Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease (AIRD) are at a higher risk for serious infections due to a combination of disease related immune dysfunction and the use of immunosuppressive therapy[1]. With the advent of the COVID-19 vaccination, there is an opportunity to protect this vulnerable patient population. However, there is inadequate data regarding vaccination rates, efficacy and vaccine related adverse events in this unique patient population.
The primary aim of this study is to assess the vaccination rates and adverse events among patients who are on immunosuppressive therapy. The secondary aim was to assess disparities in vaccination rates based on gender, age and ethnicity in patients from an underserved population.
Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted from 1st January 2021 to April 30th 2021. Patients aged 18 years and older, who were on immunosuppressive therapy (prednisone >=5mg, conventional and biologic DMARDs) presenting to the rheumatology clinic at an academic medical center, were included. Statistical analysis was done using Chi-square and a p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: 376 patients met inclusion criteria. 31.65% (119/376) received atleast one COVID-19 vaccine dose, of whom a majority 28.2% (96/376) were fully vaccinated. 69% patients received the Pfizer and 31% received the Moderna vaccine. Vaccine rates (for atleast 1dose) based on age were variable.18-24 years-41.6%; 25-44 years-16.9%, 45-64 years- 32.6% (58/178) and 65 years and above- 53.7% (36/67) (p< 0.00001). 31.7% (97/306) women and 31.4% (22/70) men receiving atleast one dose. Racial and ethnic differences in vaccinations did not reach statistical significance. 29.5% African Americans (47/159), 28.8% (39/135) Caucasians, 43.6% (17/39) Hispanics, 33.3% (3/9) Asians and 38.2% (13/34) Other received atleast one vaccine dose.
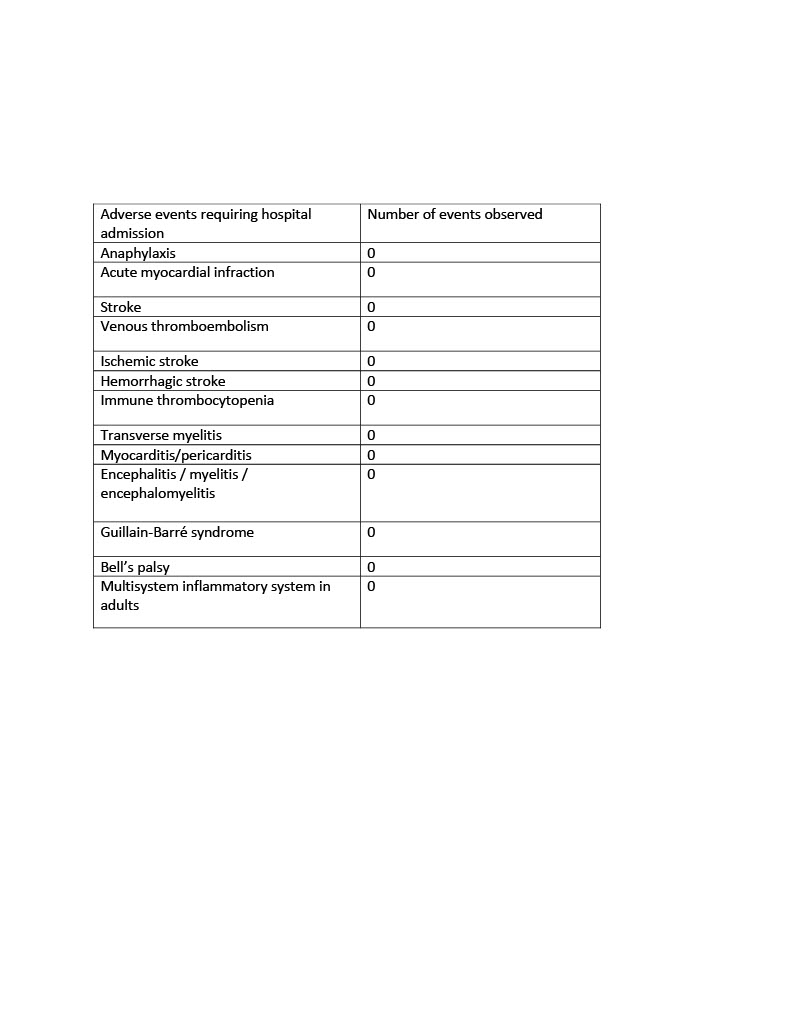
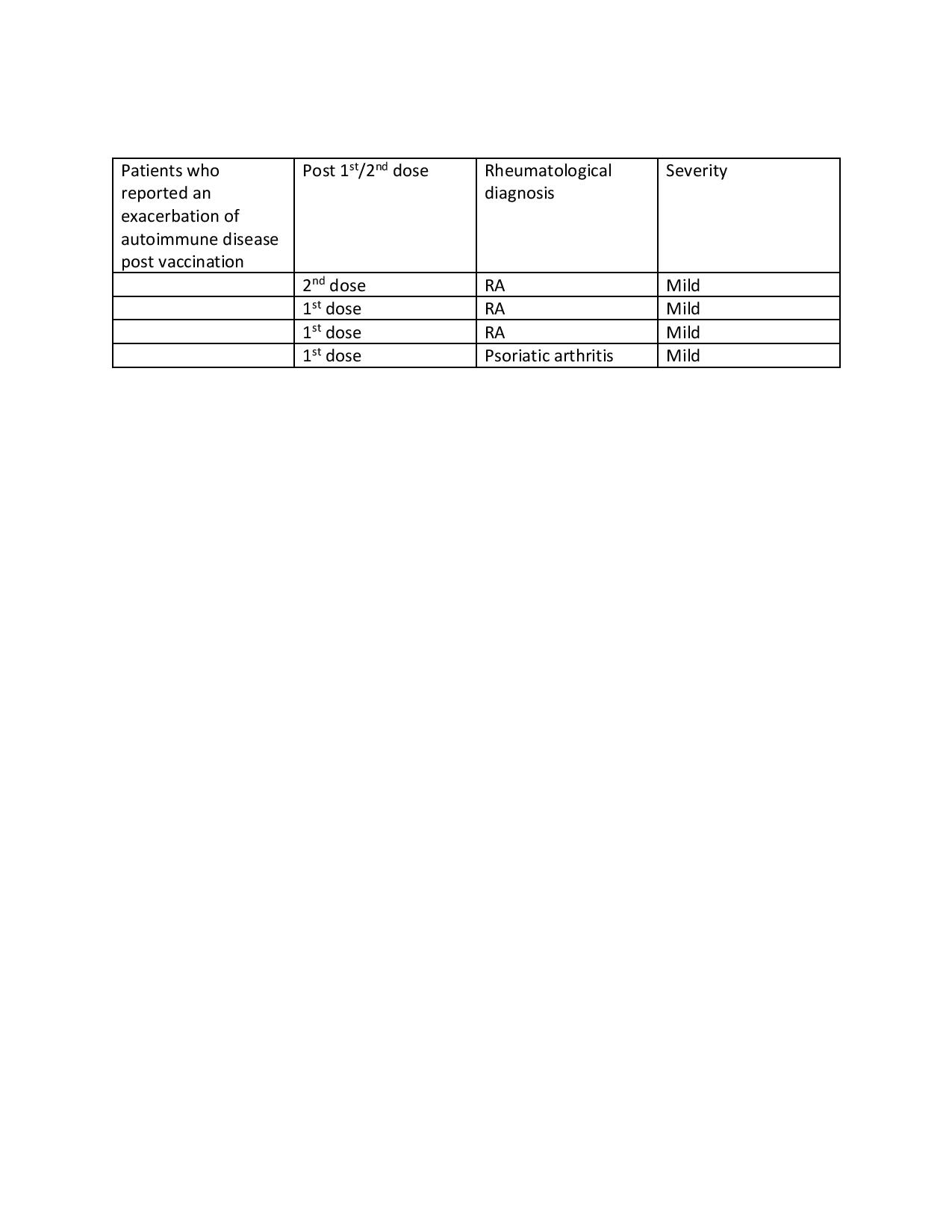
