Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab, a human IgG1λ monoclonal antibody that selectively binds B-lymphocyte stimulator, was first approved in 2011. It is the only biologic approved for LN and SLE. With greater than 10 years of real-world experience, EULAR acknowledged early use of belimumab in SLE, and ACR recommends its use in LN. Reinforcing the central role of B-cells in LN immunopathogenesis, Phase 3 trials successfully investigated belimumab (BLISS-LN; NCT016393391) and obinutuzumab (REGENCY; NCT04221477) in biopsy-proven active LN plus standard therapy (ST). Study differences (e.g. populations, concomitant medications, endpoint timings, and definitions) present challenges in comparing LN trial outcomes. In this regard, BLISS-LN’s unique design allowed inclusion of pure ISN/RPS class V and cyclophosphamide ST. To better align with the design of the REGENCY and NOBILITY (NCT02550652) trials, we analyzed post hoc a BLISS-LN subgroup of patients with active class III or IV LN ± concomitant class V who received MMF ST (i.e. excluding pure class V and cyclophosphamide ST).
Methods: BLISS-LN was a 104-week global trial of 448 adult patients with active class III or IV (± concomitant class V) or pure class V LN.1 Key features of the BLISS-LN study design (Table 1) included a stringent complete renal response (CRR) definition that differs from other trials (BLISS-LN-CRR defined as urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio [uPCR] < 0.5, eGFR ≤10% below the pre-flare value or ≥90 ml/minute/1.73 m2, and no rescue therapy).1 Additionally, BLISS-LN-CRR defined treatment failure as use of prohibited therapy and not achieving mandatory prednisone taper to ≤10 mg/day by Week 24.
Results: Of the overall 448 patients in BLISS-LN, 271 had active class III or IV LN ± concomitant class V and received MMF ST. CRR data for this subgroup (referred to as the “MMF subgroup”) using prespecified definitions are shown in Table 2. At Week 76 in the MMF subgroup, BLISS-LN-CRR treatment difference between belimumab and placebo was 11.3% for class III or IV ± concomitant class V, and 12.2% for class III or IV only. At Week 104, BLISS-LN-CRR treatment difference was 14.9% for class III or IV ± concomitant class V, and 17.4% for class III or IV only.Regarding safety, in the BLISS-LN MMF subgroup, serious adverse events up to Week 104 were lower with belimumab (24.4%, n=40/164) than placebo (32.1%, n=53/165).
