Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose . Conventional radiography (CR) is considered the gold standard for diagnosing bone erosions in rheumatic diseases. However, High-Resolution peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography (HR-pQCT) and microCT (µCT) allow analysis of bone erosions in finger joints at micro level. This study aimed to quantify cortical breaks and erosions in hand joints assessed from CR, HR-pQCT and µCT images.
Methods . Eight metacarpal phalangeal and four proximal interphalangeal joints from eight female human cadaveric index fingers with unknown medical history were scanned by HR-pQCT (82 µm, Scanco XtremeCT) and µCT (18µm, Scanco µCT 80). Also radiographs were taken. A modified SPECTRA (Study grouP for xtrEme Computed Tomography in Rheumatoid Arthritis) algorithm was used by one reader to assess all cortical breaks and erosions. A cortical break was defined as an interruption of cortical bone on two consecutive slices on two orthogonal planes for HR-pQCT, and similarly, but on eight consecutive slices, on µCT. An erosion was defined as a definite cortical break, with irregular shape, and loss of underlying trabecular bone on two consecutive slices on two orthogonal planes on HR-pQCT, and eight consecutive slices on two orthogonal planes on µCT. CRs were independently scored for erosions by two rheumatologists. Descriptives, paired samples t-test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, kappa and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated (p<.05 was considered significant).
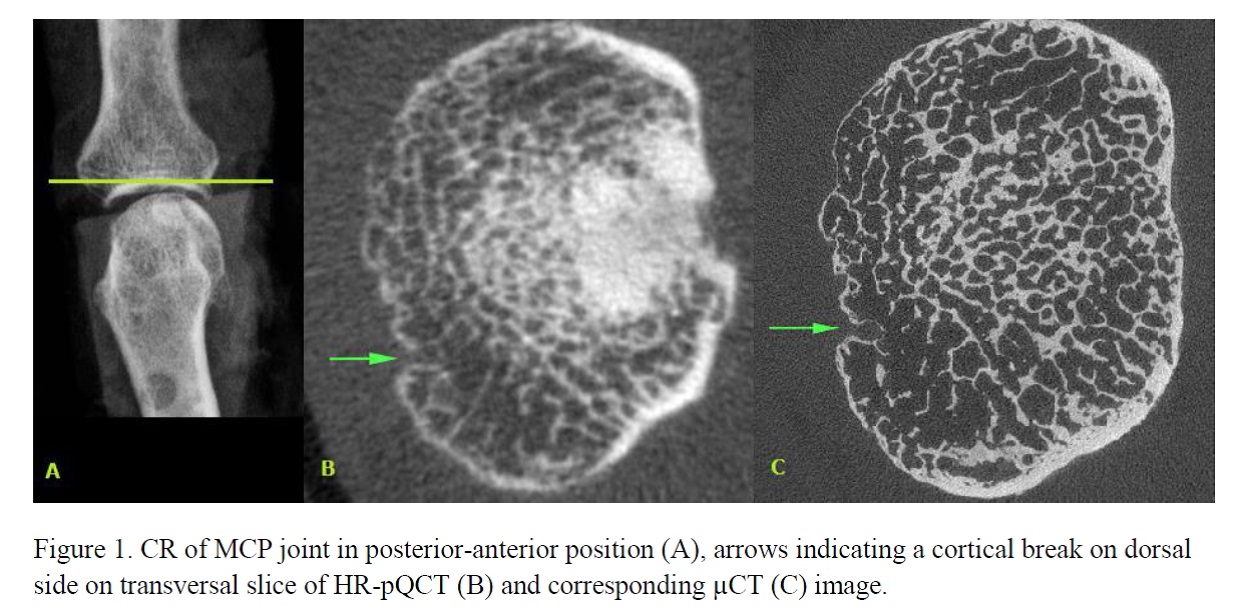
Results . Figure 1 shows a picture obtained from the three imaging modalities used in this study. In total, twelve joints (mean± SD age 82.6±9.1 years) were imaged by HR-pQCT and µCT. In total, 79 cortical breaks were detected on HR-pQCT (6.5±2.5 per joint) and 163 on µCT (13.5±4.9 per joint). A total of 11 erosions were detected on HR-pQCT (0.9±0.9 per joint) and 47 on µCT (3.9±3.0 per joint). The ICC for number of cortical breaks was .122 (p=.150), and for number of erosions -.090 (p=.699). On CR, the total number of erosions scored was four by Reader 1, and two by Reader 2. Kappa was fair (κ= .250).
Conclusion . Three times more erosions were detected on HR-pQCT than CR and four times more erosions were detected on µCT than HR-pQCT. Furthermore, twice the number of cortical breaks was scored on µCT compared to HR-pQCT. These results indicate that further research, such as histological and longitudinal studies, will be necessary to reveal the prevalence, incidence and significance of cortical breaks and erosions as found by HR-pQCT and µCT of hand joints.
Disclosure:
A. Scharmga,
None;
A. van Tubergen,
None;
J. van den Bergh,
None;
J. de Jong,
None;
M. Peters,
None;
B. van Rietbergen,
Scanco Medical AG,
9;
P. Geusens,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cortical-breaks-and-bone-erosions-in-the-hand-joints-a-cadaver-study-comparing-conventional-radiography-with-high-resolution-and-micro-computed-tomography/