Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Frailty is associated with increased risk of adverse health outcomes in SLE. Multiple definitions for frailty exist, and how best to measure frailty in SLE remains unclear. Two of the definitions used to measure frailty in SLE include the SLICC Frailty Index (SLICC-FI) and the FRAIL (Fatigue, Resistance, Ambulation, Illnesses, and Loss of weight) scale. However, the relationship between these two frailty definitions is unknown. We aimed to assess the agreement between the SLICC-FI and the FRAIL scale for identifying frailty among SLE patients. We also evaluated differences in clinical characteristics between frail and non-frail SLE patients according to each frailty definition.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of consecutive adult SLE patients assessed in the Lupus clinic at a single academic medical center from December 2020 to November 2021. All participants met the 1997 revised ACR classification criteria for SLE.
At a single visit, participants were assessed for disease activity (SLEDAI-2K), organ damage [SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI)], comorbidities, and health-related quality of life [Short-Form 36 (SF-36)]. Using data for 48 health deficits, a SLICC-FI score was calculated for each patient. A SLICC-FI score >0.21 defined frailty. The 5-item FRAIL scale was administered at the same visit. Patients with ≥ 3 of 5 items were classified as frail.
Agreement between the SLICC-FI and the FRAIL scale was evaluated using Spearman rank correlation coefficients (rs) and kappa statistics (κ). As the SLICC-FI is a continuous variable, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was also performed to determine the optimal threshold SLICC-FI value based on agreement with frailty status as determined by the FRAIL scale. Differences between frail and non-frail patients were evaluated using Fisher’s exact or Chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests or Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for continuous variables.
Results: The 181 SLE patients were mostly female (90.1%) with mean (SD) age 54.6 (14.3) years. Mean (SD) baseline SLICC-FI score was 0.17 (0.08) with 57 patients (31.5%) classified as frail (SLICC-FI >0.21). Based on the FRAIL scale, 31 patients (17.1%) were classified as frail.
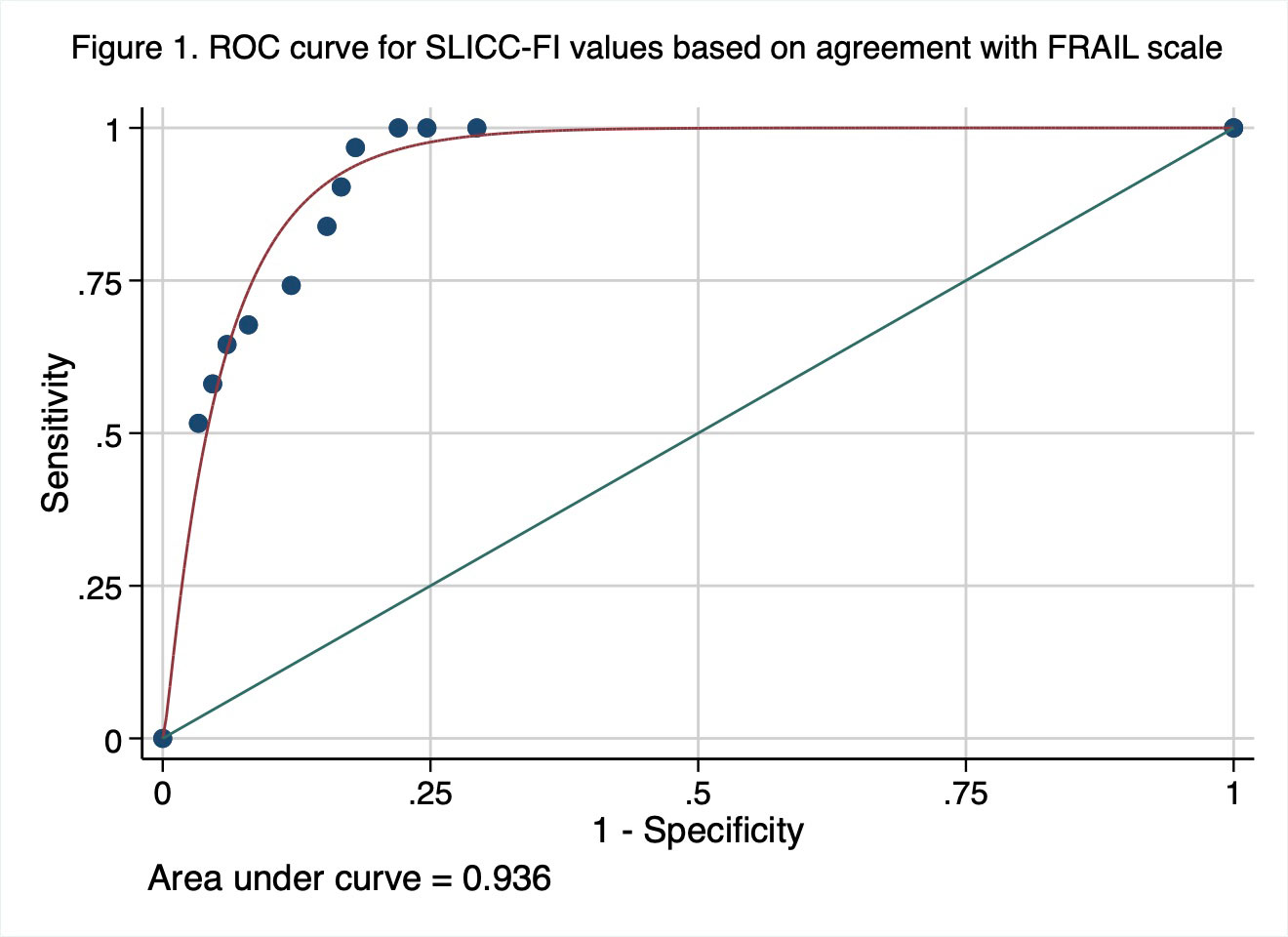
There was moderate correlation between the FRAIL scale and the SLICC-FI for identifying frailty (rs = 0.639; p < 0.0001). Agreement occurred in 84.5% of cases (κ = 0.591; p < 0.0001). The ROC curve analysis (Figure 1) yielded an AUC of 0.936, indicating excellent discriminative ability. Based on agreement with the FRAIL scale, the standard SLICC-FI cut-off value of >0.21 was the optimal threshold for identifying frailty (Sensitivity 96.8%, Specificity 82%).
