Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s disease (SjD) presents an unmet medical challenge as there is currently no cure. Despite advances in understanding the immunopathogenesis of SjD, there is still a pressing need to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets and personalized treatment.
Our objective is to create a fully-detailed molecular interaction map (MIM) including all the signalling and molecular pathways implicated in SjD pathogenesis. To create a large-scale mechanistic model to enable in silico simulations of perturbations including drug interventions, and the generation of hypothesis-driven predictions.
Methods: Differential expression analysis was performed on blood samples from SjD patients vs controls on 3 transcriptomic datasets: the publicly available GSE51092 and the accessible via the NECESSITY consortium UKPSSR and PRECISESADS datasets. GSE51092 contains 190 SjD patients and 32 controls, UKPSSR of 151 SjD patients and 29 controls, and PRECISESADS, RNASeq data for 304 SjD patients and 341 controls. Pathway enrichment analysis was subsequently performed using GSEA and the Reactome pathway database. Additional literature-based evidence was used to develop a molecular interaction map, combining the results of the previous analytical steps. The SjD specific map was then converted into a Boolean model using the CaSQ tool. Logic rules based on Boolean algebra are used to describe every interaction between the molecular entities.
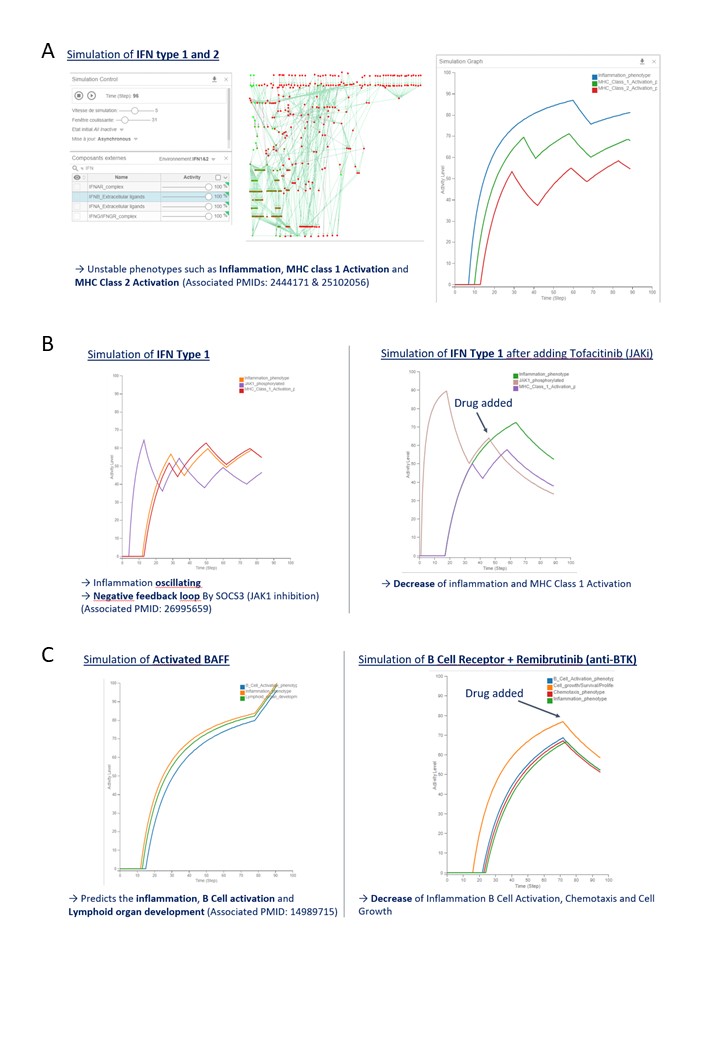
Results: Our analysis unveiled a set of differentially expressed genes (DEG) and related pathways associated with immune dysregulation and inflammatory responses in SjD. We obtained a total of 1625 DEG, 725 DEG from PRECISESADS, 1161 DEG from GSE51092 and 239 DEG from UKPSSR, with 25 DEG common for all three datasets. Nine common DEG were associated with Interferon signalling, A hallmark pathway of the disease. In total, 43 relevant pathways were identified with both GSEA and Reactome-based analysis. The building of the SjD Map was performed based on literature search and the 43 identified pathways from data analysis. The MIM includes more than 25 pathways data-driven and literature-mined, comprising 700 species (genes, RNAs, proteins) and 485 reactions. The SjD-specific Boolean model obtained after conversion of the SjD MIM, represents a fully executable version of the SjD molecular network, containing 363 nodes and 537 edges. The model is currently able to reproduce some of the biological scenarios from literature knowledge, notably the interferon (Figure 1A-B) and B cell response (Figure 1C) and to assess the impact of drug on the SjD immunopathology (Figure 1B-C).
Conclusion: We have built the first SjD-specific MIM integrating omic data analyses and information from literature-based evidence and pathway enrichment analysis. The preliminary computational model based on the SjD map is able to reproduce inflammatory response scenarios and test the impact of drugs in the system. Validation with external data and contextualization is ongoing and will allow the model to be used to decipher heterogeneity and predict drug targetability once the model is trained.
Disclosures: S. E Silva Saffar: None; J. Gottenberg: AbbVie, 2, BMS, 2, 5, Galapagos, 2, Gilead, 2, Lilly, 2, MSD, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, 5; M. Bombardieri: None; D. Cornec: None; J. Pers: None; M. Alarcon-Riquelme: None; P. Moigeon: Servier, 3; M. Barnes: None; S. Ng: None; W. Ng: Amgen, 2, Argenx, 2, IQVIA, 2, Johnson and Johnson, 2, Novartis, 2, sanofi, 2; X. Mariette: Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Galapagos, 2, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2; G. Nocturne: AbbVie/Abbott, 12, Travel fees, Amgen, 12, Travel fees, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 6, Novartis, 6; A. Niaraki: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
E Silva Saffar S, Gottenberg J, Bombardieri M, Cornec D, Pers J, Alarcon-Riquelme M, Moigeon P, Barnes M, Ng S, Ng W, Mariette X, Nocturne G, Niaraki A. Computational Systems Biology Approach to Unveil Molecular Interactions in Sjogren’s Disease Pathogenesis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/computational-systems-biology-approach-to-unveil-molecular-interactions-in-sjogrens-disease-pathogenesis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/computational-systems-biology-approach-to-unveil-molecular-interactions-in-sjogrens-disease-pathogenesis/