Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster I: Inflammatory Arthritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The imaging techniques for assessing rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including x-ray, musculoskeletal ultrasound, MRI and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT). Fibroblast-like synoviocyte cells, which are involved in inflammation of the articular cartilage and bone, overexpress fibroblast activation protein (FAP), which is a feature that could be leveraged to improve imaging assessment of disease. The purpose of our study was to determine the imaging techniques of gallium 68 (68Ga)-labeled FAP inhibitor (FAPI) and fluorine 18 (18F) fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) imaging, compared with traditional X-ray imaging in assessing disease activity and treatment response in patients with RA.
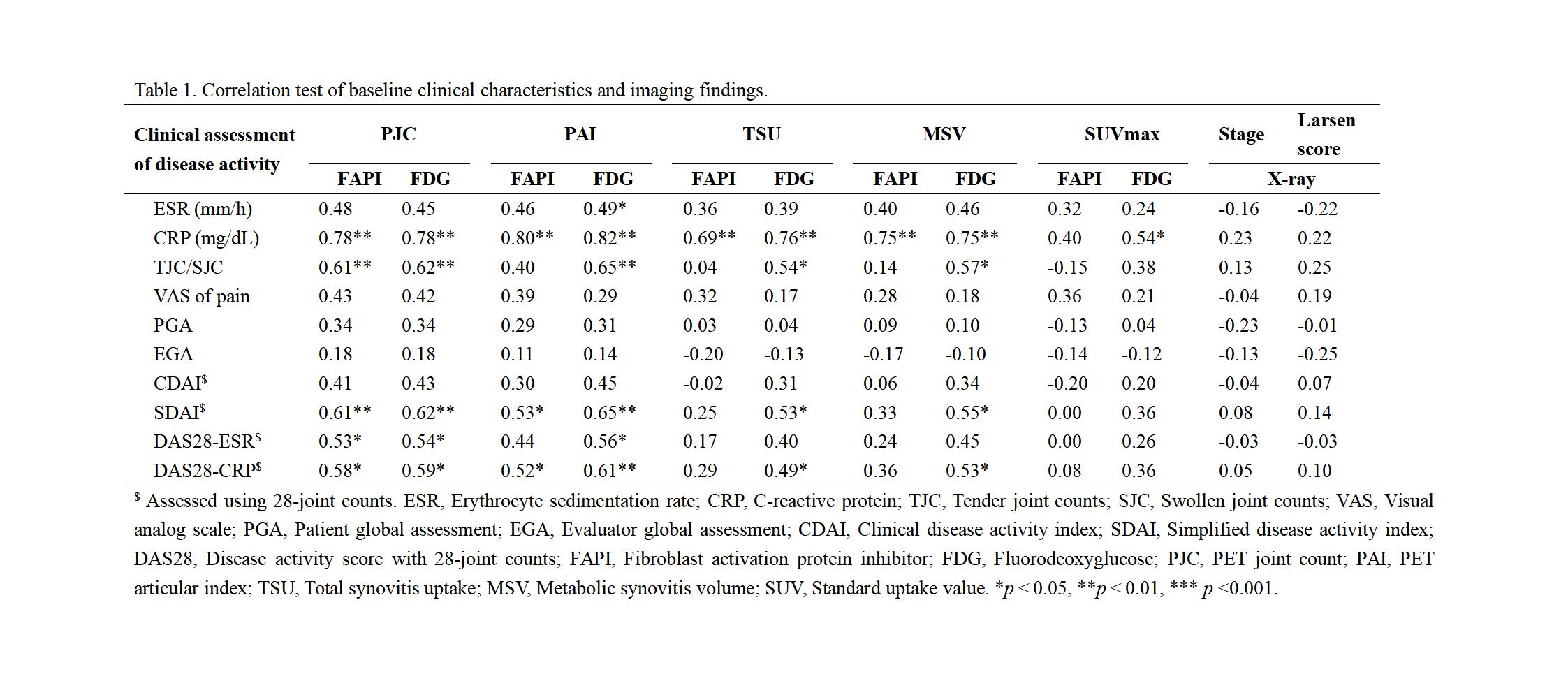
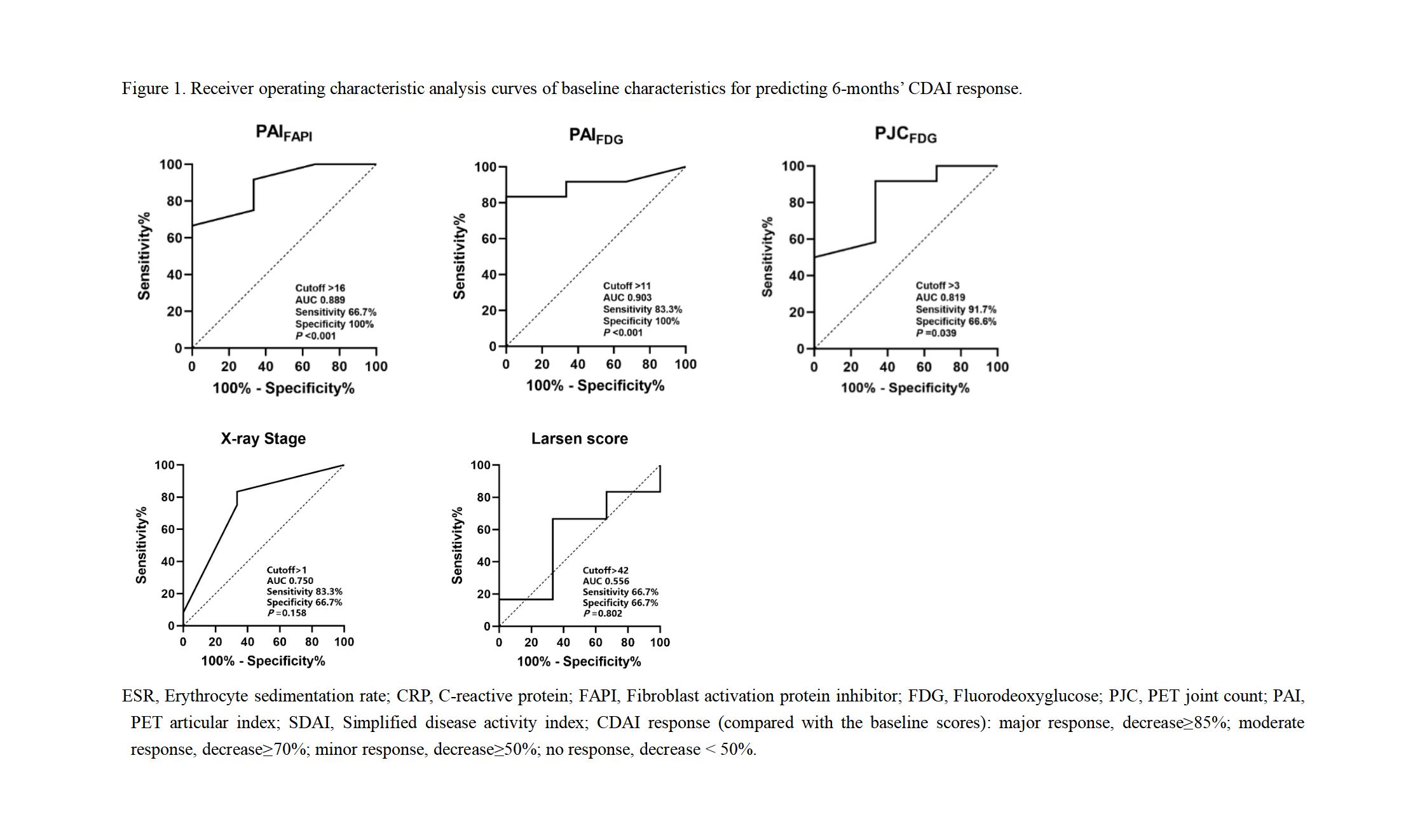
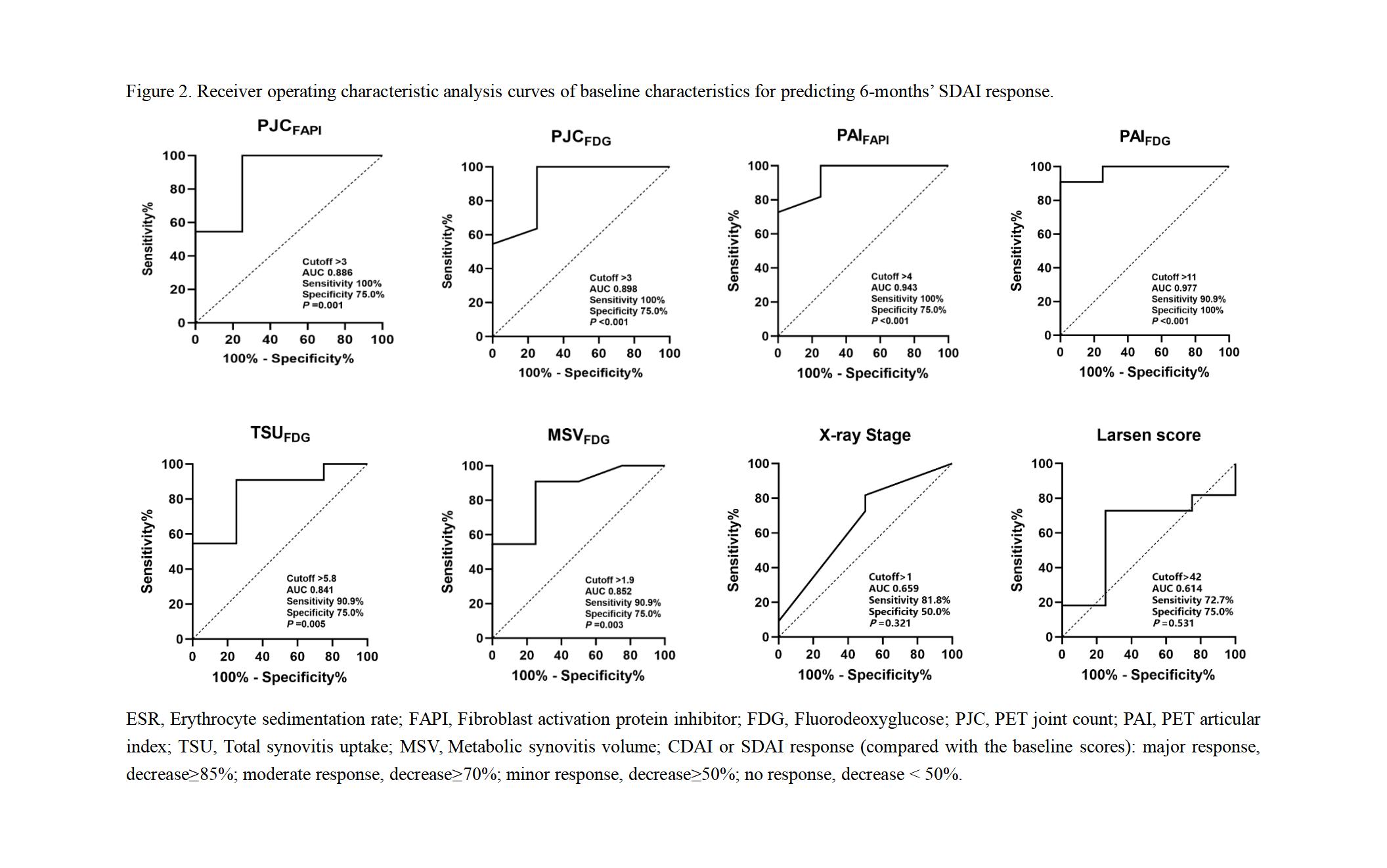