Conclusion: Building on the extensively demonstrated safety2 and efficacy profiles of belimumab across SLE and LN, this post hoc subgroup analysis of patients with active class III or IV LN ± concomitant class V receiving MMF in BLISS-LN demonstrated enhanced renal responses with belimumab versus placebo at Weeks 76 and 104. This improved outcome is also observed when compared to the overall BLISS-LN population.1 Belimumab has additionally been shown to be safe and efficacious in patients with LN in the real world.3 Benefit/risk profiles, real-world effectiveness and data from extra-renal SLE should be considered to inform LN treatment decisions.Funding: GSKReferences1Furie R et al. N Engl J Med 2020;383:1117–282Wallace D et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71:1125–343Gatto M et al. J Autoimmun 2021;124:102729Original presentation: LUPUS 2025
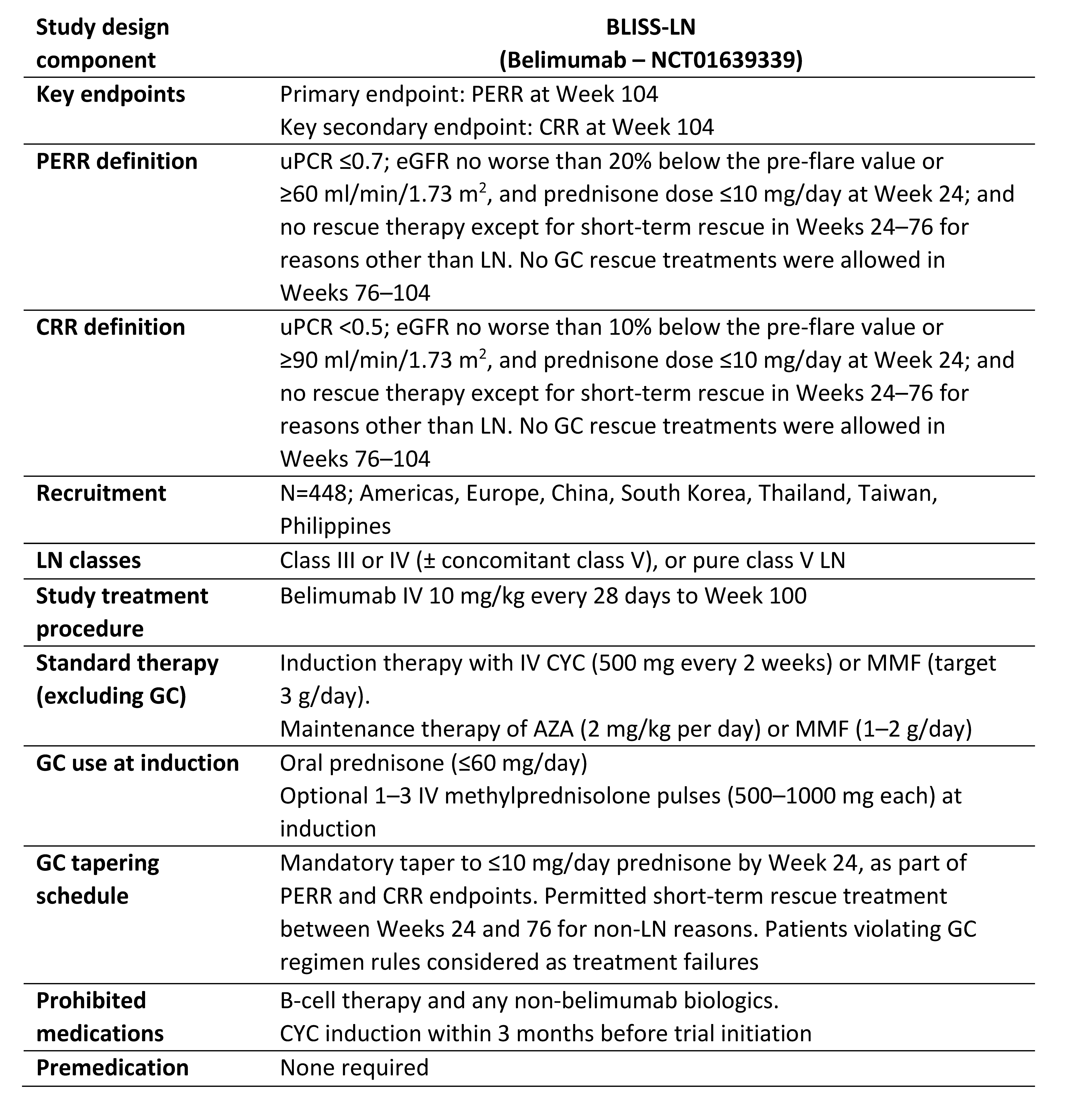 Table 1. Key features of the BLISS-LN study design.
Table 1. Key features of the BLISS-LN study design.
AZA, azathioprine; CYC, cyclophosphamide; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GC, glucocorticoid; IV, intravenous; PERR, primary efficacy renal response.
.jpg) Table 2. BLISS-LN CRR responder data at Weeks 76 and 104 for a subgroup of patients receiving MMF with active class III or IV LN ± concomitant class V.
Table 2. BLISS-LN CRR responder data at Weeks 76 and 104 for a subgroup of patients receiving MMF with active class III or IV LN ± concomitant class V.
*Data shown are for a post hoc subgroup of patients who received MMF standard therapy (No CYC); †CRR responder rates for the combined subgroups “class III or IV” and “class III or IV + V” were manually calculated using data on the number of responders in each subgroup; ‡OR adjusted for race, baseline uPCR and baseline eGFR.
BEL, belimumab; CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; PBO, placebo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Anders H, Bertsias G, Delgado A, Levy R, Curtis P, O'Shea C, Tomlinson R, Rovin B. Complete Renal Responses and Safety for Belimumab Versus Placebo in a Post Hoc Mycophenolate Mofetil Subgroup with Active Proliferative Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complete-renal-responses-and-safety-for-belimumab-versus-placebo-in-a-post-hoc-mycophenolate-mofetil-subgroup-with-active-proliferative-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complete-renal-responses-and-safety-for-belimumab-versus-placebo-in-a-post-hoc-mycophenolate-mofetil-subgroup-with-active-proliferative-lupus-nephritis/