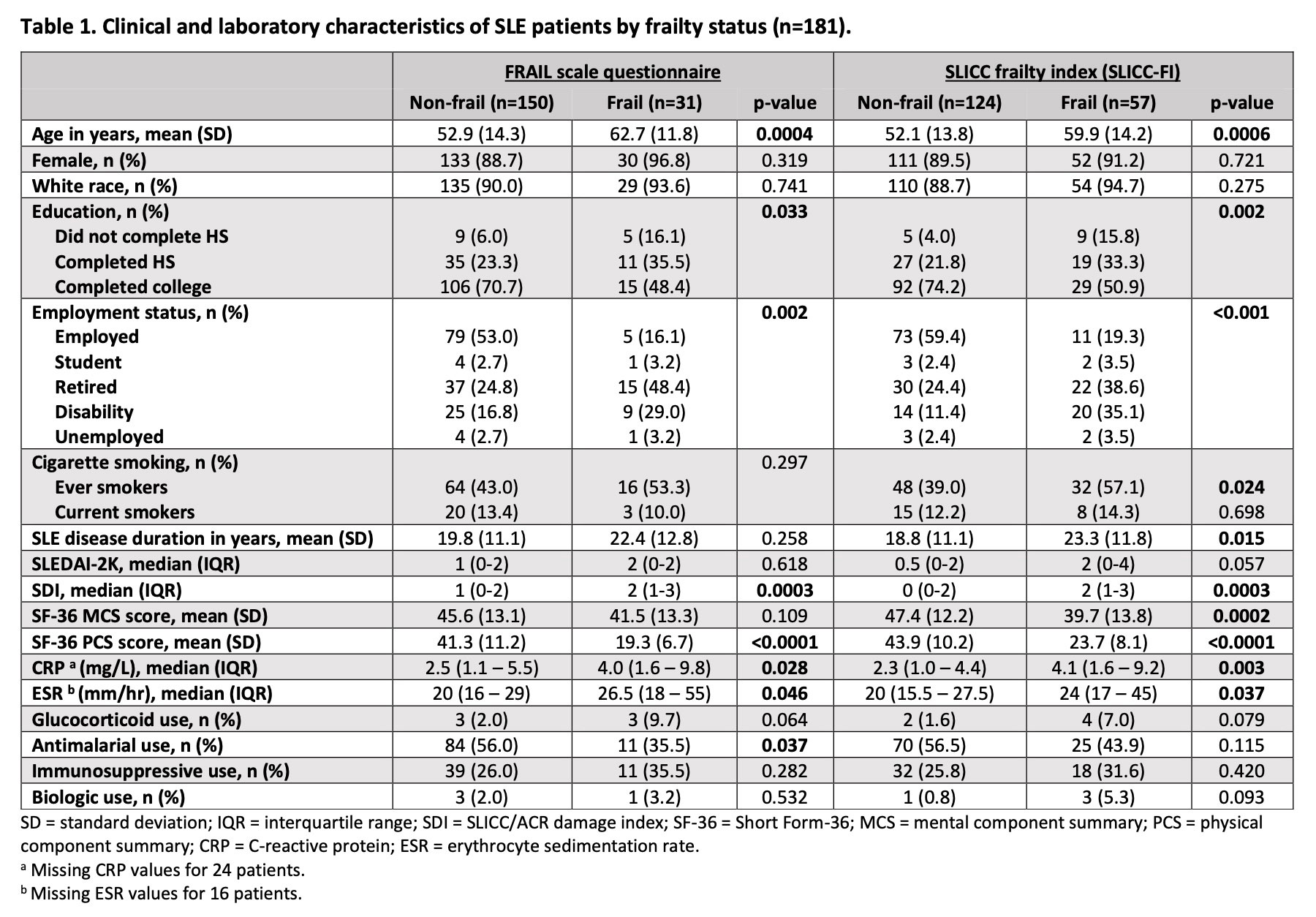
For both frailty definitions, there were significant differences between frail and non-frail SLE patients in terms of age, education, employment status, SDI scores, SF-36 physical component summary scores, CRP levels, and ESR values (Table 1).
Conclusion: There is moderate agreement between the SLICC-FI and the FRAIL scale for identifying frailty in SLE patients. Each frailty metric has distinct advantages in different settings. The FRAIL scale may be a useful point-of-care tool, while the SLICC-FI is more easily applied to existing SLE datasets.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Legge A, Lieber S, Hanly J. Comparison of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics Frailty Index (SLICC-FI) and the FRAIL Scale for Identifying Frailty Among Individuals with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-systemic-lupus-international-collaborating-clinics-frailty-index-slicc-fi-and-the-frail-scale-for-identifying-frailty-among-individuals-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-systemic-lupus-international-collaborating-clinics-frailty-index-slicc-fi-and-the-frail-scale-for-identifying-frailty-among-individuals-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/