Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: A survey was conducted to better understand the characteristics and management of axSpA and patient and physician perspectives on current treatment.
Methods: In March 2024, data were extracted from a large, cross-sectional Disease-Specific ProgrammeTM survey, which was initiated in June 2023 in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK. Rheumatologists were asked to complete an online survey for their next 8 consecutive adult patients with axSpA (4 with radiographic [r]- and 4 with non-radiographic [nr]-axSpA). The same patients could voluntarily and independently complete a survey, allowing physician- and patient-reported data to be matched. Surveys covered clinical status, treatment decisions, preferences and satisfaction. All analyses were descriptive.
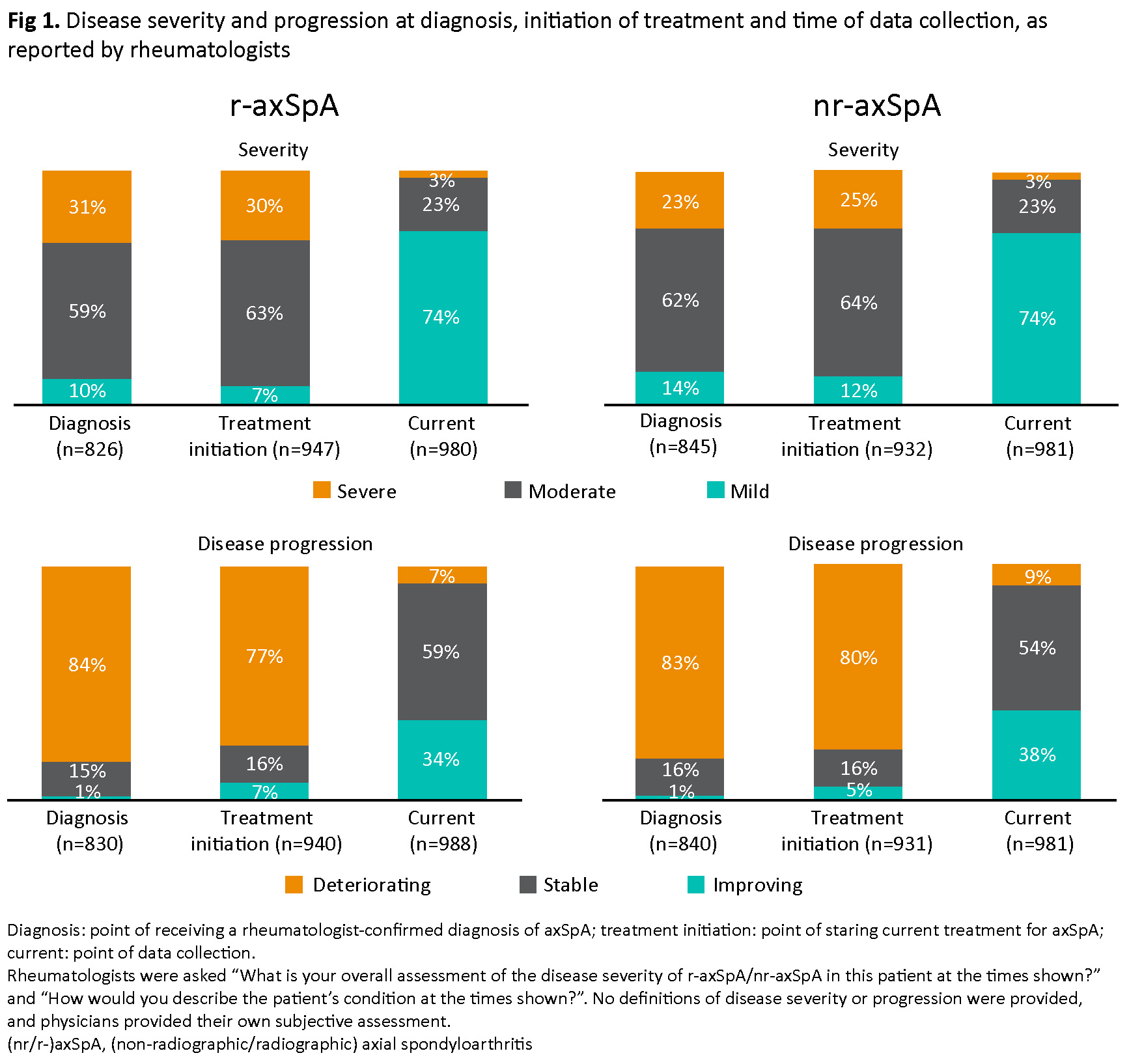
Results: Rheumatologists (N=276) provided data on 988 patients with r-axSpA and 981 with nr-axSpA. Patient-reported data were available for 265 r-axSpA and 222 nr-axSpA patients. Mean disease duration was 7.3 years for r-axSpA and 4.5 years for nr-axSpA. At diagnosis, moderate or severe disease was reported in 90% of patients with r-axSpA and 85% of those with nr-axSpA; at data collection, 26% of patients in each group had moderate or severe disease. The proportion of patients with deteriorating r-axSpA/nr-axSpA reduced from 84%/83% at diagnosis to 7%/9% at data collection (Fig 1). At data collection, the most common symptoms/features were morning stiffness, sacroiliitis, fatigue and pain (17–35%); 9% of patients were experiencing current flares. On average, patients had 3.9 consultations in the last 12 months.
