Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Pegloticase, a recombinant modified mammalian uricase that acts via enzymatic degradation of uric acid to allantoin, is approved in the US for the treatment of refractory chronic gout (RCG). Of 212 patients with RCG enrolled in two 6-month randomized, placebo-controlled trials (RCTs) of q2wk or q4wk pegloticase therapy, 155 (73%) had baseline tophi. All tophi were assessed during RCT and subsequent open-label treatment (OLE; up to 2.5 additional years) with regard to the time course of complete resolution by serial, quantitative digital photography evaluated by blinded and experienced central readers. Patients treated with placebo during the RCTs provided an additional opportunity to evaluate long-term tophus response upon initiation of pegloticase in the OLE study.
Methods: Photographs of patients’ hands and feet (and up to 2 other sites of tophi) were made at baseline, at weeks 13, 19 and 25 of RCT treatment, and at weeks 13, 25, 53, 77, 101 and final visit of the OLE. Each patient had up to 5 measurable tophi and 2 additional tophi tracked. A complete response (CR) was defined as 100% decrease in the area of the target tophus (or complete disappearance of the additional tophi) in the absence of any new or enlarging tophi.
Results: CR of at least one tophus was significantly more frequent among patients receiving pegloticase q2wk vs. placebo at 13 weeks of treatment and at all subsequent times of measurement in the RCTs. Tophus CR was achieved by 40% of patients after 6 months of q2wk pegloticase (vs. 7% with placebo; p=0.002). Although more patients treated with q4wk pegloticase had tophus CR (21%) vs placebo (7%) at the final RCT visit, this difference was not statistically significant. During the RCTs, 21 patients showed a new incident tophus (all among patients manifesting baseline tophi). New tophi were seen in 6% (4/62), 11% (7/64) and 35% (10/29) of patients receiving biweekly pegloticase, monthly pegloticase, and placebo treatment, respectively.
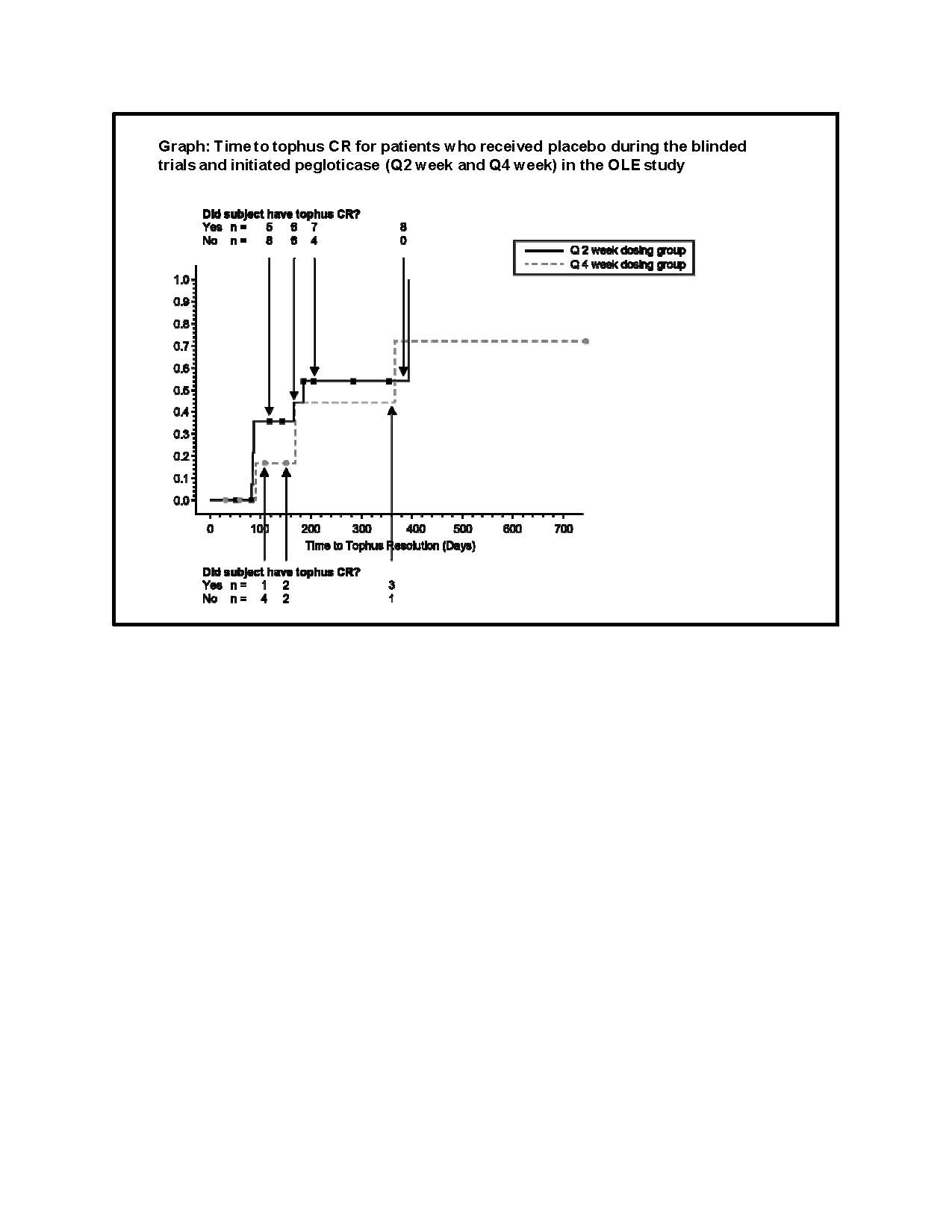
After 1 year in the OLE study, CR of at least one tophus was recorded for 74% (50/68) of patients receiving q2wk pegloticase. The Kaplan Meier curve below shows the time to first tophus CR for patients treated with placebo during the RCT followed by pegloticase in the OLE study. Despite receiving no urate-lowering therapy during the 6 months of RCT enrollment, approximately one-half of placebo-treated patients had a tophus CR within 6 months of initiation of q2wk pegloticase treatment in the extension study.
Conclusion: A significant rate of CR of at least one baseline tophus was achieved for patients treated with biweekly pegloticase within 13 weeks (compared with placebo treatment). Tophus CR rates over time are consistent and rapid for patients initiating pegloticase in both the RCTs and OLE study. The proportion of patients with a tophus CR continued to increase over time for up to 2.5 years of additional pegloticase treatment.
Disclosure:
M. A. Becker,
Takeda Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
Savient Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
Ardea Biociences INC,
5,
Metabolex Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
URL/Mutual Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc,
5,
UpToDate Inc,
7;
N. J. Gonter,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
8;
J. E. Pope,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
2;
R. L. Malamet,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
1,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
3;
H. S. B. Baraf,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Ardea Biosciences,
5,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc., Ardea Biosciences, Metabolex, Inc., Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
2,
Savient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.,
8.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complete-tophus-response-in-patients-with-chronic-gout-initiating-pegloticase-treatment/