Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Miscellaneous Aspects of RA (0786–0812)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Receiving a Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) diagnosis presents a significant health stressor. Given that little is known about how patients cope with it, we aimed to validate for the first time the Coping with Health Injuries and Problems (CHIP) questionnaire (Endler NS et al. Psychol Assessm 1998;10:195) in early RA.
Methods: Between August 2006 and October 2020, 483 consecutive patients who met the criteria for RA were enrolled at the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke (CHUS). At baseline and at each scheduled yearly study visit, patients self-administered the CHIP questionnaire. CHIP is comprised of 32 items, with 4 subscales: Distraction, Palliative, Instrumental, Emotional. Each subscale is the sum of 8 items with a score ranging from 8 to 40. CHIP’s validity was assessed for internal consistency with Cronbach’s alpha, for sensitivity to change with mixed linear model with repeated measures as well as for factor structure with factorial analysis and confirmatory analysis.
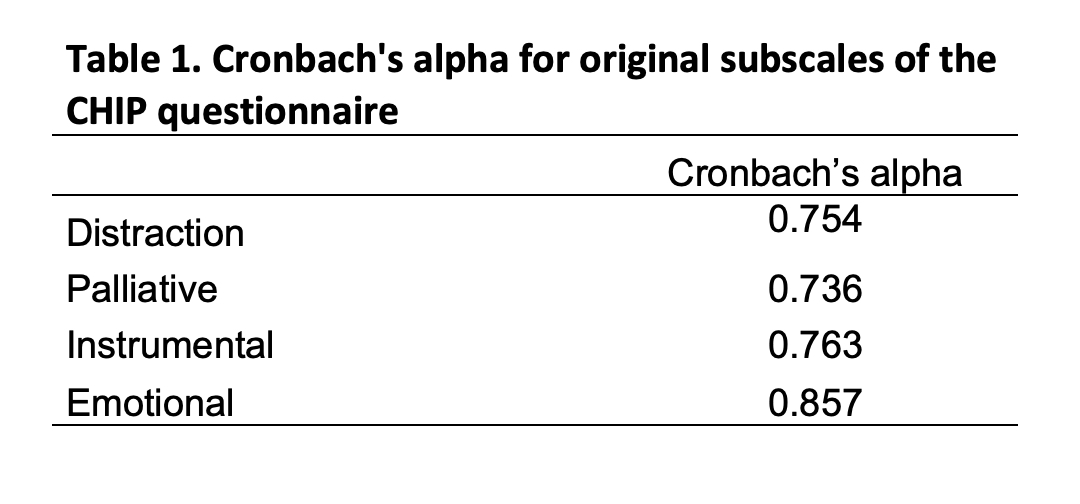
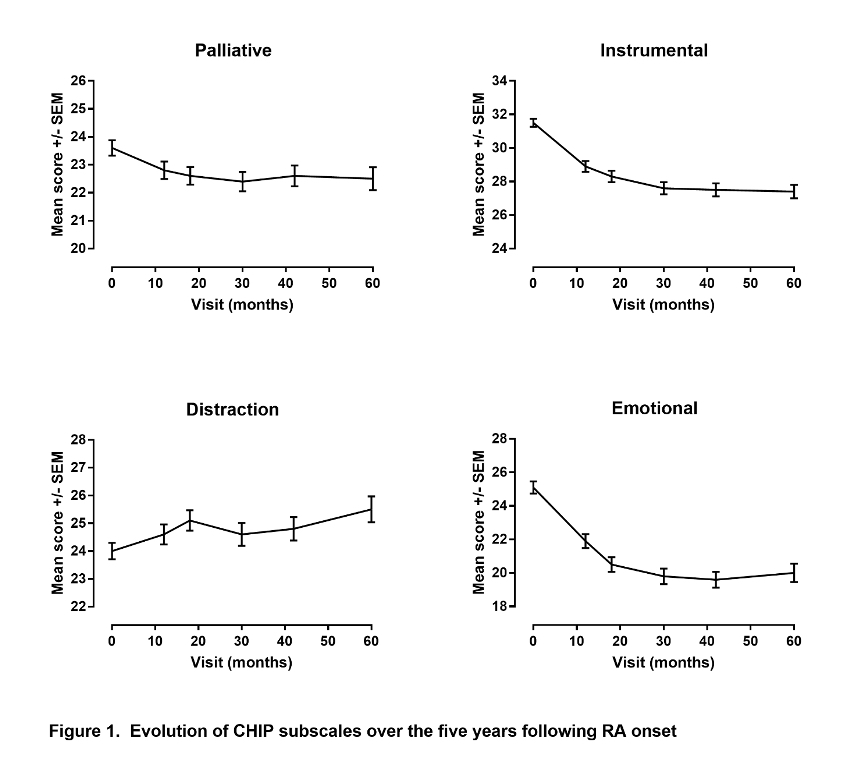
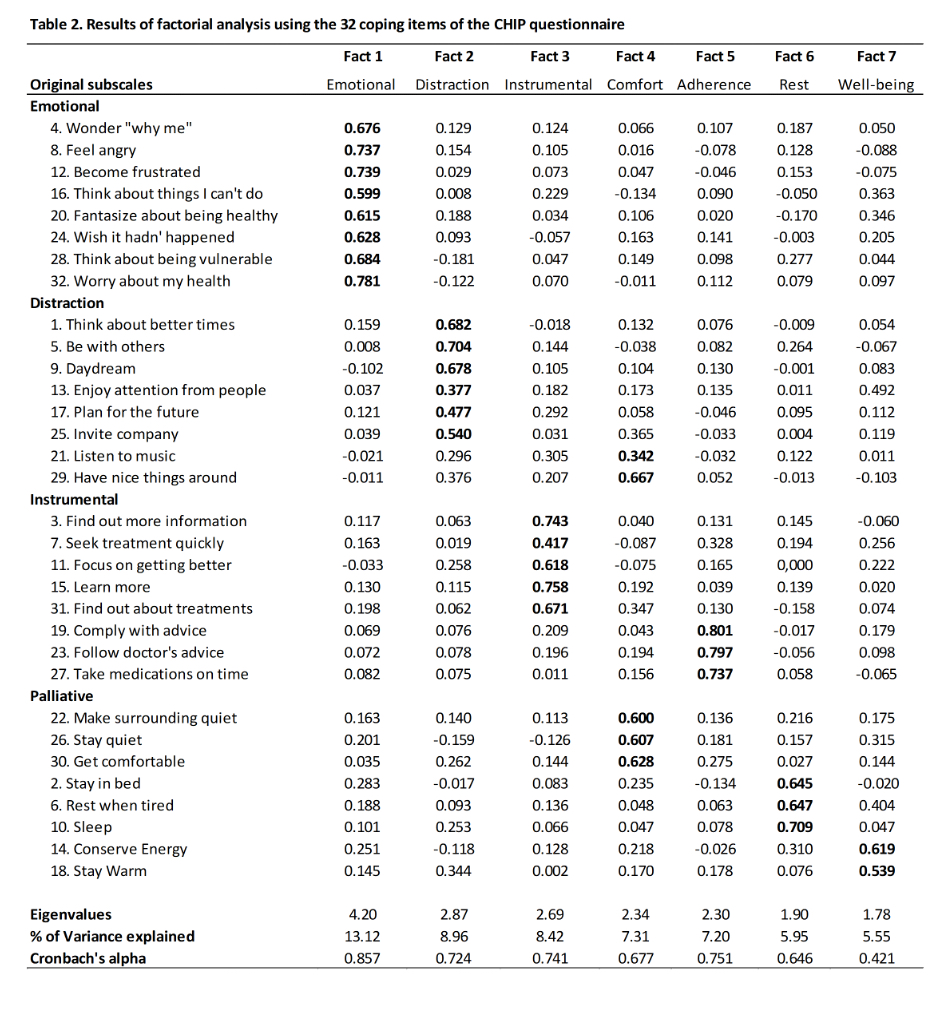
Results: A total of 420 patients were followed up to 5 years. The baseline mean (SD) of 4 subscales were 24.01 (6.46) for Distraction, 23.58 (6.07) for Palliative, 31.48 (5.35) for Instrumental and 25.10 (7.95) for Emotional. CHIP demonstrated good psychometric properties. Internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha) varied between 0.736 and 0.857 (Table 1); deleting each element separately did not improve the coefficient suggesting that each was an important contributor to the overall score. CHIP was sensitive to change with significant decreases (estimated ± SE) until 5 years for Instrumental (-4.25 ± 0.36, p< 0.001), Emotional (-5.87 ± 0.44, p< 0.001), Palliative (-1.27 ± 0.35, p< 0.001) and a significant increase for Distraction (1.15 ± 0.40, p=0.04) (Figure). Factor analysis suggested that all items were better represented on 7 subscales