Methods: We prospectively enrolled 17 participants diagnosed with RA including 14 females and 3 males (52.9±10.5 yr, range 25-65 yr). All patients were evaluated for disease activity through clinical and laboratory assessment and underwent X-ray and dual-tracer PET/CT ([68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and [18F]FDG PET/CT) imaging, with 6-months’ follow-up to monitor disease progression. Bland-Altman analysis was performed to assess the agreement in X-ray and dual-tracer PET/CT. Additionally, we explored correlations between disease activity values (including ESR, tender or swollen joint count, VAS of pain, PGA, EGA, CDAI, SDAI, DAS28-ESR, DAS28-CRP) and parameters of imaging findings (including Stage and Larsen score in X-ray, PJC, PAI, TSU, MSV and SUVmax in dual-tracer PET/CT).
Results: The Bland-Altman analysis indicated a high level of agreement between X-ray and PET-CT in evaluating joint conditions in RA patients, with mean differences within acceptable limits and narrow 95% limits of agreement. PJCFAPI, PAIFAPI, PJCFDG, and PAIFDG at baseline showed a stronger positive correlation with CRP, CDAI, SDAI, DAS28-ESR, and DAS28-CRP, while no statistical differences were observed between X-ray and clinical characteristics of RA patients. Additionally, PET/CT rather than X-ray parameters could significantly predict treatment response.
Conclusion: [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and [18F]FDG PET/CT were superior to traditional X-ray in evaluating the disease activity of RA and predicting treatment response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen J, Yang D, Zhou Z, luo Y, Yang H. Comparisons of Ga-FAPI and FDG PET/CT with X-ray Imaging in the Assessment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparisons-of-ga-fapi-and-fdg-pet-ct-with-x-ray-imaging-in-the-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparisons-of-ga-fapi-and-fdg-pet-ct-with-x-ray-imaging-in-the-assessment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/