Patient–physician matched data (N=477) showed rheumatologists perceived axSpA as less severe than patients did, reporting severe disease for 3% of patients, versus 6% reported by patients.
Rheumatologists stated they followed treatment recommendations, predominantly ASAS-EULAR, for ~60% of patients. 76% of patients were on advanced therapy (AT), most commonly TNF inhibitors (72%), followed by IL-17 inhibitors (16%) and Janus kinase inhibitors (10%). The most frequent reasons for prescribing current treatment were control of acute episodes/flares (51%) and good overall safety profile (51%). Matched data (N=483) showed patients and rheumatologists mutually agreed that treatment decisions were shared in 62% of individual cases.
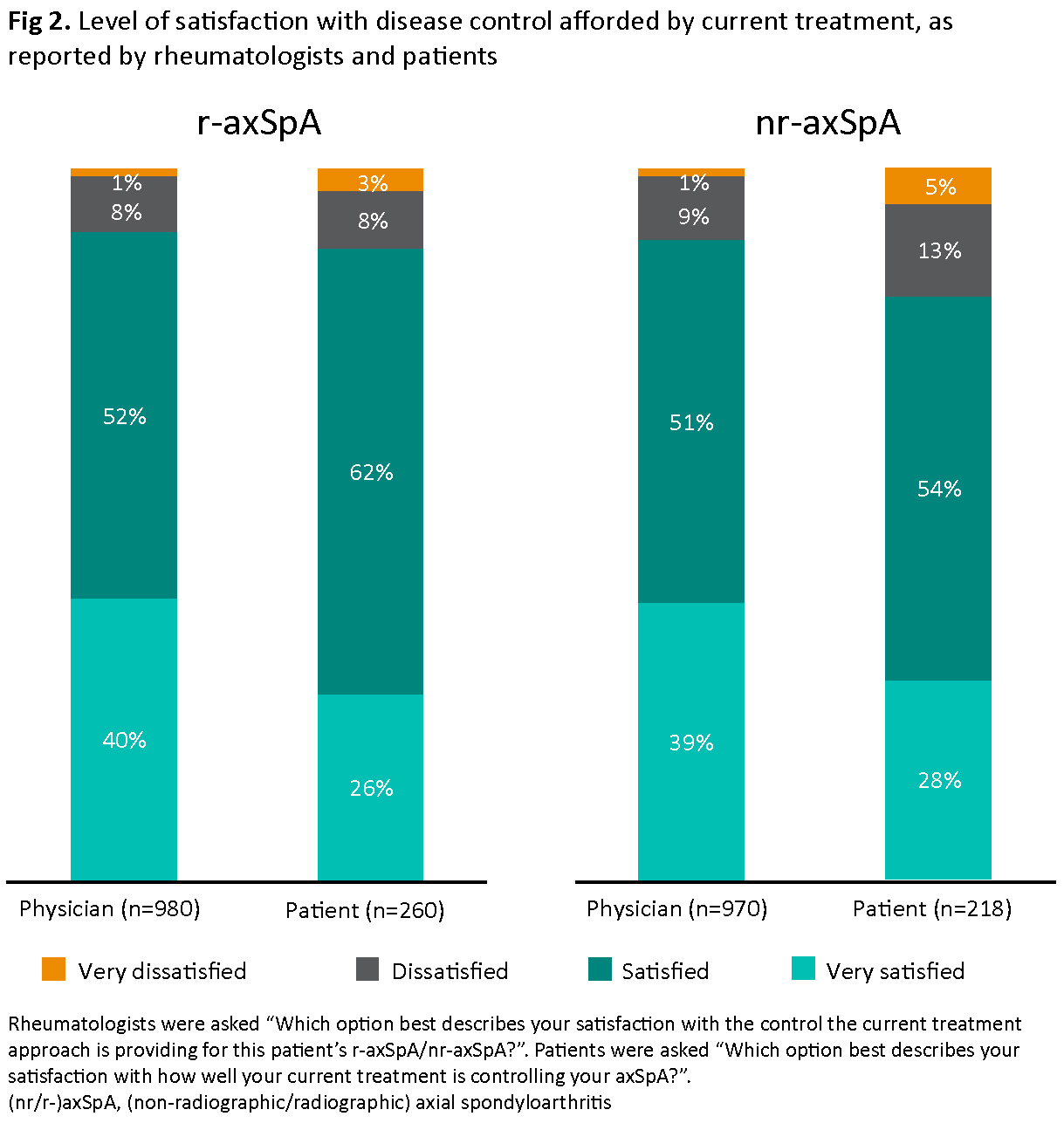
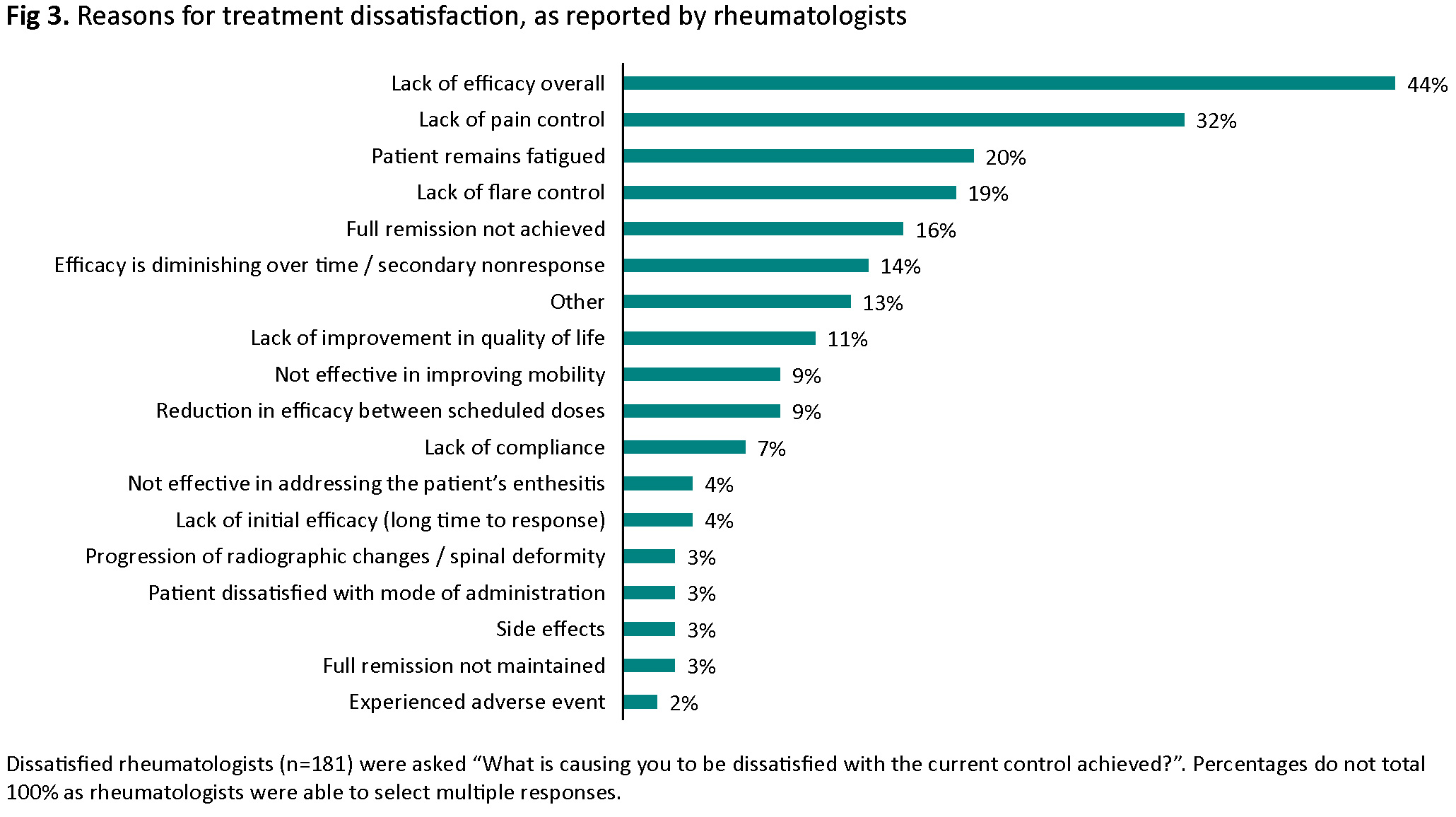
Most patients with r-axSpA (88%) and nr-axSpA (82%) were satisfied with current treatment; rheumatologists were satisfied for 92% and 90% of patients, respectively (Fig 2). Rheumatologists were very satisfied with current treatment for a higher proportion of AT-naïve versus AT-experienced patients (45% vs 31%); amongst patients, 31% (AT-naïve) and 30% (AT-experienced) were very satisfied. The most common reasons for rheumatologist dissatisfaction were lack of efficacy overall (44%), lack of pain control (32%) and fatigue (20%) (Fig 3).
Conclusion: In this cross-sectional study, rheumatologists reported following treatment recommendations for ~60% of patients, and most patients were involved in treatment decisions. Treatment dissatisfaction was reported by rheumatologists and patients for a minority of patients; amongst rheumatologists, this was most often due to lack of efficacy, pain or fatigue.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Navarro Compán V, Nikiphorou E, Pham T, Ciccia F, Hughes M, Kranz B, Jus A, Watson C, Lowe J, Ramiro S. Current Disease Management and Treatment Satisfaction in Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in Europe: Patient and Rheumatologist Perspectives [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/current-disease-management-and-treatment-satisfaction-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-in-europe-patient-and-rheumatologist-perspectives/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/current-disease-management-and-treatment-satisfaction-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-in-europe-patient-and-rheumatologist-perspectives/