Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: To determine and revalidate the definitions of disease flares in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) flares based on the changes in Clinical and Simplified Disease Activity Indices (CDAI, SDAI) and the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data (RAPID3).
Methods: A retrospective data review of rheumatology patients at a rheumatology clinic was done, tracking CDAI, SDAI, and RAPID3 scores. As part of routine clinical care, data needed to calculate disease activity scores were routinely collected. Additionally, a patient satisfaction question: “How satisfied are you with your Health Now” was completed and scored 0-4 (Very satisfied=0; Very dissatisfied=4). A flare was then calculated by the difference between the patient satisfaction score at the subsequent follow up visit, with a change >= 2 indicating an active flare. Changes in the CDAI, SDAI and RAPID3 were calculated for the same visits. Using ROC estimates, values of ∆CDAI, ∆SDAI and ∆RAPID3 corresponding to the Flare were determined. These values were then compared with current existing definitions of CDAI and SDAI from Konzett V, et al. and for the RAPID3 by Ward M, et al.
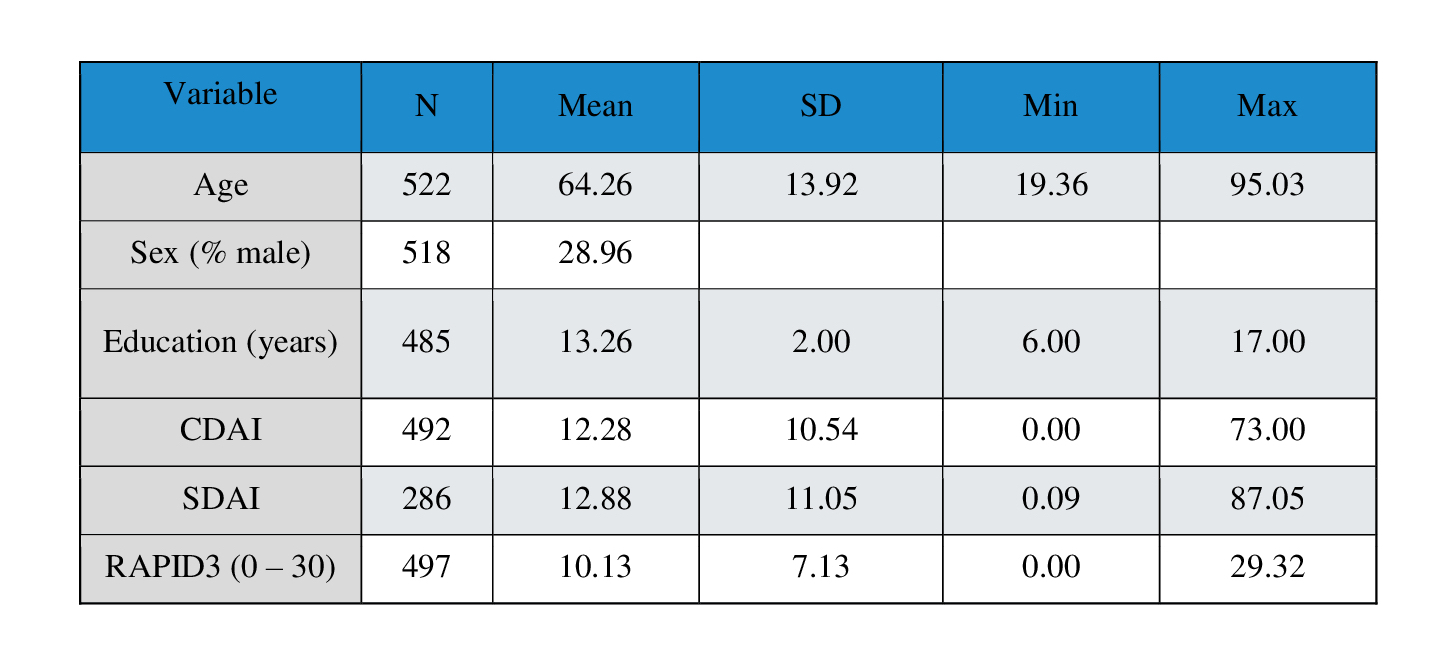
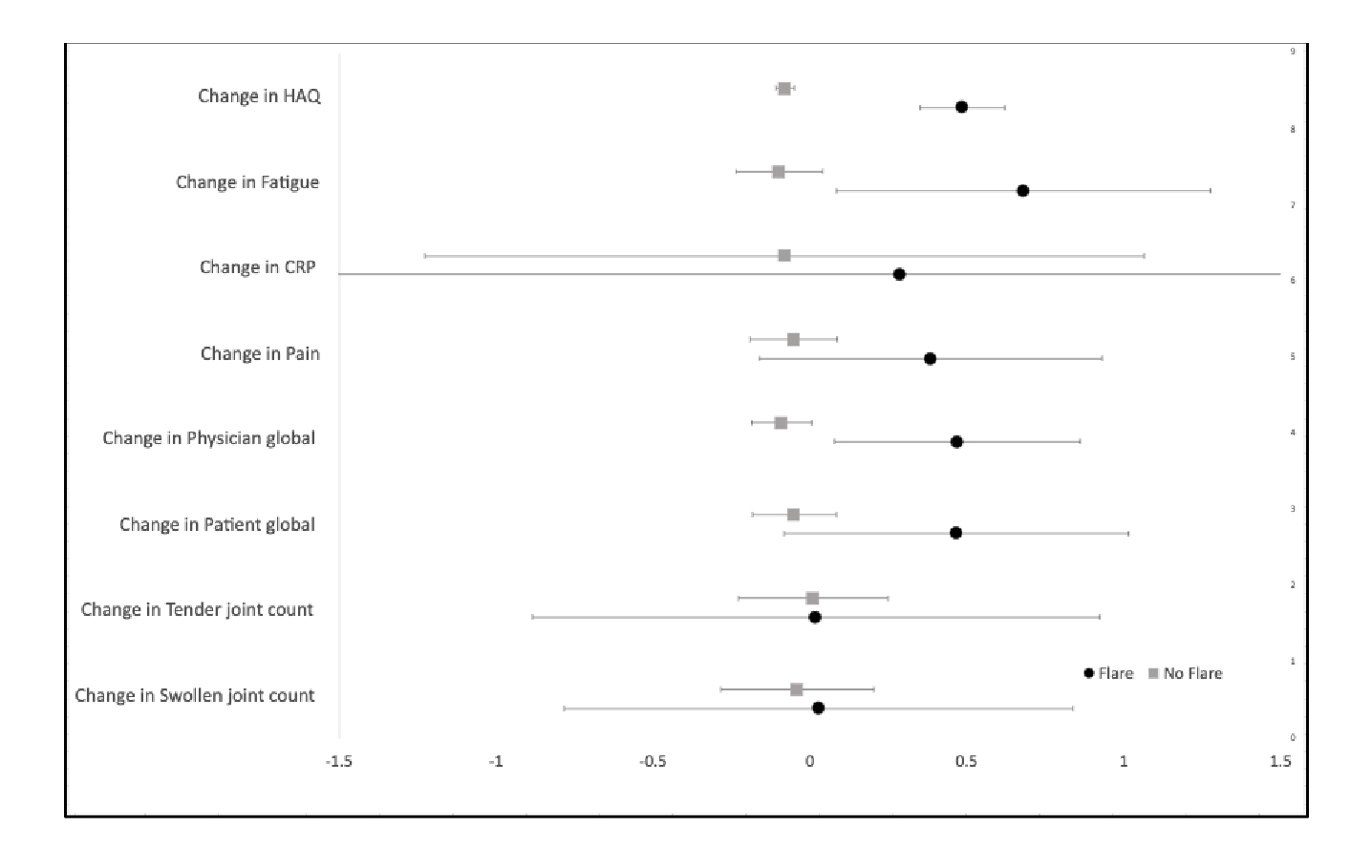
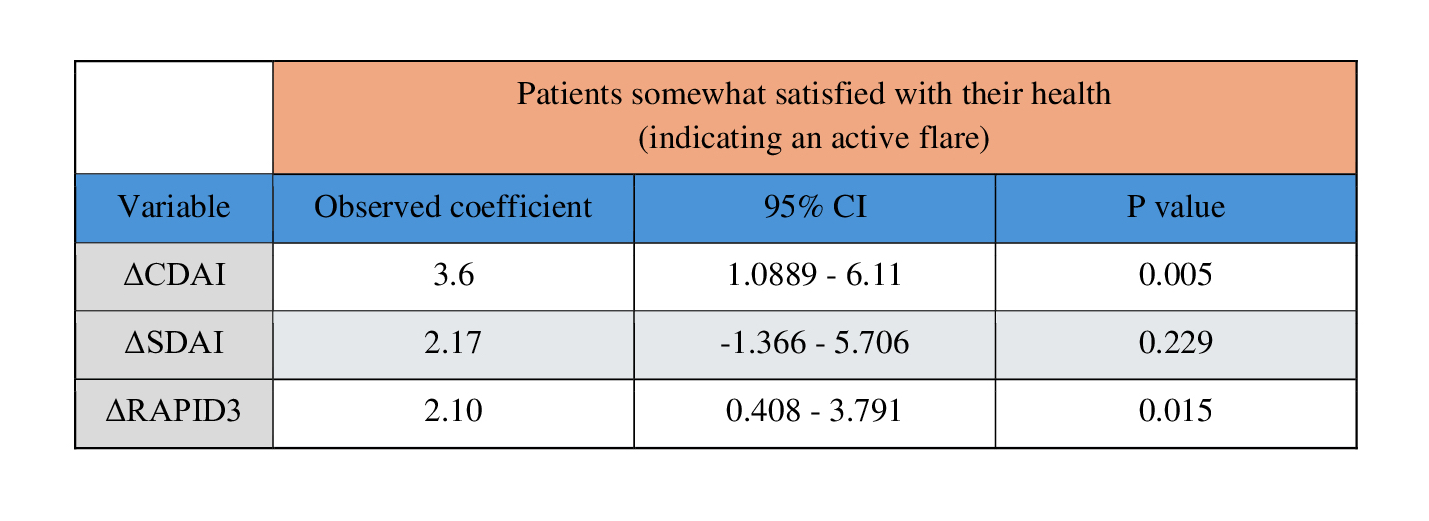
Results: Data from 522 RA patients were identified and analyzed. The mean age was 64.26, with a 71.04% female population. 16.84% of patients reported feeling very satisfied with their health while 34.39% reported feeling somewhat satisfied. 20.11% of patients were on methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy while 10.92% were on MTX + TNF-α therapy. An active flare showed a ∆CDAI score increase of 3.60 (p < 0.05, 95% CI 1.0889 – 6.111), ∆SDAI score increase of 2.17 (p < 0.229, 95% CI -1.366 – 5.706) and a ∆RAPID3 increase of 2.1 (p < 0.015, 95% CI 0.409 – 3.791). Due to the frequent absence of CRP data, calculations involving SDAI a were considered potentially inaccurate. The values reported by Konzett et al. were higher than those found in this data set (∆CDAI = 4.5; ∆SDAI = 4.7), and the value for the RAPID3 reported by Ward, M. et, al. (ΔRAPID3 = 3.8) the results would fall within the 95% CI suggesting consistency.
Conclusion: We suggest that the results of this study validate the previous determination regarding a new and updated definition of an RA flare based on the CDAI and RAPID3. However, we feel that the study be done on additional data sets to determine the most accurate values defining flare. With the development of new pharmacological managements of RA, we hope that the new updated definitions can adequately guide us in identifying patients with an active flare.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Badar I, Bergman M. Confirming a Value for Rheumatoid Arthritis Flares Based on Changes in CDAI, SDAI and RAPID3 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/confirming-a-value-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-flares-based-on-changes-in-cdai-sdai-and-rapid3/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/confirming-a-value-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-flares-based-on-changes-in-cdai-sdai-and-rapid3/