Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: COVID19 may present different degrees of severity. It is generally thought that viral infections in patients with rheumatic inflammatory diseases (R-IMID) or receiving immunosuppressive treatment tend to present more severe disease. However, data comparing the severity of the disease between R-IMID and the general population are scarce.
Our aim was to assess the predisposing factors, clinical-analytical features and severity of COVID-19 infection in R-IMID compare to patients without R-IMID.
Methods: Case-control study in a single University Hospital. We included all consecutive patients with a diagnosis of a R-IMID and a positive test for COVID-19 up to March 31st, 2021.
A total of 274 controls were selected for each case, and matched by sex, age (± 5 years), and without previous diagnosis of R-IMID or use of immunosuppresive therapy.
Confirmed infection was defined if the patient had a positive nasopharyngeal swab for SARS-CoV-2.
COVID-19 case severity was divided into mild, moderate, severe and critical according to the United States National Institute of Health (NIH) COVID-19 guidelines. Mild/moderate COVID19 was compared with critical.
Results: We included 274 patients (185 women/89 men), mean age 59.1 18 years.
More frequent R-IMID were: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n=87, 31.8%), Axial spondyloarthritis/ Psoriatic arthritis (SpA/PsA) (n=90, 32.8%), Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) (n=22, 8%) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) (n=22, 8%)
We also included 274 age and matched controls. Main characteristics of patients with R-IMID and controls are shown in TABLE.
Concerning comorbidities, hypertension and dyslipidemia were more frequent in patients with R-IMID (p< 0.05).
COVID-19 symptoms’ distribution is shown in FIGURE.
Cough and dyspnoea were more frequent and headache, odynophagia and diarrhea were less frequent in the R-IMID group.
The only analytical difference was D-Dimer that was significantly higher in patients with R-IMID.
Although most of the cases were mild, critical cases and deaths were more frequent in R-IMID (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Most of the patients present a mild COVID-19. However, a more severe syndrome was observed in R-IMID
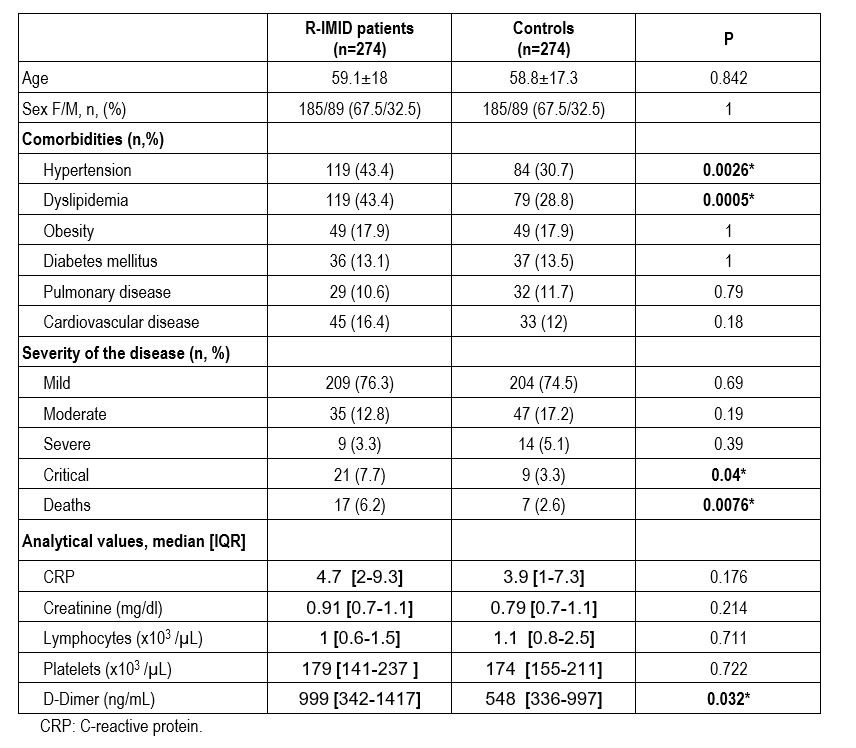 TABLE. Main clinical and analytical features of patients with R-IMID and matched controls
TABLE. Main clinical and analytical features of patients with R-IMID and matched controls
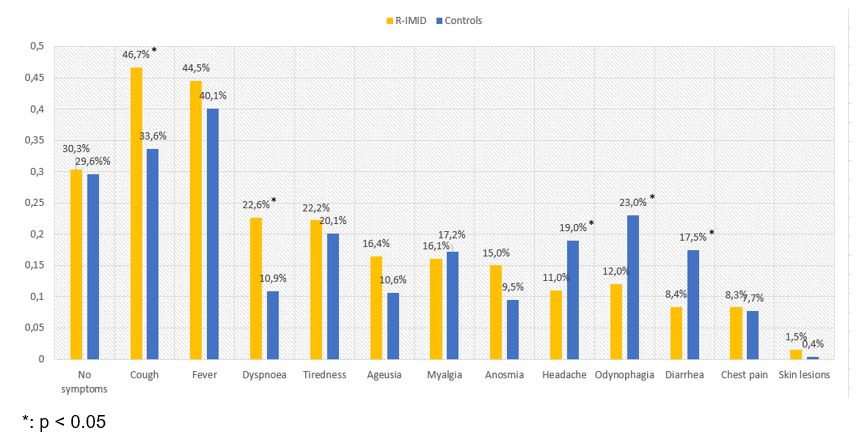 FIGURE. Symptoms in R-IMID patients and matched controls
FIGURE. Symptoms in R-IMID patients and matched controls
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez-Lopez D, Prieto-Peña D, Sánchez-Bilbao L, Álvarez-Reguera C, Herrero-Morant A, Benavides-Villanueva F, Corrales-Selaya C, Trigueros-Vazquez M, Wallmann R, gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R. COVID 19 Infection in Patients with Rheumatic Immune-mediated Diseases in a Single University Hospital: Matched Case-control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-infection-in-patients-with-rheumatic-immune-mediated-diseases-in-a-single-university-hospital-matched-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-infection-in-patients-with-rheumatic-immune-mediated-diseases-in-a-single-university-hospital-matched-case-control-study/
