Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: The impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy in patients with rheumatic disease is unknown. We describe COVID-19 outcomes in pregnant rheumatic disease patients reported to an international rheumatic diseases COVID-19 registry between March and June 2020.
Methods: Pregnant patients reported to the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance physician registries, which includes the COVID-19 EULAR registry, were included. The registry includes cases of COVID-19 in people with rheumatic diseases entered between 24 March 2020 to 22 May 2020.
Results: Eleven cases of pregnant women were reported: eight were white, one black, one Latin American, and one of other ethnicity. The mean age was 33 years (+ 6.5), range 20-45. Diagnoses included systemic lupus erythematosus (n=6), rheumatoid arthritis (n=2), inflammatory arthritis (n=1), inflammatory myositis (n=1), and axial spondyloarthritis (n=1). Two patients had coexisting antiphospholipid syndrome. None were smokers. Most patients’ rheumatic disease was either low or in remission based on physician global assessment (n=9), although 2 had moderate disease activity. Background rheumatic disease treatment is shown in the table. Five of the 11 patients stopped their anti-rheumatic treatments at the time of their infection. Seven patients had COVID-19 diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction testing, two by symptoms alone, two unknown, and one each by computed tomography scan and chest x-ray (multiple responses allowed). Five cases were reported to have close contact with a confirmed or probable case of COVID-19 infection, and one had a history of travel to an area with documented cases of COVID-19 infection. The other cases had unknown or community-acquired COVID-19. Symptoms of COVID-19 infection included cough (n=8), fever (n=7), shortness of breath (n=4), diarrhea, anosmia, and arthralgia (each n=3). Most patients (n=6) received only supportive treatment (table). Forty-five percent of patients were hospitalized; the maximum care received by hospitalized patients was supplemental oxygen (n=1). There were two COVID-19 complications, one co-infection with C. difficile and one pneumonia. None of the patients died. The outcome of pregnancies is not yet known.
Conclusion: We report on 11 pregnant women with diverse rheumatic diseases and medications who developed COVID-19 infection. Five patients were hospitalized but only one required supplemental oxygen. There were two co-infections and no deaths. In this small series, outcomes of COVID-19 infected pregnant patients with rheumatic disease were favorable.
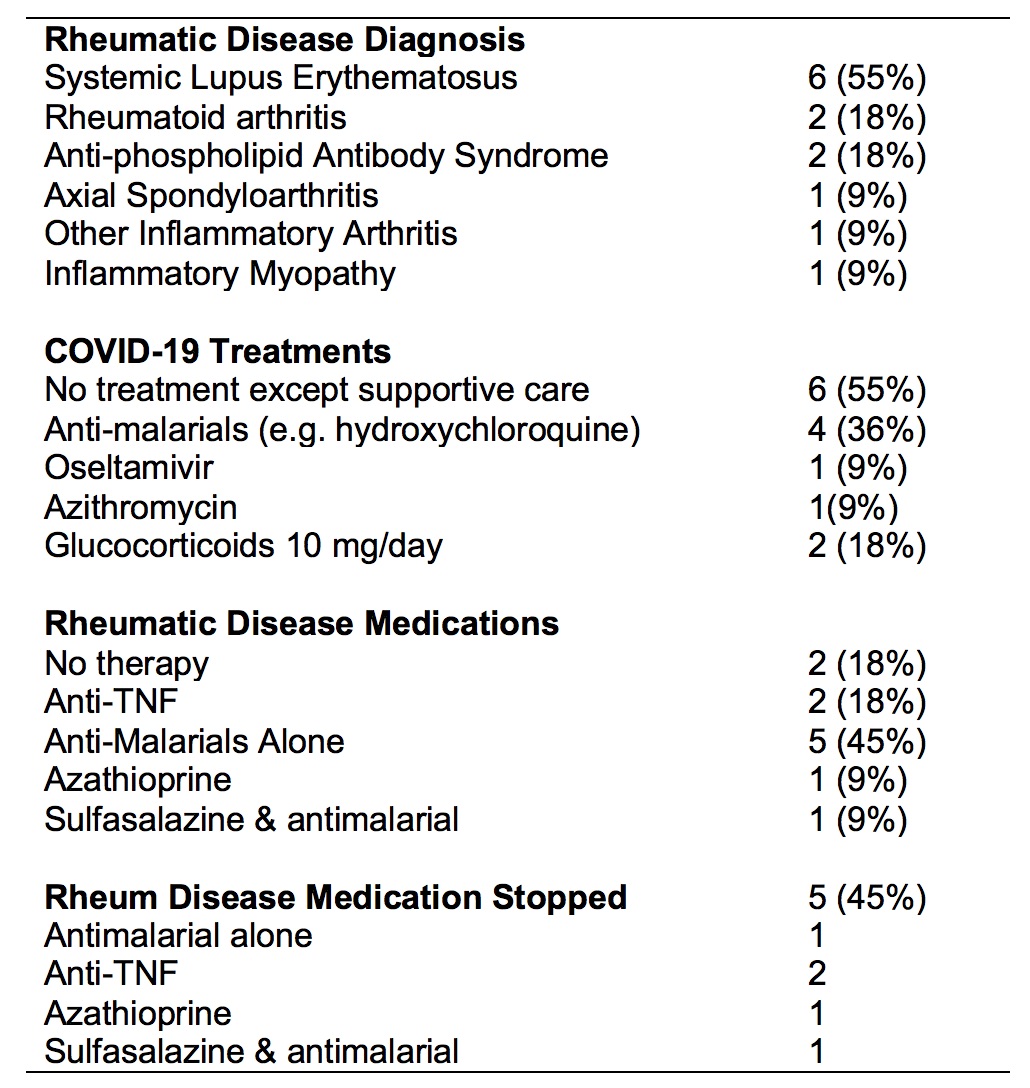 Table: Details of diagnoses and treatments
Table: Details of diagnoses and treatments
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bermas B, Clowse M, Gianfrancesco M, Hausmann J, Machado P, Sirotich E, Robinson H, Strangfeld A, Yazdany J, Robinson P. COVID-19 in Pregnant Patients with Rheumatic Disease: Data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-in-pregnant-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-data-from-the-covid-19-global-rheumatology-alliance/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/covid-19-in-pregnant-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-data-from-the-covid-19-global-rheumatology-alliance/
