Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Stanford Health Assessment
Questionnaire (HAQ) includes several questions that are more relevant to
rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in Western countries than to those in
India. The Center for Rheumatic Diseases (CRD) Pune developed a modified
version of the HAQ (CRDHAQ) to reflect daily activities unique to India and
other Asian countries, such as arising from sitting cross-legged on the floor,
which may be more difficult to perform than corresponding activities in Western
countries. We compared the performance of both questionnaires in a clinical
trial conducted in India.
Methods: Indian patients with RA for ≥2 years were
randomized in a 54-week clinical trial comparing biosimilar infliximab (IFX) BOW15
to reference IFX (rIFX), which included an initial 16-week double-blind phase
followed by an open-label extension in which responders received BOW015. All
subjects completed both HAQ and CRDHAQ at weeks 0 (baseline), 2, 6, 14 and 16.
Disability index (DI) scores from baseline for both instruments were compared
in the ITT population by analysis of covariance within and between treatments.
Results: 189 subjects were, randomized to receive BOW015
(n=127) or rIFX (n=62), of whom 181 subjects (120 receiving BOW015 and 61
receiving rIFX) completed the blinded phase of the study. Baseline HAQ-DI
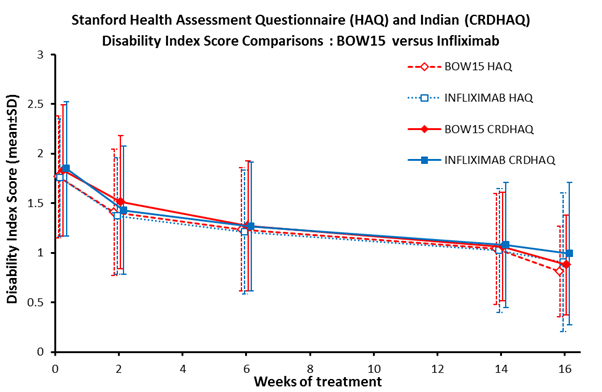
scores were 1.77±0.61 and 1.76±0.60 and baseline CRDHAQ-DI scores were
1.83±0.66 and 1.85±0.67, respectively (mean±SD). The baseline CRDHAQ-DI scores
were significantly higher than HAQ-DI scores for each treatment (P<0.05).
Data for all time points are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
There were no statistically significant differences between
HAQ-DI and CRDHAQ-DI scores from baseline between treatments across each assessment
period. Improvements from baseline in each score were statistically significant
from week 2 through week 16 for both treatments and both HAQ and CRDHAQ
(P<0.001). These decreases in DI by treatment corresponded to comparable
increases in %ACR20 responders observed at the time points.
Conclusion: CRDHAQ and HAQ, yielded comparable results when
administered to Indian RA patients, and reflected significant
functional improvement at week 2. Thus, either the Stanford HAQ or CRDHAQ can
be used to assess functional improvement in clinical trials conducted in this
patient population with daily activities different from those of Western RA
patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chopra A, Saluja M, Knight A, Shneyer L, Lassen C, Wyand M, Kay J. Comparison of the Stanford and Indian Health Assessment Questionnaires for Disability Outcomes in a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active Comparator Study of Infliximab and Biosimilar Infliximab BOW15 in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-stanford-and-indian-health-assessment-questionnaires-for-disability-outcomes-in-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-active-comparator-study-of-infliximab-and-biosimilar-infliximab-b/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparison-of-the-stanford-and-indian-health-assessment-questionnaires-for-disability-outcomes-in-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-active-comparator-study-of-infliximab-and-biosimilar-infliximab-b/