Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are present in human plasma in a stable form despite the endogenous RNase activity. Plasma miRNAs are non-invasive biomarker for cancer detection and tissue injuries. We previously showed the potential ability of the plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and designed this study to identify plasma miRNAs specific for RA by a comprehensive array approach.
Methods : We performed a systematic array-based miRNA expression analysis on plasma samples from patients with RA and healthy controls (HCs) (n=3, respectively). The expression of plasma miRNAs in the first comprehensive analysis with more than four times change or with significant (p<0.05) change between RA and HCs, or that of detectable plasma miRNAs only in RA plasma, were followed by confirmation analysis of eight patients with RA and eight HCs using real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). Plasma miRNAs consistently detectable in our system and significantly different between RA and HC were chosen for further validation with 102 RA patients and 104 HCs. Receiver operation curves were generated, and correlations between miRNAs and other biomarkers of RA were statistically examined.
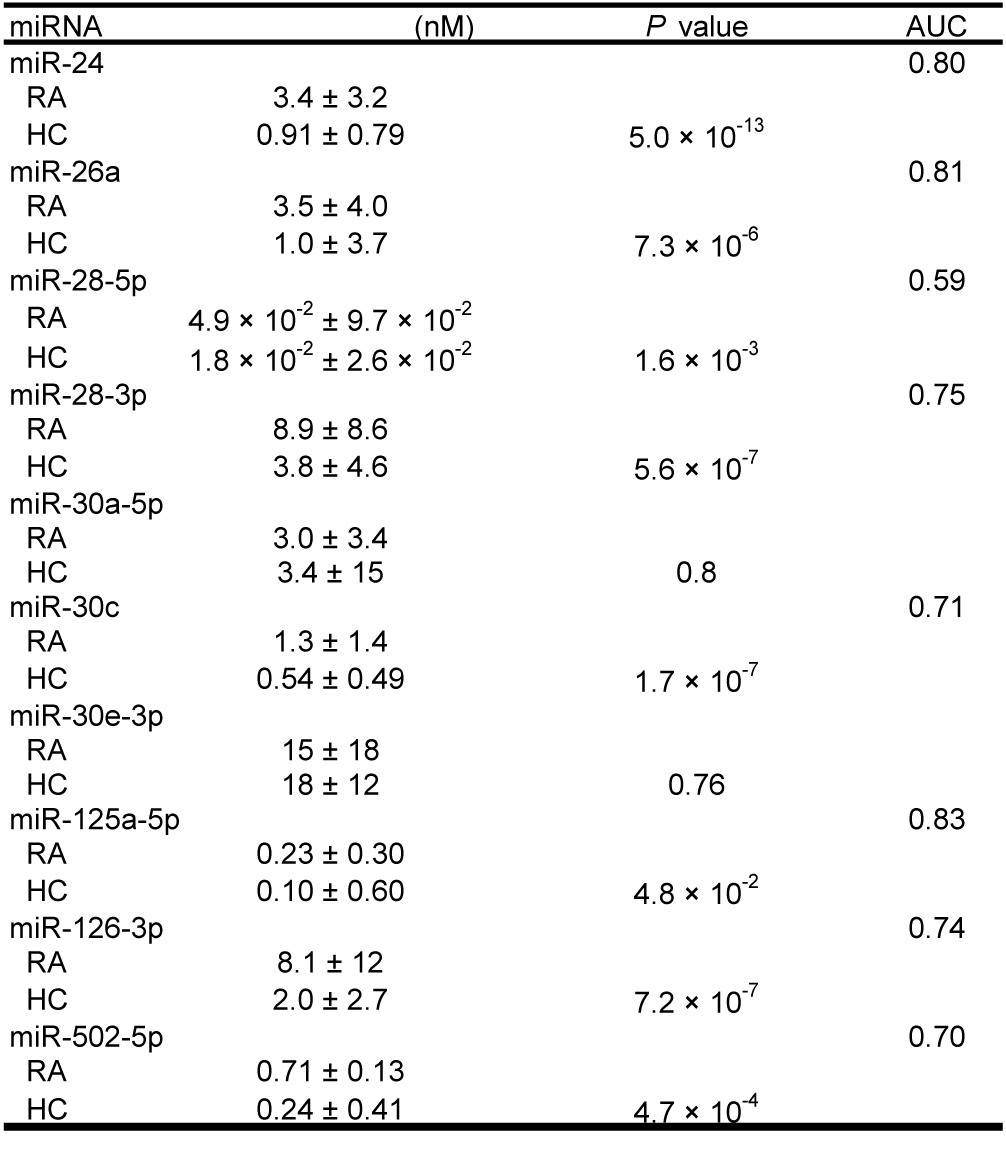
Results : The array analysis and the subsequent confirmation by qPCR in larger patient cohort identified eight RA-associated circulating miRNAs, including miR-24, miR-26a and miR-125a-5p (Table 1). The area under curve (AUCs) of each miRNA was 0.80, 0.81 and 0.83 respectively (Figure 1A). Logistic regression analysis provided a formula for estimated probability for RA by plasma miR-24, miR-30a-5p, miR-125-5p (ePRAM) with increased the diagnostic accuracy (AUC: 0.86, Figure 1B). The diagnostic ratio was not influenced by the antibody values against anti-citrullinated peptide. These miRNAs levels in OA patients were as low as in HC and these miRNA levels in RA patients showed no significant changes with the administration of biologics.
Conclusion: Plasma levels of miR-24, miR-26a, miR-125a-5p, and ePRAM can be diagnostic biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis.
Table 1.
Figure 1.
Disclosure:
K. Murata,
None;
M. Furu,
None;
H. Yoshitomi,
None;
M. Ishikawa,
None;
H. Shibuya,
None;
H. Ito,
None;
S. Matsuda,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comprehensive-microrna-analysis-identifies-mir-24-mir-26a-and-mir-125a-5p-as-plasma-biomarkers-for-rheumatoid-arthritis/