Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose
: Recent prospective data suggest that spinal inflammatory damage in patients with ankylosing spondylitis will eventually convert into fat. In these complex inflammatory lesions, bone formation and inflammation are not synchronized. The molecular basis responsible for new bone formation in SpA patients is still unclear. Serum level of dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1), the natural inhibitor of WNT protein, is a main factor in limiting new bone formation. In this study, we aimed to assess the correlation between the secreted protein Dkk-1 and abnormal findings on spinal MRI through a prospective study of SpA.Methods: Thirty patients with active axial SpA (axSpA) who fulfilled the ASAS axSpA criteria were enrolled. All patients received an injection of recombinant human TNF receptor-antibody fusion protein (YISAIPU) at a dosage of 50 mg/week for 6 months. Patient report outcome measure questionnaires and physical examination, blood tests were completed according to the study protocol. All patients were scored for bone marrow edema and fat infiltration on spinal MRI imaging. The spinal MRI imaging of the patients before and after the treatment were blindly reviewed and scored using the SPARCC scoring system by two individuals who were familiar with the system.
Results: There are 28 male and two female patients (mean age: 31 +/- 5.5 yrs, range: 22-41; mean duration: 93.5 +/- 75.8; HLA-B27(+): 96.7% (29/30)). In patients who finished the 6 month anti-TNF treatment, the ESR, CRP, BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI and ASDAS-CRP were significantly decreased (P < 0.01). Serum Dkk-1 concentration was also significantly decreased (P < 0.05), as were the edema measurements of spinal bone marrow (P < 0.05). (Table1). 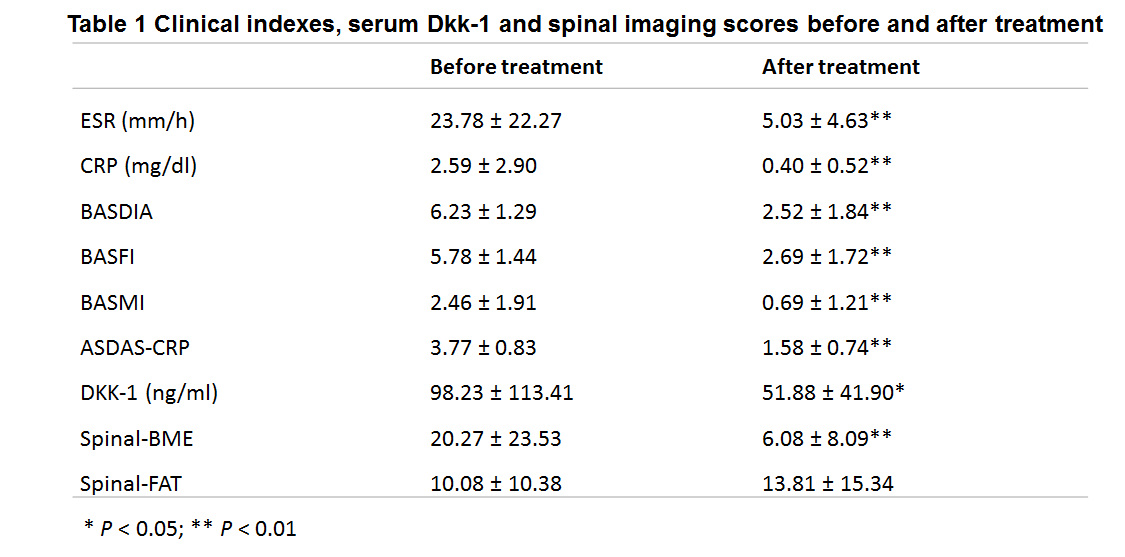
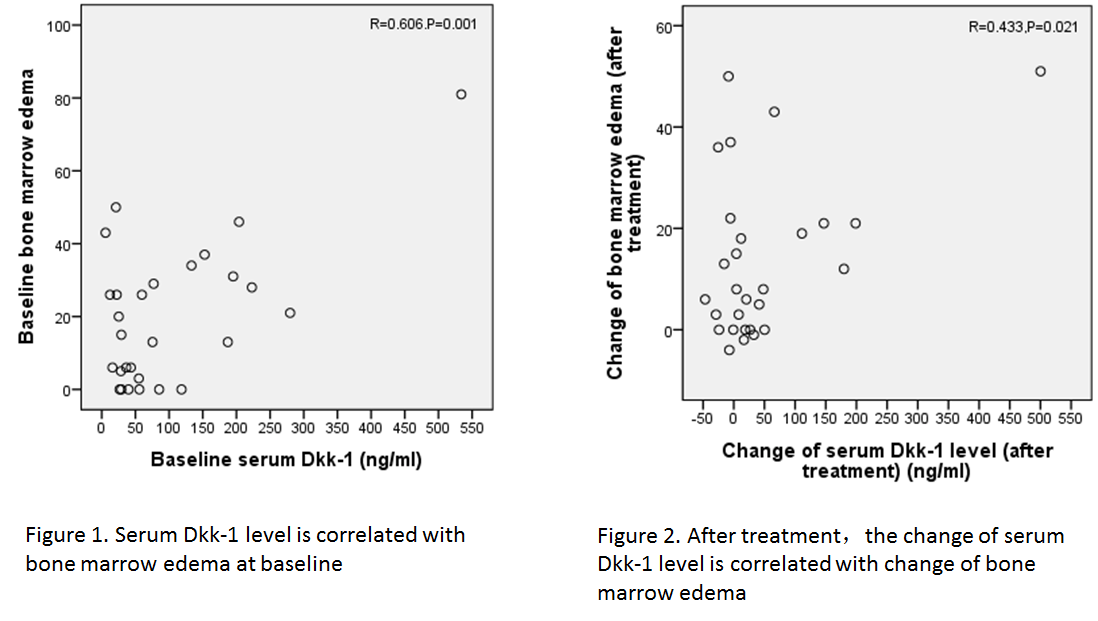
Conclusion: Spinal marrow edema may have a role in predicting new bone formation in the spine, since the change of serum Dkk-1 level is correlated with change of spinal marrow edema. And Dkk-1 may participate in the molecular basis of the TNF inhibitor¡¯s blockade of new bone formation. Further research is needed on patients who have received long-term TNF antagonist treatment to find the time points when serum Dkk-1 level reaches a stabilized plateau. Increased knowledge in this area will be helpful when assessing a predictive marker for the timing of treatment withdrawal.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhao Z, Wang G, Wang Y, Yang J, Zhu J, Huang F. Correlation Between the Spinal MRI Findings and the Serum Level of DKK-1 in Patients with Spondyloarthritis Treated with TNF Antagonist [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-the-spinal-mri-findings-and-the-serum-level-of-dkk-1-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-treated-with-tnf-antagonist/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-between-the-spinal-mri-findings-and-the-serum-level-of-dkk-1-in-patients-with-spondyloarthritis-treated-with-tnf-antagonist/