rather than 4; the 7-dimension solution explained 56.5% (versus 37.8%) of the total variability. The first subscale was defined by all 8 Emotional items; the second by 6 of 8 items of Distraction; five of the Instrumental items were found on dimension 3, the 3 others (linked to treatment adherence) were on dimension 5; Palliative items were split into 3 subscales (4, 6 and 7) that we called comfort, rest and well-being (Table 2). Confirmatory analyses showed that 7 subscales may be slightly better than the original 4, although Cronbach's alphas of the new 7 subscales were not improved when compared to the original 4.
Conclusion: CHIP questionnaire describes patient’s individual coping styles when facing recent-onset RA. Due to the prospective nature of our cohort, we could validate the questionnaire. Factor analysis suggested that coping in early RA was better characterized using 7 rather than 4 subscales, but Cronbach’s alpha suggested that using the original tool might be as good, an observation that remains to be confirmed. Discussing a patient’s results for CHIP may enable a rheumatologist to understand patients’ perspectives and address their needs better, thereby strengthening their relationship. Results from CHIP may also be used as predictor of patients’ outcomes pointing towards interventions that may help those in need to deal with their illness better.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alman Z, Boire G, Carrier N, Masetto A, deBrum Fernandes A, Liang P, Dobkin P, Hugues A, Roux S. Coping with Recent-onset Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Validation of the Coping with Health Injuries and Problems (CHIP) Questionnaire in a Longitudinal Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coping-with-recent-onset-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-validation-of-the-coping-with-health-injuries-and-problems-chip-questionnaire-in-a-longitudinal-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coping-with-recent-onset-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-validation-of-the-coping-with-health-injuries-and-problems-chip-questionnaire-in-a-longitudinal-cohort/