Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – ePoster I: Basic Science, Biomarkers, & Sclerodermic Fever
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
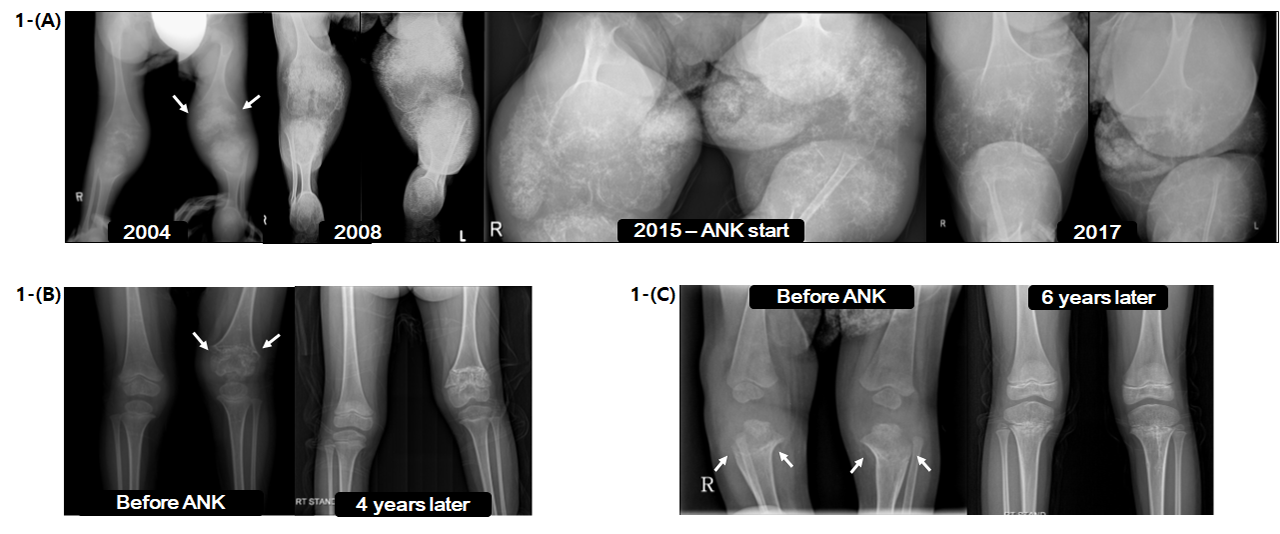
Background/Purpose: Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS) is rare auto-inflammatory disorder characterized by recurrent episodes fever with variable manifestation of systemic inflammation such as urticarial skin rash, joint destruction, sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and neurologic problems. It includes familial cold auto-inflammatory syndrome (FCAS), Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS), and neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID). Pathogenic variants in NLRP3 are thought to be responsible for most cases of CAPS by excessive production of interleukin (IL)-1β.
Methods: Patients with diagnosis of CAPS who visited Seoul National University Children’s Hospital from January 2000 to December 2018 were eligible for inclusion. Retrospective analysis was performed by review of medical records. Clinical information on symptoms and signs, inflammatory markers, pure tone audiometries, simple radiographs of joints, ophthalmoscopies, and other relevant data were collected. Molecular analysis for NLRP3 was performed by Sanger sequencing. Finally, clinical response to recombinant non-glycosylated human IL-1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) was determined by comparing symptoms and signs and changes in test results before and after the treatment.
Results: Sixteen patients were identified (11 NOMID, 3 FCAS, 2 MWS). Total of 112 person years were followed. Most consistent symptoms were fever and rash, present in all cases followed by joint symptoms (n=15), SNHL (n=9). Screening pure tone audiometry revealed high frequency hearing loss in 67% (4/6) of patients with normal hearing, including one FCAS patient. Eleven patients had onset within 1 week after birth, three patients within 3 months. Most common initial diagnoses were milk allergy (n=5), juvenile idiopathic arthritis (n=4), and neonatal sepsis (n=3). Diagnostic delay was common, ranging from 1 month to 17 years (median = 22 months). Pathogenic variation in NLRP3 gene was confirmed in fifteen patients. Anakinra was started for fifteen patients. All patients on anakinra had marked reduction of fever and rash, and 57.5% (5/8) of patients with SNHL had improved or maintained stable hearing. Three of five patients with high frequency hearing loss had improved or maintained stable hearing threshold at 8KHz. Five of eight patients with joint destruction restored normal joint anatomy. Mean initial anakinra dose was 1.19mg/kg/day, and mean final anakinra dose was 2.02mg/kg/day. Most common reason for dose escalation was relapsing clinical symptoms such as fever and rash. One patient with SNHL and one patient with high frequency hearing loss experienced improvement of hearing only after dose escalation. The most common adverse events were injection site erythema and infection.
Conclusion: This study represents the largest cohort of CAPS patients in Korea. High index of suspicion and early intervention with anakinra is crucial to prevent potentially devastating outcomes. In addition this study suggest regular audiometry is necessary and hearing problem maybe the most sensitive factor to determine anakinra dose.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim Y, Kim B, Choi B, Lee H, Jeong D, Han J, Park H, Oh J, Lee S, Oh D, Lee S. Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome in Korea: 19 Years of Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cryopyrin-associated-periodic-syndrome-in-korea-19-years-of-experience/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cryopyrin-associated-periodic-syndrome-in-korea-19-years-of-experience/