Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We reported (Ramsey-Goldman et al., Arthritis Rheumatol 2018: 70 [suppl 10]) that cell-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) and a multi-analyte assay panel with algorithm (MAP) are positive more frequently than standard immunological markers in patients with probable systemic lupus erythematosus (pSLE) who fulfilled 3 ACR criteria. We followed pSLE prospectively to evaluate whether CB-CAPs and MAP positivity at enrollment predict transition to classifiable SLE by fulfillment of a fourth ACR criterion.
Methods: pSLE were followed prospectively at academic lupus centers and clinical and laboratory data were collected. Biomarkers were measured at every visit. CB-CAPs – C4d bound to erythrocytes (EC4d) and B-cells (BC4d) – were measured by quantitative flow cytometry and expressed as mean fluorescent intensity (MFI). Serum C3 and C4 and autoantibodies were measured by turbidimetry and ELISA, respectively. Anti-dsDNA positivity was confirmed by immunofluorescence (IFA) with Crithidia Luciliae. MAP was evaluated as previously described (Dervieux T, et al. J Immunol Methods 2017) and consists of an algorithm which utilizes CB-CAPs and autoantibodies. A MAP score >0.1 is considered positive, the higher the number (to 3.5) the greater the likelihood of SLE. For this study, decision analysis with Youden index showed that MAP >0.8 and EC4d >20 MFI reflected the optimal cutoff. Data were analyzed by Fisher’s exact test and Kaplan-Meier with log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards model for time to fulfillment of a fourth ACR criterion, expressed as hazard ratios.
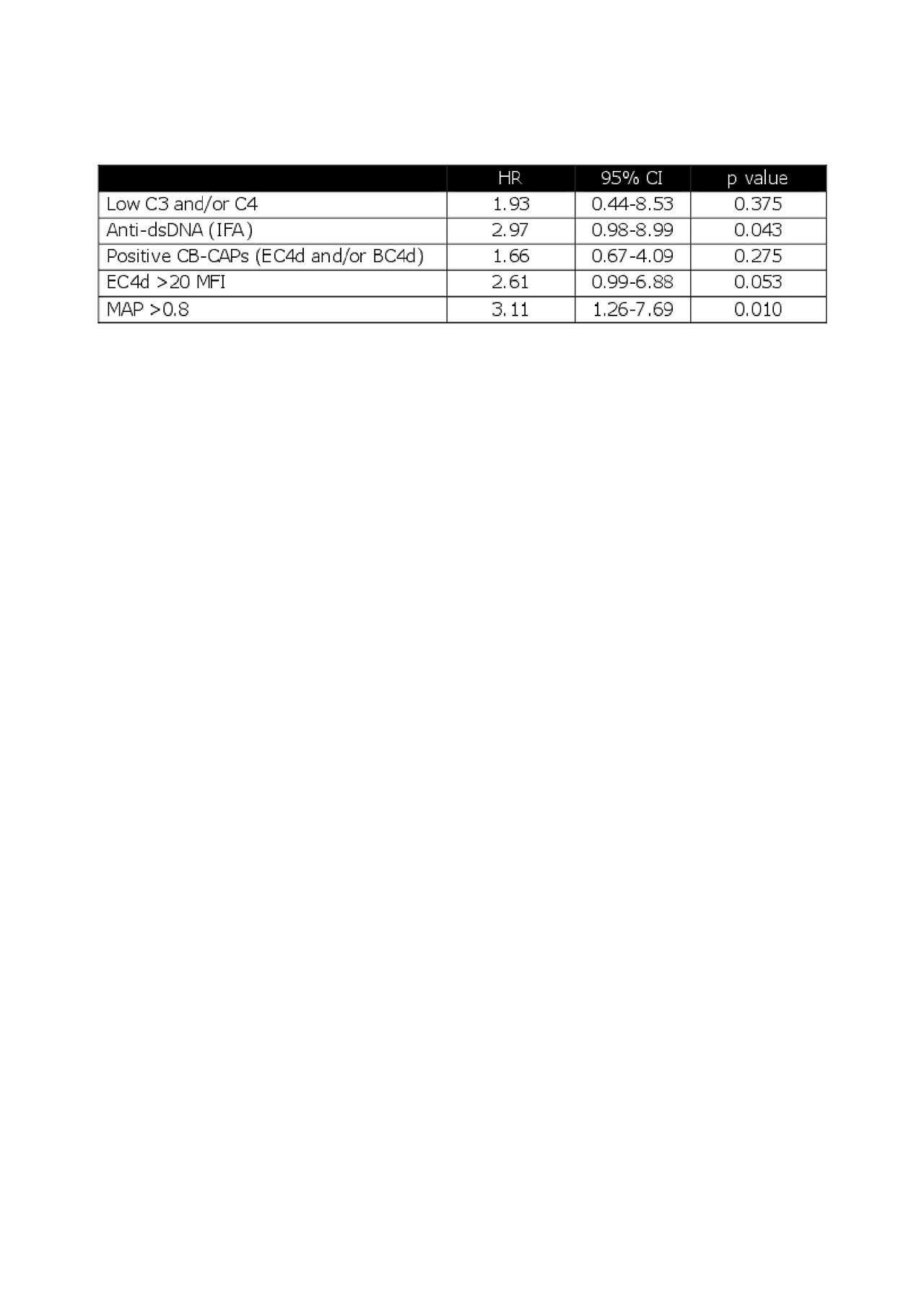
Results: Of the 92 pSLE enrolled, 69 had 1 follow up visit 9-18 months after enrollment (average±SD = 12.4±1.7 months; median = 12 months). The time to acquire the 4th ACR criterion was estimated by the investigators at the follow up visit. Twenty pSLE (29%) fulfilled a fourth ACR criterion during this time. SLICC fulfillment at enrollment did not predict fulfillment of ACR criteria (p =0.27). Eight of the 20 (40%) pSLE who transitioned to classifiable SLE by ACR criteria had MAP >0.8 at enrollment while 8/48 (17%) non-transitioned patients had MAP > 0.8 at enrollment (p =0.06). Patients with MAP >0.8 at enrollment fulfilled ACR criteria with a hazard ratio (HR) =3.11 within 18 months (p < 0.01 by log-rank test). HR of MAP was higher than other individual biomarkers, although anti-dsDNA and EC4d >20 MFI were of borderline significance (Table).
Conclusion: Complement activation as detected by MAP >0.8 at enrollment may predict disease evolution of pSLE into classifiable SLE by ACR criteria better than anti-dsDNA and low serum complement.
Data of 69 follow-up visits -n = 68 for MAP- that occurred 9 to 18 months after enrollment were analyzed. CB-CAPs: cell-bound complement activation products; MAP: multianalyte assay panel with algorithm; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramsey-Goldman R, Alexander R, Narain S, Arriens C, Massarotti E, Wallace D, Saxena A, Collins C, Putterman C, Kalunian K, O'Malley T, Sace A, LaFon R, Ligayon J, Ibarra C, Conklin J, Dervieux T, Weinstein A. Complement Activation in Probable Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (pSLE) May Predict Progression to SLE Defined by Fulfillment of ACR Classification Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-activation-in-probable-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-psle-may-predict-progression-to-sle-defined-by-fulfillment-of-acr-classification-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/complement-activation-in-probable-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-psle-may-predict-progression-to-sle-defined-by-fulfillment-of-acr-classification-criteria/