Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III (1836–1861)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In the SENSCIS trial in patients with SSc-ILD, nintedanib reduced the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) (mL/year) over 52 weeks by 44% compared with placebo, with adverse events that were manageable for most patients. The safety and efficacy of nintedanib over the longer term are being assessed in the open-label extension trial, SENSCIS-ON.
Methods: In the SENSCIS trial, patients were randomized to receive nintedanib or placebo until the last patient reached week 52 but for ≤100 weeks. Patients with SSc-ILD who completed the SENSCIS trial or a drug–drug interaction (DDI) study of nintedanib and oral contraceptive (NCT03675581) were eligible to enter SENSCIS-ON. In descriptive analyses, we analyzed changes from baseline in FVC (mL) and adverse events over 100 weeks in patients who received nintedanib in SENSCIS and continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON (the “continued nintedanib” group) and in patients who received placebo in SENSCIS and initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON or who received nintedanib for ≤28 days in the DDI study (the “initiated nintedanib” group). Analyses were based on observed FVC data available at the respective time-point.
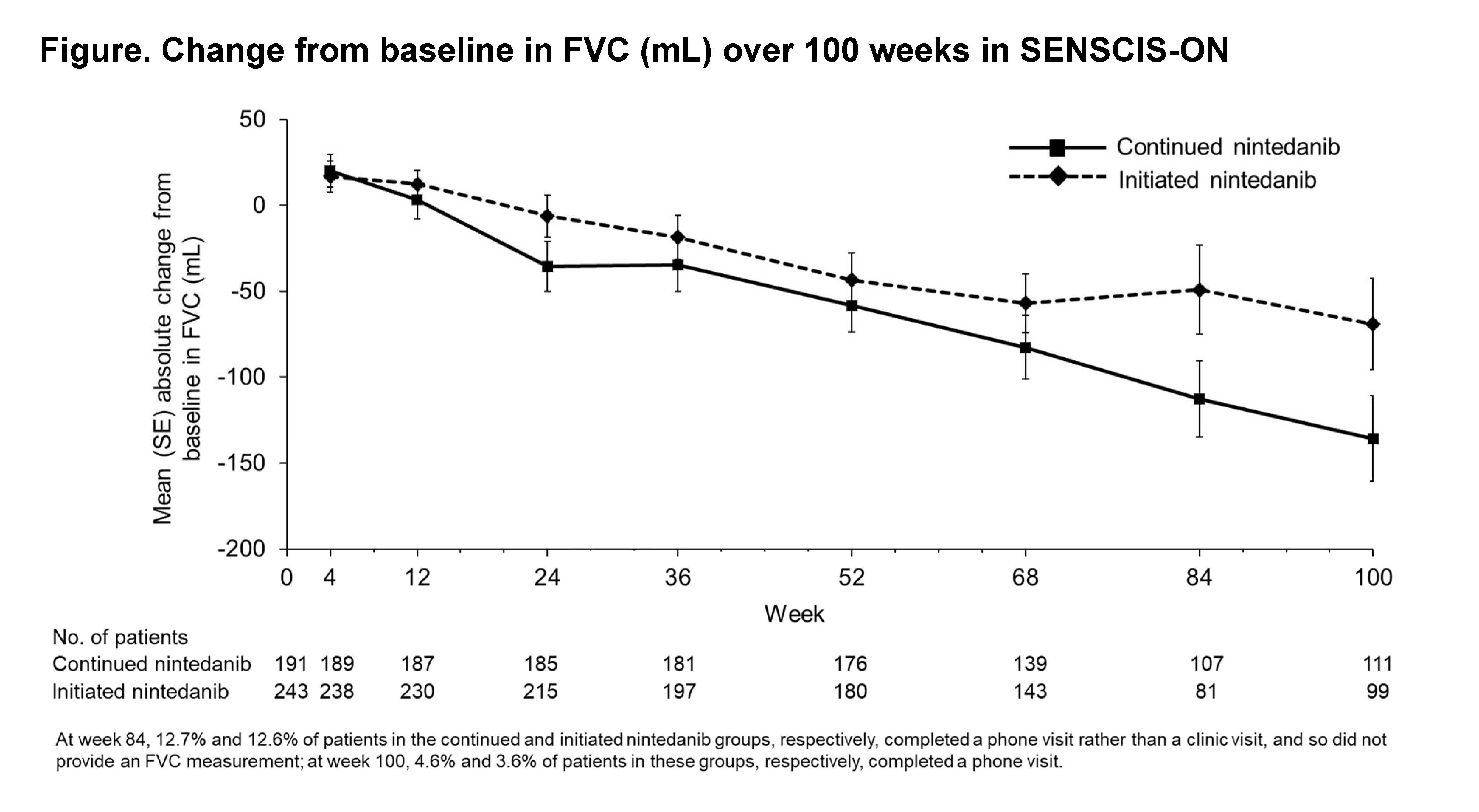
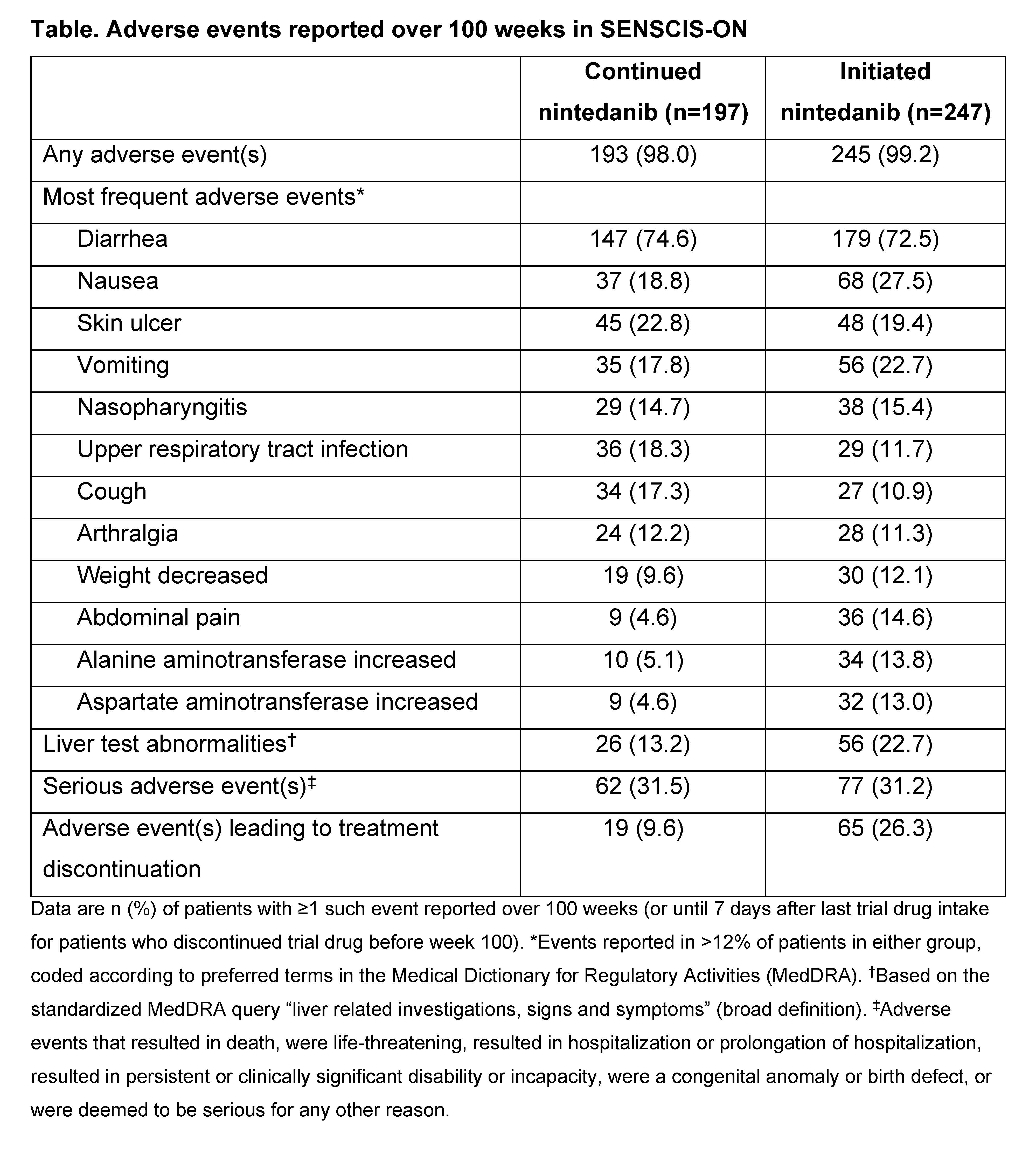
Results: The continued nintedanib group comprised 197 patients and the initiated nintedanib group comprised 247 patients (231 from SENSCIS; 16 from the DDI study). In these groups, respectively, mean (SD) FVC at inclusion in SENSCIS-ON was 2379 (754) mL and 70.4 (18.1) % predicted and 2443 (814) mL and 70.8 (17.9) % predicted. In total, 148 (75.1%) and 145 (58.7%) patients in the continued nintedanib and initiated nintedanib groups, respectively, were receiving nintedanib at week 100 of SENSCIS-ON. Mean (SE) changes in FVC from baseline to week 100 of