Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Complement components, including C4d, can be detected on the surface of activated platelets and they have been associated with vascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In the current study, we investigate whether platelet C4d (PC4d) adds additional value to traditional and known SLE-associated risk factors when identifying SLE patients with vascular disease.
Methods: We included 308 well-characterized SLE patients and 308 matched population controls in a cross-sectional design. Traditional risk factors including age, gender, smoking, hypertension and lupus associated risk factors aPL and glomerular filtration rate measured by MDRD formula were tabulated. PC4d deposition was analyzed using flow cytometry. Values >95% of controls were considered as PC4d positivity (+). Antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) were determined by Luminex, and the lupus anticoagulant (LA) test was performed by a Dilute Russel Viper Venom Time method.
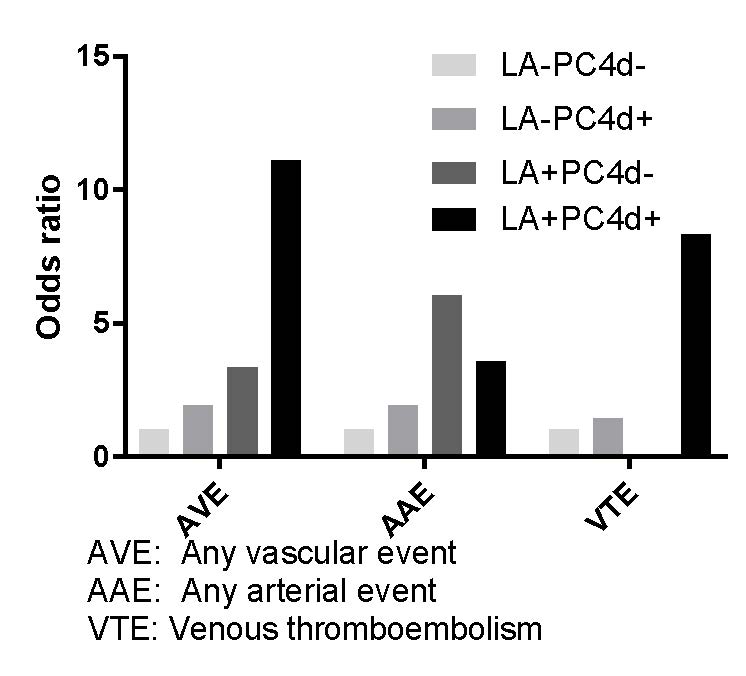
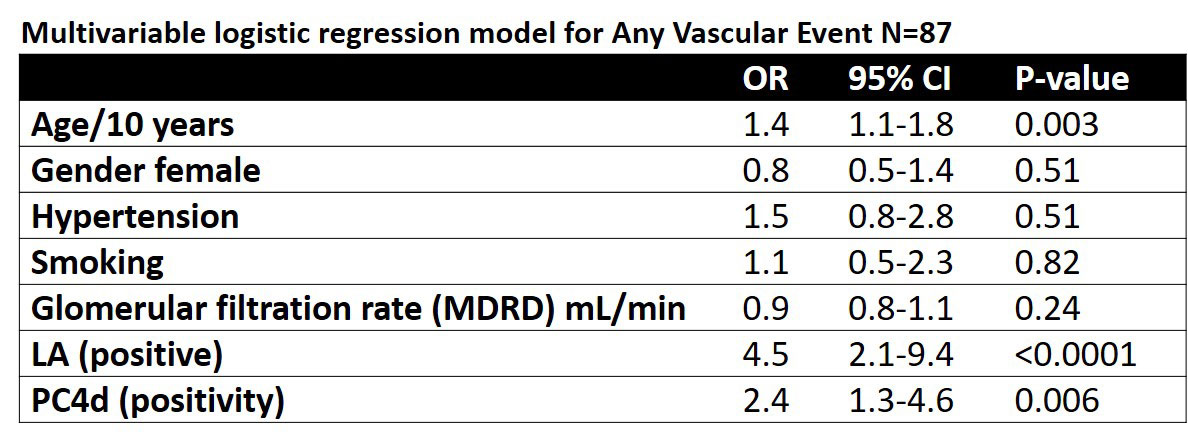
Results: SLE patients had increased PC4d deposition as compared to population controls (p< 0.0001). 50.3% of SLE patients were PC4d+. In SLE patients, PC4d+ associated with previous vascular events (AVE), specifically with venous and cerebrovascular, but not with ischemic heart events. PC4d was also associated with all investigated aPL profiles and the anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS, p< 0.0001). After adjustment for traditional and SLE-associated risk factors that were associated with any vascular event in uni-variable analyses, previous vascular events remained associated with PC4d+ (OR:2.4, 95% CI 1.3-4.5, p=0.006, table). There was furthermore a positive interaction between PC4d+ and LA+ regarding any vascular events (OR:11.1, 95% 5.1-24.3, p< 0.0001, Figure 1) versus patients negative for both PC4d and LA.
Conclusion: PC4d+ is associated with vascular events in SLE, independently of traditional and SLE-associated risk factors. The combination of PC4d+ and LA+ interacted positively and increased the association with vascular events even further. If measurement of both aPL and PC4d can predict vascular events in patients with SLE and/or APS should be evaluated in prospective studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Svenungsson E, Gustavsson J, Grosso G, Gunnarsson I, Nilsson B, Larsson A, Bengtsson A, Lood C. Complement Deposition C4d on Platelets Is Associated with Vascular Events in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-deposition-c4d-on-platelets-is-associated-with-vascular-events-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-deposition-c4d-on-platelets-is-associated-with-vascular-events-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/