Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: In the SENSCIS trial in patients with SSc-ILD, nintedanib reduced the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) (mL/year) over 52 weeks by 44% compared with placebo, with adverse events that were manageable for most patients. The SENSCIS trial (NCT02597933) was followed by an open-label extension trial, SENSCIS-ON (NCT03313180), to provide safety data, including data on decline in FVC and adverse events, in patients treated with nintedanib over the longer term.
Methods: Patients who completed the SENSCIS trial on treatment (nintedanib or placebo) and attended a follow-up visit 28 days later were eligible to participate in SENSCIS-ON. Female patients with SSc-ILD who completed an open-label, drug–drug interaction study of nintedanib plus oral contraceptive (ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel), in which patients received nintedanib for up to 28 days (NCT03675581), were also eligible to enter SENSCIS-ON to enable treatment continuation. In an interim analysis, we analyzed the change from baseline in FVC (mL) and adverse events over 52 weeks in SENSCIS-ON, a) in patients who had received nintedanib in the SENSCIS trial and continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON (“continued nintedanib” group), and b) in patients who had received placebo in the SENSCIS trial and initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON or who had received nintedanib in the drug-drug interaction study (“initiated nintedanib” group). Analyses were pre-specified and descriptive.
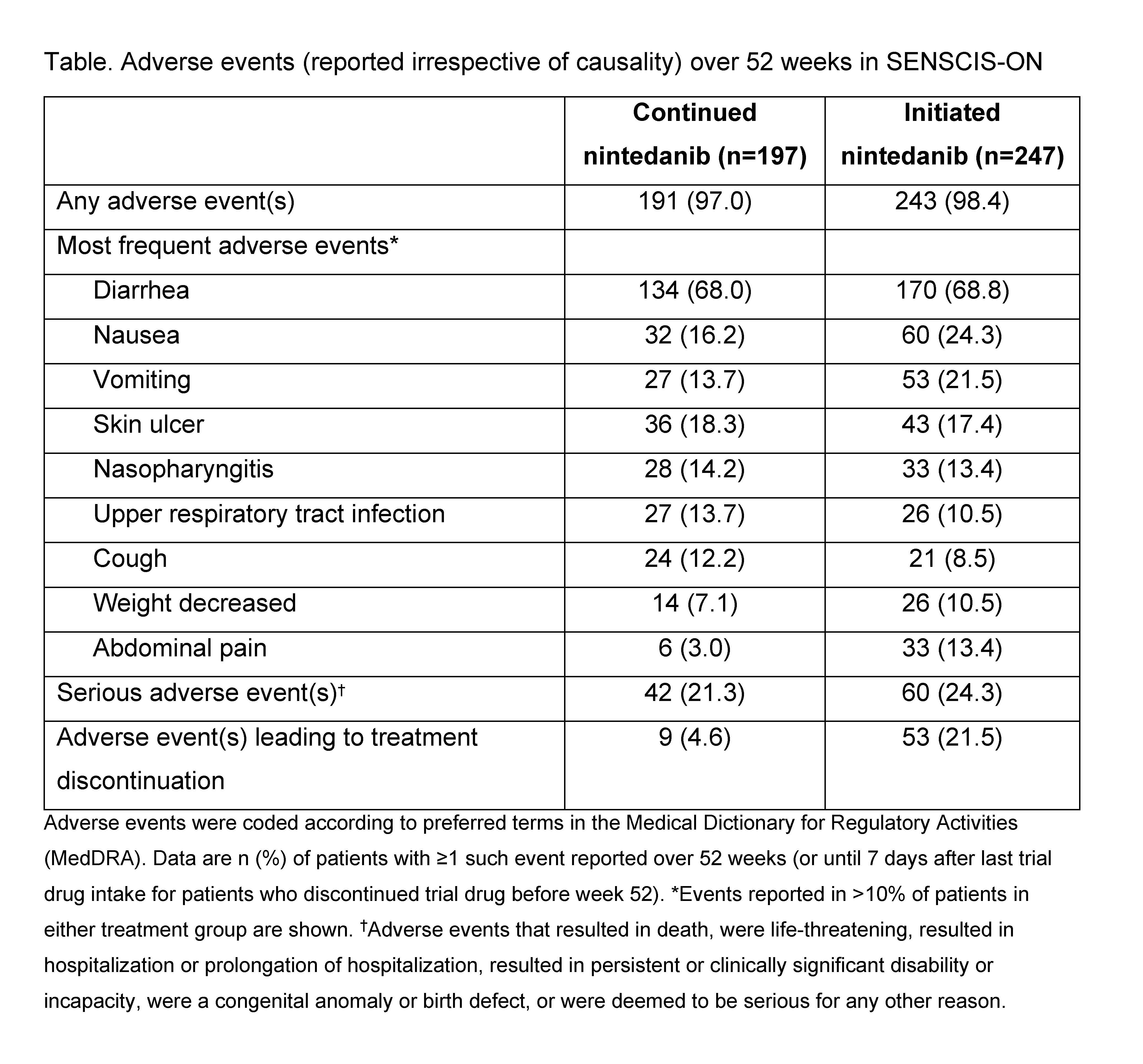
Results: In SENSCIS-ON, there were 197 patients in the “continued nintedanib” group and 247 patients (231 from SENSCIS, 16 from the drug-drug interaction study) in the “initiated nintedanib” group. In these groups, respectively, mean (SD) FVC at inclusion in SENSCIS-ON was 2379 (754) mL and 70.4 (18.1) % predicted and 2443 (814) mL and 70.8 (17.9) % predicted. Mean (SE) changes in FVC from baseline to week 52 of SENSCIS-ON were −58.3 (15.5) mL in patients who continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON, −44.0 (16.2) mL in patients who initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON (Figure), and −51.3 (11.2) mL in all patients treated in SENSCIS-ON, similar to the change from baseline to week 52 in the SENSCIS trial (−42.7 [14.2] mL). Diarrhea was the most frequently reported adverse event (Table). Adverse events led to discontinuation of nintedanib in 9 patients (4.6%) who continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON and 53 patients (21.5%) who initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON. Elevations in alanine aminotransferase and/or aspartate aminotransferase to ≥3 times the upper limit of the normal range were reported in 3 patients (1.5%) who continued nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON and 20 patients (8.1%) who initiated nintedanib in SENSCIS-ON.
Conclusion: The change in FVC in patients who received nintedanib over 52 weeks of SENSCIS-ON was similar to the change in FVC in patients who received nintedanib over 52 weeks of the SENSCIS trial. The adverse event profile of nintedanib over longer-term use was consistent with that reported over 52 weeks in the SENSCIS trial. These findings support a clinically meaningful benefit of nintedanib in slowing the progression of SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Allanore Y, Vonk M, Azuma A, Mayes M, Gahlemann M, James A, Kohlbrenner V, Stowasser S, Highland K. Continued Treatment with Nintedanib in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (SSc-ILD): Interim Analysis of SENSCIS-ON [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/continued-treatment-with-nintedanib-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-interim-analysis-of-senscis-on/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/continued-treatment-with-nintedanib-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-ssc-ild-interim-analysis-of-senscis-on/