SENSCIS-ON were −135.7 (24.7) mL in patients who continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON, −69.2 (26.5) mL in patients who initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON, and −104.3 (18.2) mL in all patients in SENSCIS-ON (Figure), similar to the change from baseline to week 100 in nintedanib-treated patients in the SENSCIS trial (−100.0 [36.7] mL) and lower than the change from baseline to week 100 in the placebo group of the SENSCIS trial (−164.4 [38.4] mL). Diarrhea was the most frequent adverse event (Table). Over 100 weeks, liver test abnormalities were reported in 26 patients (13.2%) in the continued nintedanib group and 56 patients (22.7%) in the initiated nintedanib group. Adverse events led to discontinuation of nintedanib in 19 (9.6%) patients in the continued nintedanib group and 65 (26.3%) patients in the initiated nintedanib group.
Conclusion: The safety profile of nintedanib over 100 weeks in SENSCIS-ON was consistent with that reported in the SENSCIS trial. The decline in FVC over 100 weeks in patients treated with nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON was consistent with the decline in FVC in patients treated with nintedanib over 100 weeks in the SENSCIS trial. These findings support a clinically meaningful benefit of nintedanib in slowing the progression of SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Allanore Y, Vonk M, Distler O, Azuma A, Mayes M, Gahlemann M, James A, Kohlbrenner V, Alves M, Khanna D, Highland K. Continued Treatment with Nintedanib in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD): Two-Year Data from SENSCIS-ON [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/continued-treatment-with-nintedanib-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-two-year-data-from-senscis-on/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/continued-treatment-with-nintedanib-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-two-year-data-from-senscis-on/