No major adverse events were reported (Table 1). Only 3 vaccinated patients (1.3%) presented to the ED with presumed post vaccination side effects. Complaints included rash, dizziness and headache. 4 vaccinated patients (1.7%) reported a mild exacerbation of their underlying rheumatologic disease. Only 2 vaccinated patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 infection with one patient having received only the 1st dose. The 2nd patient was found to be COVID-19 + within 3 weeks of receiving the 2nd vaccine.
Conclusion: Vaccination rates observed in our patient population was comparable to rates in Missouri (MO)- 31.65% v/s 37.3%(MO) and 28.2% v/s 27.4% (MO) for the 1st and 2nd Covid vaccine doses respectively as of April 30th 2021. Severe adverse events were not seen and the vaccine was well tolerated by our patients. Statistically significant differences were not seen based on gender and ethnicity. Age differences were statistically significant with patients aged 65+ being more likely to get vaccinated, which is likely a reflection of preferential vaccine rollout in more vulnerable populations. Vaccine hesitancy or disparity in access was not seen in our patient population based on preliminary data. Our goal is to reassess the data again in 6 – 12 months to identify any vaccination disparities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gallappaththy S, Ifteqar S, Edrees A. COVID-19 Vaccination Rates and Adverse Events Among Patients on Immunosuppressive Therapy in the Rheumatology Clinic Caring for an Underserved Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-rates-and-adverse-events-among-patients-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-in-the-rheumatology-clinic-caring-for-an-underserved-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-vaccination-rates-and-adverse-events-among-patients-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-in-the-rheumatology-clinic-caring-for-an-underserved-population/