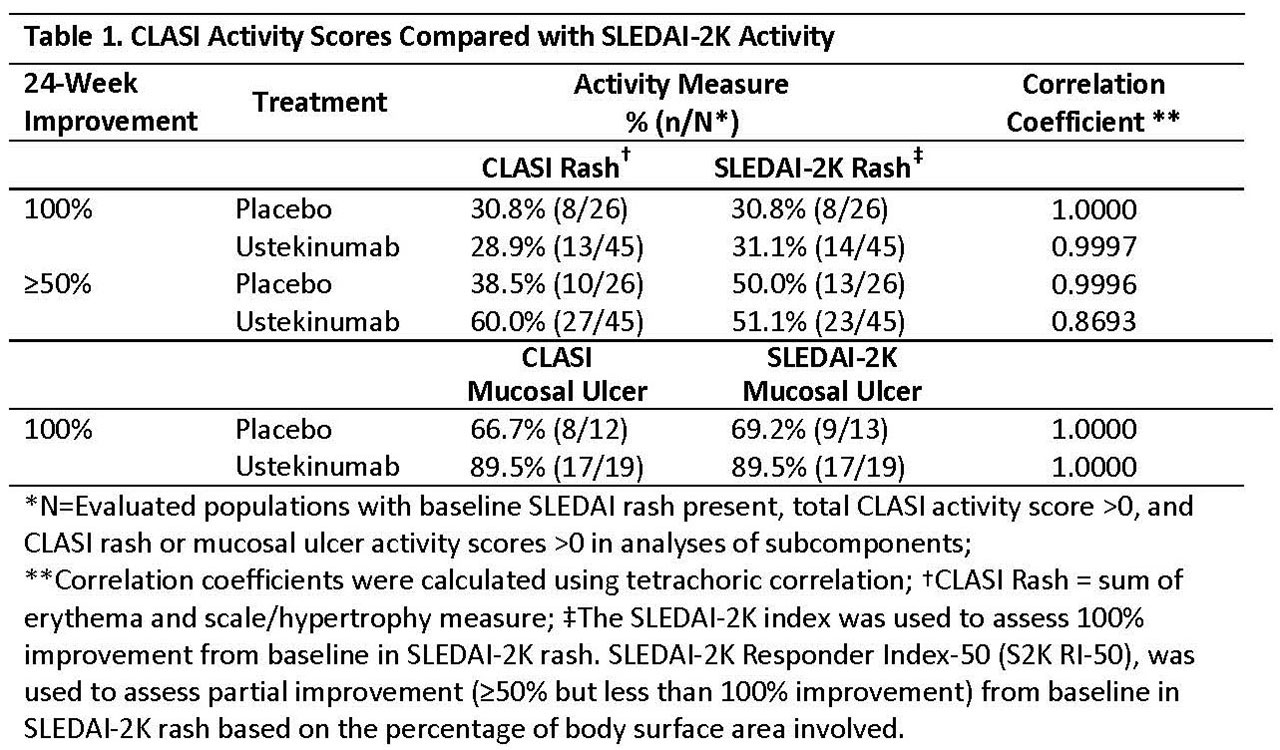
Results: Complete improvement from BL in rash was concordant between CLASI and S2K (correlation coefficients ≥0.997, Table 1). There was less agreement between CLASI and S2K RI-50 when assessing partial improvement in rash. A treatment difference (UST vs PBO) in the proportion of pts achieving partial improvement in rash was observed for CLASI (60% UST vs PBO 38.5%), but not S2K RI-50 (51.1% UST vs 50% PBO) (Table 1). Complete improvement from BL in mucosal ulceration was congruent between CLASI and S2K (correlation coefficient=1). Both instruments demonstrated greater proportions of responders to UST compared with PBO (Table 1). Treatment differences between UST and PBO in achievement of ≥20%, ≥35%, and ≥50% improvement from BL in total CLASI activity score were noteworthy at various thresholds of BL disease activity (Table 2).
Conclusion: CLASI was able to demonstrate partial improvement in active mucocutaneous disease that was not captured by S2K RI-50. A treatment effect favoring UST vs PBO was observed across a range of thresholds of BL CLASI activity and various cut points used to define improvement, which have previously been shown to be clinically meaningful.2 While these findings are based on a limited sample size and duration of therapy, the results will be confirmed in an ongoing Phase 3 clinical trial of UST in SLE (NCT03517722).
- Van Vollenhoven Lancet. 2018;392:1330.
- Chakka S. J Invest Dermatol 139: S101 (abstract #587), 2019.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werth V, Hahn B, Tsokos G, Rose S, Fei K, Gregan Y, Gordon R, Lo K, van Vollenhoven R. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area & Severity Index (CLASI) Demonstrates Thresholds for Detection of Treatment Response in a Phase-2, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Ustekinumab in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-disease-area-severity-index-clasi-demonstrates-thresholds-for-detection-of-treatment-response-in-a-phase-2-placebo-controlled-trial-of-ustekinumab-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-disease-area-severity-index-clasi-demonstrates-thresholds-for-detection-of-treatment-response-in-a-phase-2-placebo-controlled-trial-of-ustekinumab-in-sle/