Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the early phase of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), PGE2 recruits different immune cells from the blood stream into target tissues. Via the EP4 receptor, PGE2 acts as a cytokine amplifier (e.g. triggers IL-6 expression in macrophages) and induces the expansion of inflammatory T helper 17 (Th17) cells by increasing the activity of IL-23/IL-17 axis. These mechanisms play a pivotal role in the development of autoimmunity. 2 Interestingly, in a mouse model of collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA), EP4 knockout mice were resistant to the development of experimental arthritis.3 These findings strongly suggest that EP4 receptor antagonists may potentially act as novel early DMARDs. CR6086, a selective antagonist of EP4 receptor, was previously found to improve or resolve disease features in the rat and mouse CIA model of RA.4,5 In this study we present a pharmacological characterization of CR6086, and provide evidence for its immunomodulatory effects on in vitro models of IL-23 and IL-17 release from human cells.
Methods: We assessed first the functional effect of CR6086 on the human EP4 receptor by measuring the levels of PGE2-stimulated cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) production in stably transfected HEK293 cells, and on human THP1 cells differentiated with PMA to macrophages. Different models of immune cell differentiation and expansion were used, and the effect of CR6086 was evaluated by ELISA on IL-23 release from human dendritic cells, and on IL-17 release from human Th17 cells.
Results: CR6086 showed high affinity for the human EP4 receptor with a Ki = 16.6 nM, and strong inhibitory effect on PGE2-stimulated cAMP levels, with an IC50 of 22nM and 58nM in stably transfected HEK293 cells, and in THP1 differentiated macrophages, respectively. The analysis of the immunomodulatory potential for CR6086 was made by analyzing the release of selected cytokines (i.e. IL-23 and IL-17, Table 1) related with the activation and progression of the immune response in the RA pathology. We found that CR6086 dose-dependently reduced IL-23 release in activated human dendritic cells, and inhibited IL-17 release in activated human Th17 cells. In both the cell models CR6086 appeared more effective than naproxen.
Conclusion: CR6086 is a new potent EP4 receptor antagonist with immunomodulatory potential. In fact, it significantly reduced the release of IL-23 and IL-17, two cytokines important for the activation of the immune response during the early phases of RA. References: <>1 Aoki T, Narumiya S. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Jun;33(6):304-11. <>2 Lubberts E. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 Jul;11(7):415-29. <>3McCoy JM et al J Clin Invest. 2002 Sep;110(5):651-8. <>4Chiusaroli R et al. (abs) Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:215. <>5Chiusaroli R et al. (abs) Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74: 216. 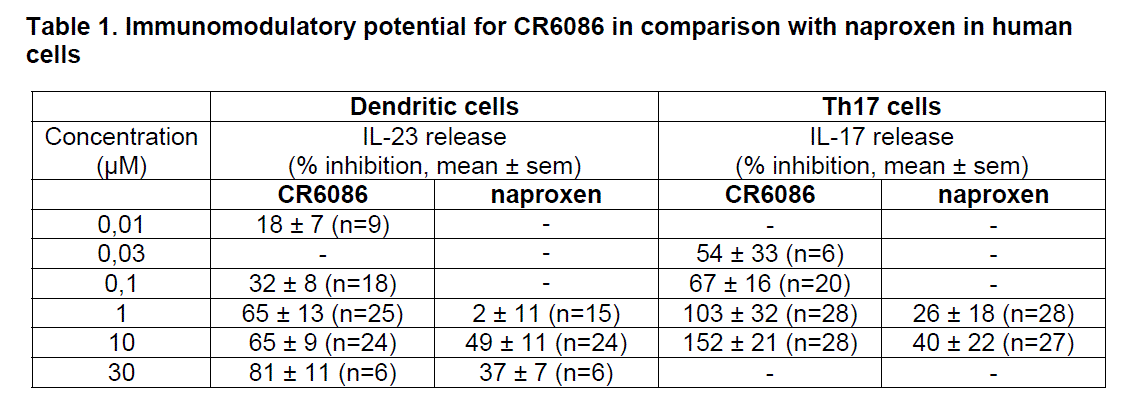
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Piepoli T, Maggioni D, Zerbi S, Stucchi A, Mennuni L, Lanza M, Caselli G, Rovati LC. CR6086 a New Potent EP4 Receptor Antagonist with Immunomodulatory Activities [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cr6086-a-new-potent-ep4-receptor-antagonist-with-immunomodulatory-activities/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cr6086-a-new-potent-ep4-receptor-antagonist-with-immunomodulatory-activities/
