Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CR6086, a selective EP4 antagonist, dose-dependently improves disease features in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) models in rodents. Indeed, recent studies highlight the role of the EP4 receptor in modulating autoimmunity and in counteracting bone erosion. Aim of the present study was to test CR6086 as an add-on medication with methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: DBA/1 male mice were immunized with bovine type II collagen (BCII) in CFA. On arthritis onset, animals were assigned to the following experimental groups: vehicle, oral CR6086 30 mg/kg/day, MTX 1 or 3 mg/kg/three times a week alone or in combination with daily CR6086 30 mg/kg. Edema measurement and clinical scores were blindly determined daily before drug administration. After 2 weeks of treatment, mice were sacrificed and serum BCII antibodies measured. Paw joints were blindly scored for histological features. Data were analyzed by ANOVA or by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by appropriate post-hoc comparison test.
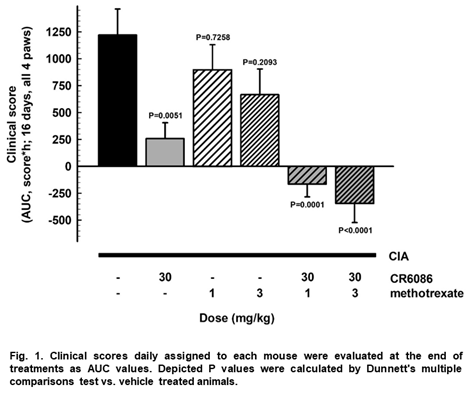
Results: CR6086 strongly and significantly reduced score and edema within the first week of treatment compared to vehicle. MTX 3 mg/kg modestly reduced clinical signs over the second week of treatment, while MTX 1 mg/kg was inactive. CR6086/MTX combined treatments significantly reduced clinical score and edema within the first week of treatment. Figure 1 reports the AUC analysis of the whole treatment. Post-hoc pairwise comparisons showed that combined treatments were significantly superior to each single treatment (P<0.05 and P<0.01 vs. CR6086 and MTX alone, respectively).
Histological features showed a similar treatment pattern (Fig.2), but the effects of CR6086 were so strong when given alone that we could not show a significant synergism with MTX but only a trend.
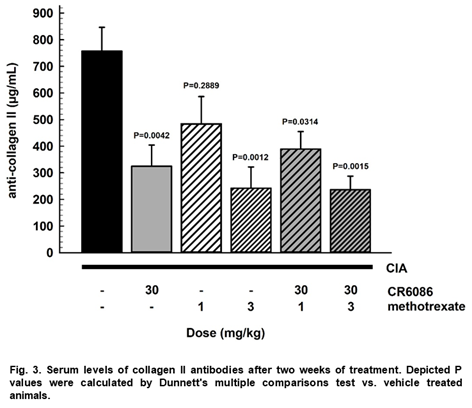
All treatments, but MTX 1 mg/kg, decreased BCII antibodies serum levels (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: In a widely used animal model for RA, CR6086 was effective on all parameters examined both alone and combined with MTX. The superior overall efficacy of CR6086 vs. a classical immunosuppressant as MTX, at equally effective doses on BCII antibodies, outlines that CR6086 independently controls various pathological RA pathways. Moreover, the fact that CR6086 improved MTX effect strengthens its use in early RA in DMARD naïve patients, as presently investigated in clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Caselli G, Ferrari F, Comi E, Perrella M, Recordati C, Grotti A, Cavagnoli R, Lanza M, Rovati LC. CR6086 Is Highly Effective and Improves Methotrexate Effect in a Mouse Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cr6086-is-highly-effective-and-improves-methotrexate-effect-in-a-mouse-model-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cr6086-is-highly-effective-and-improves-methotrexate-effect-in-a-mouse-model-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/